1)Non-aligned movement:
Context: India’s external affairs minister Jaishankar said recently that non alignment was the concept of relevance in specific era and a particular context, though the independence of action enriched in it remains a factor of continuity in India’s foreign policy
What is Non – Alignment?
- Non-alignment was a policy during the cold war to retain an autonomy of policy between two political military blocks
- The non-aligned movement provided a platform for newly independent developing Nations to join together to protect this autonomy, decolonization, Universal nuclear disarmament and against apartheid.
- Freed from the shackles of the cold war the NAM countries were able to diversify their network of relationships across the erstwhile east-west divide
Non alignment lost its relevance
- For a few years now non alignment has not been projected by our policy makers as a tenet of India’s foreign policy
- Strategic autonomy was one which soon acquired a connotation similar to Non-alignment with an anti-US tint
- Multi alignment has not found Universal favor since it may convey the impression of opportunism where as we seek strategic convergences
- Seeking issue based partnerships or coalitions is a description that has not stuck advancing prosperity and influence will dominate was a description Dr. Jaishankar settle for, to describe the aspirations that our network of international partnerships seeks to further
The China factor
- In the wake of the current standoff with China there have been calls for India’s foreign policy to shed its inhibitions and make a decisive shift towards the United States as the only viable option to counter China
- The external affairs minister clarified that a rejection of non-alignment does not mean a rush to alignment. India will not join in an Alliance system
- The fact is that alliance is as much a cold war concept as non-alignment
- During the cold war, the Glue that held countries of an Alliance together was composed of ideological convergence and an existential military threat.
- With the disintegration of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, (USSR) and the Warsaw pact, this glue dissolved and the international options of alliance partners widened just like those of NAM.
- The strategic interest of alliance partners are no longer congruent
- This is evident in the Euro-Atlantic Alliance US President Donald Trump’s words and deeds have highlighted divergences with in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization in (NATO) and even widened them but strains have periodically surface even earlier over the 2003 U.S invasion of Iraq for example for on Policy towards Russia or West Asia. Turkey is constantly exploring the limits of NATO discipline.
- Alliances in the Asia-Pacific face a bigger definitional dilemma, they were originally forged to deter the USSR,
- The threat to the alliance partners today is from an assertive China which they are reluctant to define as a strategic adversary because of their economic engagement with it and the huge military asymmetry
Geography link:
- While politics is dynamic, Geography is immutable
- Two major imperatives flow from India’s geography are economic and security interest in the Indo-Pacific space and the strategic importance of the continental landmass to its North and West
- The former has inspired the Act East Policy of bilateral and multilateral engagements in Southeast Asia and East Asia and the Pacific
- Shared India-US interest in dealing with the challenge from China in the maritime domain have been a strategic underpinning of the bilateral partnership since the early 2000’s
- Connectivity and cooperation with Afghanistan in Central Asia need engagement with Iran and Russia as well as with the Russia China dynamics in the region
- Seemingly paradoxically a close Russia-China partnership should move India to broad-based relations with Russia
- A strong state in relations with India could reinforce Russia’s reluctance to be a junior partner of China
- As the US confronts the challenge to its dominance from China, classical balance of power considerations would dictate a degree of accommodation with Russia
- There was an analogous logic in the Richard –Nixon- Henry Kissinger outreach to China in 1971 when the Soviet Union was the more formidable rival.
Political lessons from the current pandemic could help reawaken that historical memory
- Equally the US Could acknowledge that India’s development of trade routes through Iran would also serve its strategic interest of finding routes to Afghanistan and Central Asia bypassing Pakistan and Russia respectively
- Five years ago a group of US strategic analysts had suggested that the US should see ties with India as a joint venture and not an an Alliance in which they could pursue Shared objectives to mutual benefit and accept the differences of perspectives will have to be addressed
- India will acquire a larger Global profile next year when it commences a two-year term on the UNSC 9 a non – permanent member)
The strategic choice that it makes in its bilateral partnerships will be closely watched.
2) Himalayan Day:
Context: Speaking at a webinar on the occasion Himalayan Day, 10 September, of the Vice President called for rethinking our development paradigm in such a way that human beings and nature co-exist and thrive together.
- Various government programs for the conservation of Himalayan ecology such as ‘National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem’ and ‘SECURE Himalayas’.
SECURE HIMALAYAS SCHEME:
- The Government of India and United Nations Development Programme, with support from the Global Environment Facility, are implementing a new programme in the high altitude Himalayas
- SECURE Himalayas – Securing livelihoods, conservation, sustainable use and restoration of high range Himalayan ecosystems
- To ensure conservation of locally and globally significant biodiversity, land and forest resources in the high Himalayan ecosystem, while enhancing the lives and livelihoods of local communities.
Key Components
- Conservation of key biodiversity areas and their effective management to secure long-term ecosystem resilience, habitat connectivity and conservation of snow leopard and other endangered species and their habitats
- Securing sustainable community livelihoods and natural resource management in high range Himalayan ecosystems
- Enhancing enforcement, monitoring and cooperation to reduce wildlife crime and related threats
- Knowledge, advocacy, communication and information systems established
3) Svanidhi Samvaad:
Context: The Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi held ‘Svanidhi Samvaad’ with street vendors from Madhya Pradesh, the government to come up with a digital platform for street vendors
- The Government of India had launched PM Svanidhi scheme on 1st June, 2020 to help poor street vendors, impacted by COVID-19, resume livelihood activities.
- To provide cheap Capital to street vendors.
Aim
- Facilitate working capital up to rupees 10,000 term loan for one year
- Incentize regular/early repayment of loan with 7 %interest subsidy and
- Reward digital transactions with monthly cash back
- To provide Swarozgar, Svavlamban and Swabhimaan (Self Employment, Self-Sustenance and Self-Confidence) to the Street Vendors.
He said that one can get registered with the scheme through the common service center or in the municipality office by uploading the application and no need to stand in queue.
Not only this, Business Correspondent from the bank and municipal staff can also come and take the application from the street vendors.
4) e-Gopala App:
Context: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi to digitally launch the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) on 10th September. Prime Minister will also launch e-Gopala App
e-Gopala App:
A comprehensive breed improvement marketplace and information portal for direct use of farmers
Need for e- Gopala:
- At present no digital platform is available in the country for farmers managing livestock including buying and selling of disease free germplasm in all forms (semen, embryos, etc.).
- Availability of quality breeding services (Artificial Insemination, veterinary first aid, vaccination, treatment etc.) and guiding farmers for animal nutrition, treatment of animals using appropriate ayurvedic medicine/ethno veterinary medicine.
- There is no mechanism to send alerts (on due date for vaccination, pregnancy diagnosis, calving etc) and inform farmers about various government schemes and campaigns in the area.
The e-Gopala App will provide solutions to farmers on all these aspects.
5) Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana:
A flagship scheme for focused and sustainable development of fisheries sector in the country
With an estimated investment of Rs. 20,050 crores for its implementation during a period of 5 years from FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25 in all States/Union Territories, as a part of AatmaNirbhar Bharat Package.
Out of this, an investment of about Rs 12340 crores is proposed for beneficiary-oriented activities in Marine, Inland fisheries and Aquaculture and about Rs 7710 crores investment for Fisheries Infrastructure.
PMMSY Aim:
- Enhancing fish production by an additional 70 lakh tone by 2024-25
- Increasing fisheries export earnings to Rs.1, 00,000 crore by 2024-25
- Doubling of incomes of fishers and fish farmers
- Reducing post-harvest losses from 20-25% to about 10%
- Generation of additional 55 lakhs direct and indirect gainful employment opportunities in fisheries sector and allied activities.
PMMSY is designed to address critical gaps in fish production and productivity, quality, technology, post-harvest infrastructure and management, modernization and strengthening of value chain, traceability, establishing a robust fisheries management framework and fishers’ welfare.
Focus of PMMSY:
- PMMSY scheme focuses on adopting ‘Cluster or Area based approaches’ and creation of Fisheries clusters through backward and forward linkages.
- Special focus will be given for employment generation activities such as seaweed and ornamental fish cultivation.
- It emphasizes on interventions for quality brood, seed and feed, special focus on species diversification, critical infrastructure, marketing networks etc.
Other inaugurations related to Fisheries sector
- Prime Minister will announce the establishment of Fish Brood Bank at Sitamarhi
- Aquatic Disease Referral Laboratory at Kishanganj, for which assistance has been provided under PMMSY.
- These facilities will help in enhancing production and productivity of fish by ensuring timely availability of quality and affordable fish seed for the fish farmers and address the need for disease diagnosis as well as water and soil testing facilities.
One-unit fish feed mill at Madhepura and two units of ‘Fish on Wheels’ assisted at Patna under Blue Revolution.
Prime Minister will also inaugurate the Comprehensive Fish Production Technology Centre at Dr. Rajendra Prasad Central Agricultural University, Pusa, and Bihar.
6) Micro Irrigation Fund:
Context: Union Minister for Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Rural Development and Pachayati Raj Shri Narendra Singh Tomar today inaugurated a Webinar on Enhancing Water Use Efficiency and Coverage of Micro Irrigation in Indian Agriculture
- In the year 2019-20, about 11 lakh farmers have benefited by the adoption of drip and sprinkler irrigation system.
- During the last five years, an area of 47.92 lakh ha has been covered under micro irrigation in the country which includes 11.72 lakh ha for the year 2019-20 which is a significant achievement.
- Further, he informed that the Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers Welfare (DAC &FW) is implementing Per Drop More Crop component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayi Yojana (PMKSY-PDMC)
Micro Irrigation Fund:
- The Union Agriculture Minister said that Government has created a dedicated Micro Irrigation Fund (MIF) of Rs. 5000 crores with National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
Objective
- To facilitate States in mobilizing resources for expanding coverage of Micro Irrigation. The Steering Committee of MIF and NABARD has sanctioned projects of Rs. 3805.67 crore for covering 12.53 lakh ha under MIF.
- States can access MIF for incentivizing micro irrigation through an additional (top up) subsidy over and above the one available under PMKSY- PDMC for achieving the target.
- The Government has set the target of covering 100 lakh ha in five years under micro-irrigation.
States can access the fund for innovative integrated projects including projects in the Public Private Partnership (PPP) mode depending on State specific requirements to bring additional area under micro irrigation PDMC.
Stressing that micro irrigation not only increases water use efficiency but also the productivity of the crops
Panels appointed to discuss issues:
The Panel on Enhancing water use efficiency in Indian Agriculture was chaired by Prof Ramesh Chand, Member NITI Aayog.
The panel on Enhancing Coverage of Micro Irrigation was chaired by Shri Parshottam Rupala
Panel on Precision Irrigation Systems and role of private sector was chaired by Dr. Alka Bhargava, Additional Secretary.
7) KISAN rail:
Context: Second Kisan Rail, Anantapur – New Delhi Kisan Rail.
The Centre had announced plans of starting special parcel trains called ‘Kisan Rail’ in the Budget 2020-21.
Key Points:
- Kisan Rails are the first ever multi commodity trains.
- These trains with refrigerated coaches will help in bringing perishable agricultural products like vegetables, fruits to the market in a short period of time.
- These will ensure that agro products reach from one corner to another corner of the country.
- These trains are a step towards realizing the goal of doubling farmers’ incomes by 2022.
- These are expected to be a great help to the farmers, as freight of these trains will be charged as per parcel tariff of normal trains.
First Kisan Rail:
The first Kisan Rail was flagged off between Devlali in Maharashtra and Danapur in Bihar as a weekly service, which was later made bi-weekly due to increasing demand.
8) Village Poverty Reduction Plan
Context: Self Help Groups across the country being geared up to prepare the Village Poverty Reduction Plan for integration with the Gram Panchayat Development Plans
The Article 243G of the Constitution intended to empower the Gram Panchayats (GPs) by enabling the State Governments to devolve powers and authority in respect of all 29 Subjects listed in the Eleventh Schedule for local planning and implementation of schemes for economic development and social justice.
- In 2015, the Fourteenth Finance Commission grants were devolved to GPs that provided them with an enormous opportunity to plan for their development themselves. Since then, local bodies, across the country are expected to prepare context specific, need based Gram Panchayat Development Plans (GPDP).
Gram Panchayat Development Plan (GPDP)
Brings together both the citizens and their elected representatives in the decentralized planning processes.
GPDP is expected to reflect the development issues, perceived needs and priorities of the community, including that of the marginalized sections.
Apart from the demand related to basic infrastructure and services, resource development and convergence of departmental schemes, GPDP has potential to address the social issues.
GPDP is conducted from 2nd October to 31st December, every year across the country, under the People’s Plan Campaign (PPC).
The PPC guidelines and the joint advisory issued by the Ministry of Panchayati Raj and Ministry of Rural Development, has mandated Self
Help Groups and their federations under Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) to participate in the annual GPDP planning process and prepare the Village Poverty Reduction Plan (VPRP).
What is VPRP?
- VPRP is a comprehensive demand plan prepared by the Self Help Group (SHG) network and their federations for projecting their demands and local area development which needs to be integrated with the Gram Panchayat Development Plan (GPDP).
- The VPRP is presented in the Gram Sabha meetings from Oct. to Dec. every year.
Objectives of VPRP are three-foldPrepare a comprehensive and an inclusive demand plan of the community for local development - Facilitate an interface between the SHG federation and Panchayati Raj institutions for development of demand plan
- Strengthen the community based organization’s and their leadership for active participation in poverty reduction activities
Components of VPRP:
Demands under VPRP are categorized into five major components:
- Social inclusion – plan for inclusion of vulnerable people/household into SHGs under NRLM
- Entitlement – demand for various schemes such as MGNREGS, SBM, NSAP, PMAY, Ujjwala, Ration card etc.
- Livelihoods – specific demand for enhancing livelihood through developing agriculture, animal husbandry, production and service enterprises and skilled training for placement etc.
- Public Goods and Services – demand for necessary basic infrastructure, for renovation of the existing infrastructure and for better service delivery
- Resource Development – demand for protection and development of natural resources like land, water, forest and other locally available resources
- Social Development – plans prepared for addressing specific social development issues of a village under the low cost no cost component of GPDP
Training on VPRP for State Missions
With the current Covid-19 situation, DAY-NRLM designed an online training program to train all State Missions across the country on VPRP, in partnership with Kudumbashree (National Resource Organization), National Institute of Rural Development & Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR), Hyderabad and Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
9) Indo – China border Tension
Context: As Indian troops are engaged in a standoff on the south bank of Pangong Tso (lake) for the past one week, a massive build-up had again begun in the Finger area of the north bank.
- People’s Liberation Army had occupied the ridge lines and gathered troops on the Northern Bank where fingers 4 to 8 are located
- China has entered about 8 kilo meters in the finger area, India has not been able to patrol beyond finger 4, and earlier India was able to patrol till finger 8.
- China is dominating the ridges in the finger area of the Pangong Tso for the past four months
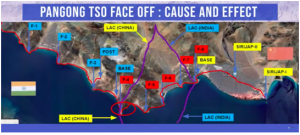
The development comes a day before the Foreign Ministers of both countries are expected to meet in Moscow on the sidelines of a meeting of the eight-nation Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
- Earlier, Indian troops could patrol up to Finger 8.
- Several rounds of meetings at the military and diplomatic levels have not yielded any results. China partially retreated to Finger 5 and as per the agreement, Indian troops were pulled back to Finger 2.
- The ground commanders met on Wednesday to solve the stalemate but it remained inconclusive
- For the first time in 45 years, aerial shots were fired along the disputed LAC.
- Brigade Commander-level talks were held at Chushul on Wednesday in the wake of Monday’s firing incident which.
- Both sides agreed to hold another round of Corps Commander-level talks, for which the date was yet to be finalized
- China has repeated its accusations of India firing first.
- Tensions have been high since August 29, when Chinese troops engaged in a “provocative action” trying to change the status quo on the south bank
- The official said the issue was raised with the Chinese commander. “The Chinese say that the rods and spears are for construction work to build temporary sheds on their side of the LAC. But it is evident that such tools serve no such purpose,” the official pointed out.
10) BT COTTON:
Why was BT Cotton Introduced?
- Rising debts, and reducing yields, coupled with increasing insect resistance, worsened the plight of cotton farmers.
- Genetically modified cotton are the plants containing the pesticides gene from the bacteria bacillus thuringiensis it has been grown in India for about 20 years
- This pesticide now produced in each BT plant cell ought to protect the plant from Bollwarm increasing yields and reducing insecticides spraying on the cotton plant
- Studies examining BT Cotton in early years pronounce that BT was a Panacea for dwindling yields and pesticides expenses
- The two decade mark now provided an opportunity to review GM cotton in India more comprehensively.
Review of BT cotton:
- Earlier studies reviewed that BT tripled the Cotton yield between 2002-2014
- Needs pesticide more and more fertilizers and so cost of production increases
- There were many states where cotton production has increased because of the increased irrigation facilities for example Gujarat had increased its cotton production by 138 percent in 2003 but this doesn’t mean it is all the BT Cotton that was grown, BT Cotton was used only for 5% of land under cotton cultivation.
- But over the years the production cost has increased also sap sucking insects have increased for the hydrides and BT is even more vulnerable, expenditure for spraying has increased and it is 37% more than pre BT levels.
NATIONAL SAFAI KARAMCHARIS FINANCE & DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION (NSKFDC):
- National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation (NSKFDC) an apex corporation under the Ministry of Social justice & Empowerment.
- Government of India has launched a new scheme with a view to promote mechanized cleaning and to minimize the incidents of Manual Hazardous cleaning to providing financial assistance to its target group for procurement and operation of mechanized cleaning equipment under its Swachhta Udyami Yojna (SUY) with a provision of 50% capital subsidy for equipment costing up-to Rs.5 Lakh.
Vanchit Ikai Samooh aur Vargon ki Aarthik Sahayta Yojana (VISVAS Yojana)
- Is for the benefit of Scheduled Castes and OBC Self Help Groups/Individual member with annual family income up-to Rs. 3 Lakh.
- Under the scheme SC and OBC Self Help Groups and Individuals will be able to avail Interest Subvention on bank loans at 5%.
- VISVAS Yojana will be implemented by the apex corporation of MoSJ&E i.e. National Scheduled Castes Finance Development Corporation (NSFDC) and National Backward Classes Finance and Development Corporation (NBCFDC).
- The scheme will significantly help to expand the outreach to OBC and SC members and reduce interest burden in these times of pandemic.
