CURRENT AFFAIRS 06-09-2021
Topics
- India and 6th Eastern Economic Forum (EEF).
- The 24th Meeting of The Financial Stability and Development Council
- Chief Justice of India (CJI) on Virtual Courts
- Perseverance rover: final stretch towards destination Mars.
- WHO: Variant of Interest (VOI) and Mu variant.
-
India and 6th Eastern Economic Forum (EEF).
#GS2: Groupings & Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
Context:
- The Prime Minister of India (PM) recently addressed the plenary session of the 6th Eastern Economic Forum via video conferencing (EEF).
- In keeping with the ‘Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership,’ the Prime Minister emphasized the significance of India-Russia relations and potential areas of cooperation.
Highlights of the Prime Minister’s Address:
- Applauded Russia’s vision for the development of the Russian Far East region and reaffirmed India’s commitment (as part of its “Act East Policy”) to being a dependable partner for Russia in this regard.
- The importance of the health and pharmaceutical sectors as important areas of cooperation that have emerged during the pandemic has been highlighted.
- Other potential areas of economic cooperation mentioned include diamond, coking coal, steel, timber, and so on.
What exactly is the Eastern Economic Forum?
- The EEF was established by a decree issued by the Russian Federation’s President in 2015.
- It is held every year in the Russian city of Vladivostok.
- It serves as a forum for discussion of global economic issues, regional integration, and the development of new industrial and technological sectors, as well as global challenges confronting Russia and other countries.
- The Forum’s business agenda includes a number of business dialogues with leading Asia-Pacific partner countries, as well as ASEAN, a vital integration organization of Southeast Asia’s dynamically developing states.
- Over the years, it has evolved into an international forum for discussing Russia’s strategy for strengthening political, economic, and cultural ties with the Asia-Pacific region.
What is the Importance of Indian-Russian Relations?
- China’s Balance of Power:
- China’s aggressiveness in the border areas of eastern Ladakh strained India-China relations, but it also revealed that Russia can help defuse tensions with China.
- Following violent clashes in the disputed territory of Ladakh’s Galwan Valley, Russia convened a trilateral conference of Russia’s, India’s, and China’s foreign ministries.
- Aside from established fields of collaboration such as weaponry, hydrocarbons, nuclear energy (Kudankulam), space (Gaganyaan), and diamonds, new areas of economic engagement such as mining, agro-industrial, and high technology such as robotics, nanotech, and biotech are expected to emerge.
- The Indian presence in Russia’s Far East and Arctic is expected to grow. Projects involving connectivity may benefit as well.
- Reviving the Eurasian Economic Union:
- Russia wants to use India’s soft power to gain credibility in the success of the Eurasian Economic Union and reclaim its Cold War-era primacy.
- Terrorism:
- India and Russia are attempting to close the gap with Afghanistan by pressing for the completion of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism as soon as possible.
- Russia also supports India’s bid for permanent membership in a reconstituted United Nations Security Council as well as the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
- Diplomacy:
- Russia has been a long-time friend of India, not only providing it with armaments to maintain a formidable military profile, but also crucial diplomatic assistance on a variety of regional issues.
- Defense Cooperation:
- Although India has made a concerted effort to diversify its new defence purchases, Russia continues to supply the majority of its defence equipment (60 to 70 percent).
- The BrahMos Missile System and the licenced production of SU-30 aircraft and T-90 tanks in India are two examples.
- Indra Exercises are joint tri-services (Army, Navy, and Air Force) exercises.
2.The 24th Meeting of The Financial Stability and Development Council
#GS3: Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Context:
- The FSDC’s 24th meeting focused on the organization’s various mandates, including financial stability, financial sector development, inter-regulatory coordination, financial literacy, financial inclusion, and macroprudential supervision of the economy, including the operation of large financial conglomerates.
The council also discussed issues concerning
- Management of stressed assets, institutional strengthening for financial stability analysis, framework for financial institution resolution and IBC issues, data sharing mechanisms of government authorities, internationalisation of the Indian rupee, and pension sector issues
About FSDC
- The Financial Stability and Development Council was established as an independent body tasked with dealing with macroprudential and financial regularities in India’s entire financial sector.
- The body intends to strengthen and institutionalise the mechanism for ensuring financial stability, financial sector development, inter-regulatory coordination, and monitoring the economy’s macro-prudential regulation.
- It should be noted that the council receives no separate funding to carry out its activities.
Members of the FSDC Council
- The FSDC is chaired by the Finance Minister.
- FSDC members include the following heads of financial sector regulators:
- Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) (PFRDA)
- Other members include the Finance Secretary, the Chief Economic Advisor, and the Secretary of Financial Services.
FSDC’s Responsibilities
- Bringing about financial sector stability
- Growth of the Financial Sector
- Inter-Regulatory Body Coordination
- Increasing financial literacy
- Providing financial inclusion
- Macroprudential oversight of the economy, including the operation of large financial conglomerates.
- Coordination of India’s international interface with financial sector bodies such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF), the Financial Stability Board (FSB), and any other bodies as determined by the finance minister on a case-by-case basis.
3.Chief Justice of India (CJI) on Virtual Courts
#GS2 : Judiciary #E-Governance #Transparency & Accountability
Context:
- Recently, Chief Justice of India (CJI) N.V. Ramana expressed his displeasure with the Supreme Court’s newly implemented open court software for virtual hearings.
- The dissatisfaction stems from the issue of disconnections, as well as the reverberation of voices during virtual hearings.
The eCourts Initiative:
- It was conceptualised on the basis of the “National Policy and Action Plan for Implementation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the Indian Judiciary – 2005” submitted by the eCommittee of the Supreme Court of India, with the goal of transforming the Indian Judiciary through Court ICT enablement.
The project intends to
- To deliver efficient and time-bound citizen-centric services as outlined in the eCourt Project Litigant’s Charter.
- Creating, installing, and implementing decision support systems in courts.
- To automate processes in order to provide transparency in information accessibility to its stakeholders.
- Improving judicial productivity, both qualitatively and quantitatively, in order to make the justice delivery system more affordable, accessible, cost effective, predictable, dependable, and transparent.
Benefits of e-courts:
- The primary benefits of establishing Electronic Courts in India include introducing a justice-serving mechanism that is transparent, efficient, affordable, time-saving, protects the interests of witnesses, reduces the backlog of pending cases, and, most importantly, reduces the number of unethical activities.
- The entirety of information pertaining to a specific case would be available online. It would be accessible to attorneys, parties, and the general public via the internet.
- Registered attorneys can file their case documents from the comfort of their own homes or offices. They don’t have to deal with postage, traffic, or messenger services. They can make a docket sheet and update it as soon as the documents are filed.
- The documents of a case can be easily accessed from anywhere at any time using the internet.
- E-courts would aid in the computerization of courtwork flow management. As a result, it would aid in the development of a better court and case management system. Every court complex would have video conferencing capabilities. This method can be used to record evidence from eyewitnesses who are unable to attend court.
- The information would not be misplaced because all information pertaining to the case would be meticulously recorded and saved. Data keeping would entail keeping track of e-file minute entries, bail orders, warrants, and so on.
- In many cases, witnesses are unable to appear in court and make their statements because the opposing party is too powerful and threatens them with dire consequences. In such cases, e-Courts can be useful.
Demerits of e-courts:
- In India, e-courts are a never-ending and complicated process. It is a difficult process to e-file a document. All of the evidence cannot be produced digitally.
- The main reason for the poor status of e-courts in India is a lack of technological legal expertise. Electronic courts cannot be established in India due to a lack of technological legal expertise. To ensure the success of the e-court project, the country requires more technological legal e-court centres.
- The e-court project will cost a lot of money. It necessitates the use of numerous computers and infrastructures. In the long run, e-courts may run into financial difficulties.
- Hackers are becoming more powerful by the day. In such a case, the possibility of e-Courts being hacked cannot be ruled out.
Suggestions:
- Infrastructure should be updated with enough machinery and data connectivity to support the virtual proceeding.
- Virtual proceedings can be extended indefinitely to various Appellate Tribunals located throughout the country, such as the Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal, the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal, and others, which do not require personal appearances of the parties/advocates.
- It has been recommended that the Ministries of Law and Justice and Electronics and Information Technology address data privacy and security concerns while developing a new platform for India’s judicial system.
The Way Forward
- While India is dealing with a health and economic crisis, there is a need to think outside the box, and a shift in mindset regarding work culture is required.
- It is past time for the courtroom, which is often regarded as the last bastion of antiquated working practises, to embrace cutting-edge technology.
- A virtual judiciary can become a part of the Indian judiciary if vested interests are set aside and the collective will to initiate what is for the common good takes precedence.
4.Perseverance rover: final stretch towards destination Mars.
#GS 3:Space Technology achievements of Indians in Science & Technology
Context:
- After a seven months’ journey from Earth, the NASA Perseverance is in its final stretch towards destination Mars.
In details:
The following is information about the Perseverance rover:
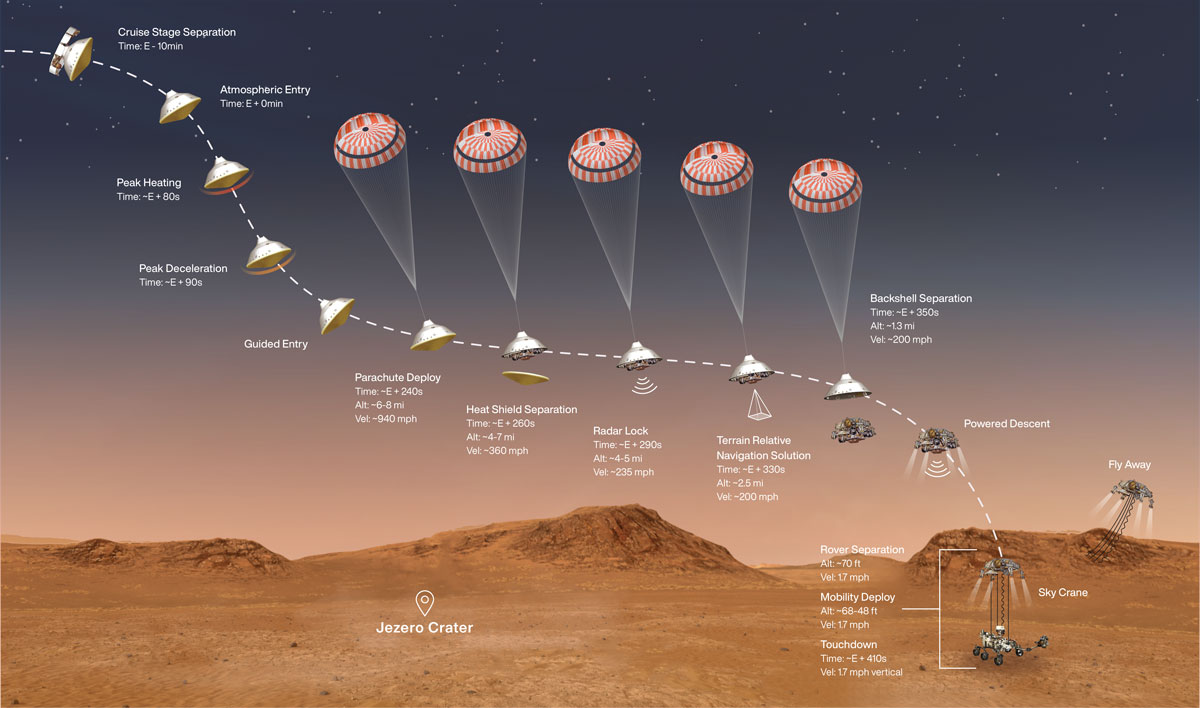
- In July of 2020, it will be launched.
- It is expected to land in the Jezero Crater on Mars.
- Perseverance’s primary mission is to search for signs of ancient life and collect samples of rock and reglolith to possibly return to Earth.
- Perseverance is powered by electricity generated by the radioactive decay of plutonium.
- NASA Perseverance obtains shape memory alloys to keep the surface of Mars stable.
- Perseverance is ready to explore Mars, armed with drills, cameras, and lasers.
What is the significance of Perseverance Rover?
- Perseverance tackles two critical themes surrounding Mars: the search for life and a human mission to Mars.
- It’s not just another Rover Mission; it’s the most advanced, expensive, and sophisticated mobile laboratory ever sent to Mars.
- The outcomes of the Perseverance experiments will most likely define the next couple of decades of Mars exploration.
- It will shape the course of the search for life on Earth as well as a future manned mission to Mars.
What will the Perseverance Rover achieve?
- The Perseverance Sample Return Mission is the first step in a multi-step project to bring back samples from Mars.
- The analysis of the returned rock samples should provide a definitive answer as to whether life existed on Mars in the past.
- The following are the steps in the Sample Return:
- Fill 43 cigar-sized tubes with rock and soil samples. – Samples will be collected, canisters sealed, and left on the ground by the Mars Fetch Rover (provided by the European Space Agency) – land, drive, and collect all samples from various locations before returning to the lander.
- The canisters will then be transferred to the Ascent Vehicle by the Fetch Rover.
- The Mars Ascent Vehicle will collide with an Orbiter, which will then transport the samples back to Earth.
- MSR, or Mars Sample Return, is the name given to this long-term project.
- MSR will transform our understanding of Mars’ evolutionary history.
- If MSR is successful, it will provide a reasonable answer as to whether there was microscopic life on Mars.
- However, there are risks associated with MSR.
- MSR is doomed if one of its components, such as the Fetch Rover or the Mars Ascent Vehicle, fails.
- A strategic risk is one that is hidden. At the cost of MSR, 5-10 spacecraft missions to various parts of the solar system could be launched.
- Making oxygen on Mars: It is critical to have the technology and infrastructure in place to manufacture oxygen on Mars using raw materials found on Mars in order to launch a human mission to Mars at a reasonable cost.
- MOXIE, or Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilisation Experiment, will be aboard Perseverance.
- This will require 300 watts of power to generate approximately 10 grammes of oxygen from atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- If this experiment is successful, MOXIE can be scaled up by a factor of 100 to meet two critical human needs:oxygen for respiration rocket fuel for the return trip to Earth
- On Mars, researchers are looking for underground water. The Radar Imager for Mars’ Subsurface Experiment will be carried by Perseverance (RIMFAX).
- RIMFAX will provide high-resolution mapping of the landing site’s subsurface structure.
- In addition, the instrument will search for subsurface water on Mars.
- If discovered, it would greatly strengthen the case for a human mission to Mars or the cause of human settlement on Mars.
- Testing a Mars-flying helicopter:
- The Mars Helicopter is essentially a miniature drone.
- It’s a technology demonstration experiment to see if the helicopter can fly in Mars’ thin atmosphere.
- The low density of the Martian atmosphere makes the odds of actually flying a helicopter or an aircraft on Mars very low.
-
WHO: Variant of Interest (VOI) and Mu variant.
#GS 3: Issues related to biotechnology.
Context:
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has designated B.1.621 as a variant of interest (VOI) and dubbed it the Mu variant.
- Eta, Iota, Kappa, and Lambda are the four other variants of interest.
- Mu variant was discovered in Colombia in January 2021 and has since been discovered in approximately 39 countries.
- There have been a few reported cases of the Mu variant, as well as some larger outbreaks from countries in South America and Europe.
What exactly is a variant of interest? (VOI)
- A VOI is classified based on factors like genetic changes that affect virus characteristics like transmissibility, disease severity, immune escape, and so on.
- A variant of concern (VOC) such as Alpha, Beta, or Gamma represents a lower level of concern than a VOI. and
- Concerning factors include an increase in transmissibility or a negative change in epidemiology, among others.
How and why do virus variants emerge?
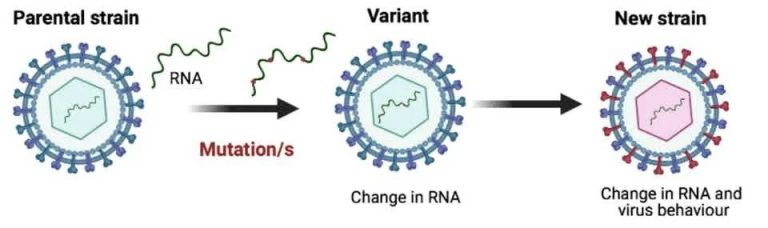
- Variants of a virus have one or more mutations that distinguish them from other variants in circulation.
- Essentially, the virus’s goal is to evolve to the point where it can coexist with humans because it requires a host to survive.
- Errors in viral RNA are referred to as mutations, and viruses with these mutations are referred to as variants. Variants may differ due to a single or multiple mutations.
What exactly is a mutation?
- A mutation is a change in the virus’s genetic sequence.
- A mutation in the case of SARS-CoV-2, a Ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus, means a change in the sequence in which its molecules are arranged.
- A mutation in an RNA virus occurs when the virus makes a mistake while replicating itself.
What are the issues?
- Concerns are growing about the emergence of new virus mutations as infection rates rise globally due to the highly transmissible Delta variant. Cases are increasing, particularly in unvaccinated areas and in areas where covid-19 measures have been relaxed.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 06th September -2021
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube

