1) Keshavananda Bharti case:
Context: keshvananda Bharati Swami passed away on 6 September
- Pioneer in the landmark judgement of Supreme Court on fundamental rights and basic structure doctrine
- In 1973 constitutional bench headed by the then chief justice S M Sikri delivered the judgement in the Keshvananda Bharati vs. State of Kerala case which held that the Parliament could amend any part of the Constitution so long as it did not alter or amend the basic structure or essential features of the constitution
- Keshvanananda Bharati judgement is a Landmark decision of the Supreme Court of India that outlined the Basic Structure Doctrine.
Golaknath case vs. State of Punjab 1967
Parliament cannot abridge or take away any of the fundamental rights which are sacrosanct in nature
Fundamental rights cannot be amended for implementation of Directive Principles of State Policy
Parliament’s reaction to Supreme Court judgement
- Parliament enacted 24th and 25th Constitutional Amendment Act
24th Amendment Act -Parliament has power to abridge or take away any of the fundamental rights by enacting Constitutional Amendment Act
25th Constitutional Amendment Act inserted new article 31c which have two provisions
- First provision – no law which seeks to implement the socialistic directive principles specified in article 39 (b) and 39(c) shall be void
- Second provision no law under above first provisioned can be questioned
Keshavananda Bharati case- 1973
Supreme Court declared about provision of article 31(C) as unconstitutional and invalid on the grounds of judicial review, judicial review constitutes the basic structure of the constitution and hence cannot be taken away
But second provision of article 31(C) is held constitutional and valid
42nd amendment act 1976- extended the scope of first provision by including any law and not merely specified in article 39(b) and 39(c) and hence Directive Principles prevail over fundamental rights
These Provisions were declared unconstitutional and invalid by Supreme Court
The Basic Structure Doctrine forms the Basis of power of Indian Judiciary to review and strike down amendments in the constitution of India enacted by the Indian Parliament which conflict with or alter the basic structure of the constitution
But the term basic structure was not defined anywhere
The Basic Structure of the constitution in Indira Nehru vs. Raj Narain and also in Minerva Mills case it was observed that the claim of any particular feature of the constitution to be a basic feature would be determined by the court in each case that comes before it
Some of the features of the Constitution termed as basic are listed below
- Supreme Court of the constitution
- Rule of law
- The principle of separation of powers
- Judicial review
- Preamble of the constitution
2) Pradhanmantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP):
Context: 8 immunity boosters launched under Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana for sale across the country.
About PMBJP
- Launched in 2008
- By Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
Aim – to bring down the Healthcare budget of citizens of India by providing quality medicines at affordable cost
Implementation by Bureau of Pharma PSUs of India (BPPI)
About BPPI:
- Established in 2008
- Parent Organization- The Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers
- Got registered as an independent society in 2010 under Societies Registration Act 1860
3) India -Afghan meeting:
Context: Defence Minister of India and Afghanistan Discussed ways to take forward bilateral cooperation and exchange views on regional security issues including peace and stability in Afghanistan
- Afghan minister raised the issue of recent reports citing the safety of minorities in India
- Both leaders emphasized upon cultural, linguistic and civilizational ties between India and Iran
India Iran relationship - India and Iran have friendly relations in many areas despite India not welcoming the 1979 revolution. Trade between two countries is significant particularly in crude oil imports into India and diesel exports to Iran .India welcomed Iran’s inclusion as an observer state in SAARC Regional organization.
- India’s Interest in Afghanistan
Economic and Strategic Interest: Afghanistan is a gateway to the oil and mineral-rich Central Asian republics.
-Afghanistan’s main advantage is its geography, as anyone who is in power in Afghanistan controls the land routes connecting India with Central Asia (via Afghanistan).
-The massive reconstruction plans for the country to offer a lot of opportunities for Indian companies.
-Three major projects: the Afghan Parliament, the Zaranj-Delaram Highway, and the Afghanistan-India Friendship Dam (Salma Dam), along with India’s assistance of more than $3 billion in projects, hundreds of small development projects (of schools, hospitals and water projects) have cemented India’s position in Afghanistan
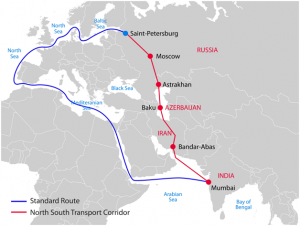
The North South Transport Corridor is the ship, rail and road route for moving freight between India, Russia, Iran, Europe the Caucasus and Central Asia
The present route primarily involved moving freight from India Iran Azerbaijan Russia via ship rail and Road
4) Foreign contribution Regulation Act (FCRA):
Context: concerns have been raised regarding the impact of 4 US based evangelical donors in regard to Indian associations and the license of the four groups was suspended
- An FCRA license is mandatory for a non-profit organization to receive foreign funds
- The reason for the suspension or violation was not specified
- The reason specified was religious conversion
What is FCRA?
- It is a law enacted by Parliament to regulate foreign contribution (especially monetary donation) provided by certain individuals or associations to NGOs and others within India.
- FCRA Act was originally passed in 1976 and majorly modified in 2010.
- The government has used the act over the years to freeze bank accounts of certain NGOs who it found were affecting India’s national interest for wrong purposes.
- As per the FCRA Act 2010, all NGOs are required to be registered under the Act to receive foreign funding.
- According to terms stipulated in the FCRA, an organization cannot receive foreign funding unless it is registered under the 2010 Act, except when it gets government approval for a specific project.
- Under the FCRA Act, registered NGOs can receive foreign contribution for five purposes — social, educational, religious, economic and cultural.
5) BT Brinjal:
Context: Centre has given nod for trials of BT brinjal varieties, approval given for confined field trials to to BT brinjal varieties after imposing a Moratorium on commercial release of genetically modified BT brinjal.
Biosafety evaluation is by the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) raise concerns
GEAC:
- India’s Apex Biotech regulatory committee a statutory body under Environment protection Act 1986
- The genetic engineering approval committee has been now changed as Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee
- Objective is to control the use of GMO crops in fields without harm to the environment
- The indigenous transgenic varieties of brinjal hybrid namely Janak and BSS 793 containing BT cry1 fa1 gene are developed by ICAR Indian Council of Agricultural Research’s -National Research Centre on plant biotechnology
Concerns about GM crops
- Would be hazardous for soil and overall environment
- They are also called Terminator seeds
6) Novichok:
Context: Germany says Russia used Novichok to poison Alexei Navalny a critique of Russian President Putin
- The name novichok means newcomer in Russian and applies to a group of Advanced nerve agents developed by the Soviet Union in 1970s and 1980s
- It was developed under a codenamed Foliant if by Soviet Union
- Available in liquid, powder or aerosol and said to be more Lethal than nerve agents
- In causes muscle spam that can stop the heart can also cause fluid buildup in the lungs and also damage Nerve cells
- Russia is believed to have never declared novichok or its ingredients to the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) which oversees a Treaty banning their use
Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons
- It implementing body for Chemical Weapons Convention 1997
- It has 193 members including India
- It’s aim is to promote and verify the adherence to the Chemical Weapons Convention which prohibits the use of chemical weapons and requires the destruction
- Headquarters Hague, Netherlands
- The Organization was awarded the 2013 Nobel Peace Prize for its extensive efforts to eliminate chemical weapons
Chemical Weapons convention
- It is a multilateral Treaty that bans chemical weapons and requires their destruction within a specified period of time
- The CWC is open to all Nations and currently has 193 state parties Israel has signed but has yet to ratify the convention
- Three states have signed nor ratified the convention Egypt, North Korea, and South Sudan
7) The three language formula in Tamil Nadu:
Three language formula is enunciated in the 1968 national policy resolution which provided for the study of “Hindi”, English and modern Indian languages (Preferably one of the southern languages ) in the Hindi speaking states and Hindi, English and the regional language in the non-Hindi speaking States .
In two language formula, beyond Tamil and English (in order of preference) no other language would be taught in the schools of Tamil Nadu
Policy lessons in Tamil Nadu’s language formula:
C.N. Annadurai’s argument was that the official language should be equidistant to all in a multilingual society.
- Annadurai insisted that all the national languages be made official languages and English should be common link language
- English would fit for both students of Hindi and Tamil
- Making Hindi as official language would create disparity.
- Annadurai was also particular that English is the Language we communicate with larger world.
- The New Education Policy misses the vital empirical evidence of Tamil Nadu following a language formula that is distinctly at variance with that of Delhi for the past 50 years and yet achieving significant positive social and economic changes.
- Most countries follow a one language formula (invariably mother tongue) for teaching children in the primary classes.
- On reaching middle school they are given a chance to learn one more language, mostly English.
- As there is no imposition through schools, voluntary learning of other languages is widely prevalent in these countries.
- Be it students of literature, sociology, of people involved in international trade, their knowledge of 5 or 6 languages is quite normal.
Singapore Case:
All countries faced with the enormous challenge posed by the new century, invariably give Preference to the English language after their Mother tongue.
Japan and Singapore can be cited as two countries which handle language policy as a strategic tool to achieve social economic development.
Singapore in this area is phenomenal and closely comparable to the situation in India.
- It was the mission of Lee Kuan yew the architect of modern Singapore giving equal status to English and mother tongue as a prerequisite not only to work closely with the International community but also bring in big ticket changes in many ways this can be compared to Annadurai’s mission.
- Lee kuan yew attributed the international acclaim, Singapore received for its success mainly to its two language formula.
- The Chinese by birth, his elitist family spoke English at home. Having studied in English schools and receiving his higher education in Cambridge, he understood the importance of English for the then undeveloped society in coping with international competition.
- Importantly Lee kuan yew realized that a multi-cultural society such as Singapore could enhance its status only if each of its cultural groups thinks that it was on a par with others.
- He is viewed that the lingua Franca of the country should be equidistant to all cultural groups, thereby creating their competition and opportunities. Only in this background were Malay, Chinese, Tamil and English declared as common languages with the lingua franca being English.
- American example – when US emerged as a nation only 20% of the people went from the British Isles…yet America has chosen English as the official language.
Comparison of Tamil Nadu with other states:
How the experts ever discuss the contribution of Annadurai to language formula in the background of Tamil Nadu being one of the developed states in India despite not possessing a trade and big capital like Gujarat or Maharashtra nor having water resources and land fertility like Kerala and Punjab or the political bargaining power by sheer size and operation by States such as Uttar Pradesh?
And when will they be discussing the Indian government’s failure in the language policy in the backdrop of inequalities prevailing among societies since independence?
In Singapore:
The world celebrates the decisions made by Lee kuan yew after taking into consideration the possibilities, limitations and challenges faced by a third world country. They praise him for his two language policy which prepared Singaporean’s in advance for globalization.
Singapore has much more justification to dopt the Chinese as its sole official language than India insisting on Hindi being the sole official language.
Even today the population of Hindi speaking people has not crossed 50% in India; in Singapore, 74.2 percent of the population is Chinese, 13.2% malays and 9.2 % Indians.
Lee kuan yew had wished he could have well declared Chinese to be the sole official language and satisfied the Chinese who were in a majority. He could have used this as a nationalistic tool and cemented his place politically forever but he resisted this temptation.
Reality check in Tamil Nadu:
Though comparable to Singapore in far-sightedness and in the forefront as for as India is concerned, in the present scenario, Tamil Nadu education standards are not compatible to Singapore’s in terms of outcomes.
Infrastructure:
- Our students suffer a serious handicap while dealing with English and Tamil languages. And they do not have command over either.
- This is not the failure of the two language formula per but of its implementation and present Indian educational ecosystem.
