Topics
- 50% funds allocated for ongoing MPLADS projects lapse
- Key Administrative Reforms in recent years
- Report by Standing Committee on Water Resource management
- Status of the E-Prisons Project
- The Limited Liability Partnership (Amendment) Bill 2021
- Sunscreens and Corals
1.50% funds allocated for ongoing MPLADS projects lapse
#GS2 #Functions & Responsibilities of the Union and the States
#Government Budgeting
Context: Recently, the parliamentary committee has criticized Finance ministry on its move about giving just a week’s time to the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation for funding ongoing Member of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) projects, due to which 50% funds lapsed.
Background of the issue:
- In 2020, due to Covid-19 pandemic, the union government had decided not to operate MPLADS for the Financial Years 2020-21 and 2021-22; and place these funds at the disposal of the Finance ministry to meet the emergency needs of people.
- From ?5,012 crore spent during 2018-19, an expenditure of just ?2,491.45 crore was taken up under the scheme in 2019-20.
Findings of the Standing Committee on Finance:
- The resulting funding crisis would have hit numerous local area development projects under operation across the country.
- Particularly in the States that went to elections this year as no funds were given for these States due to the Model Code of Conduct.
- Under MPLADs, funds released to district authorities are not lapsable, while funds not released by the government in a particular year are carried forward.
- However, the decision of the Finance ministry that made funds lapsable, contains ad-hocism and a serious lapse in fiscal management with negative consequences for communities across the country.
About the MPLAD Scheme:

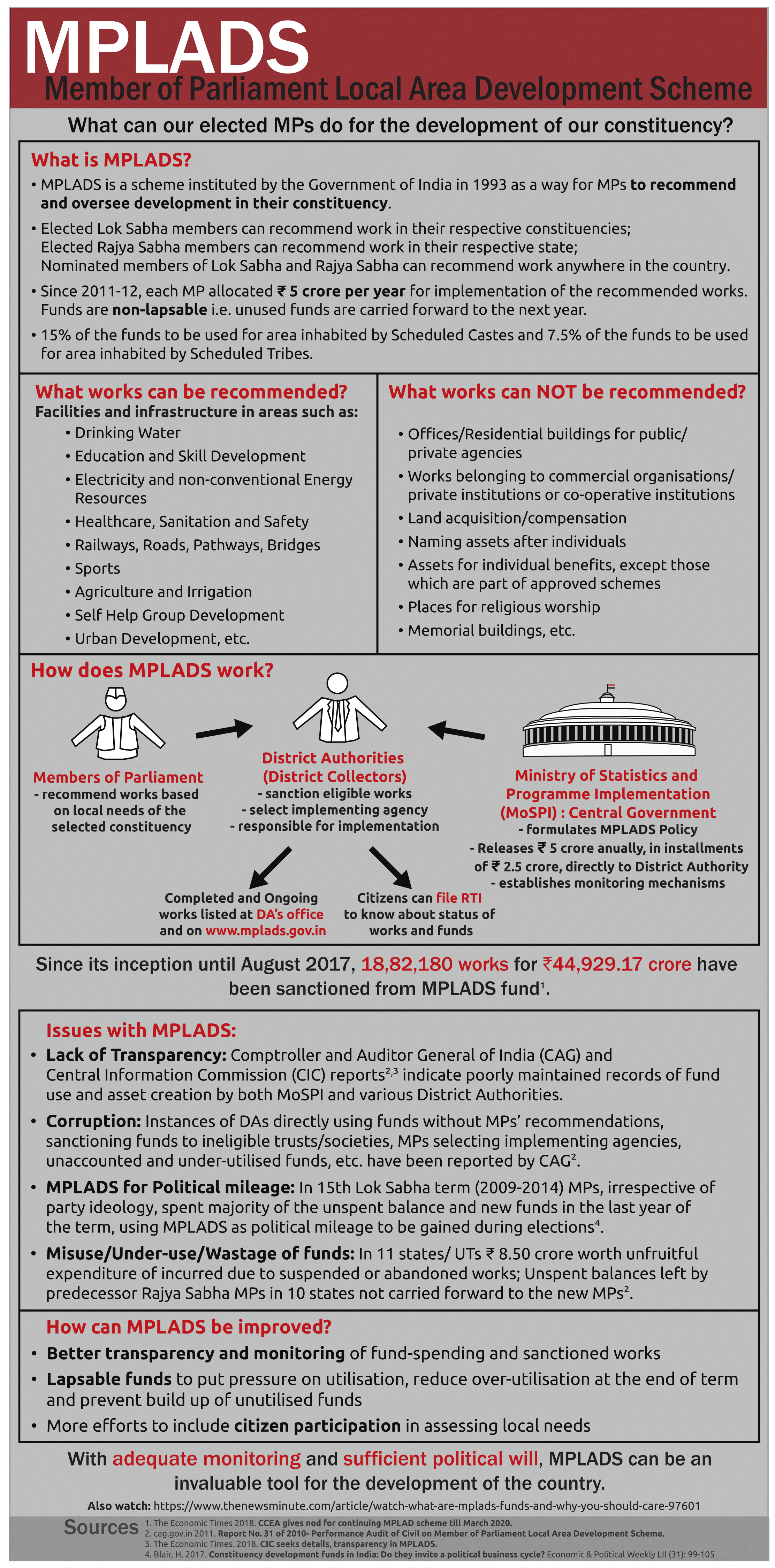
2.Key Administrative Reforms in recent years
#GS2 #Government Policies & Interventions for Development #Important Aspects of Governance, Transparency & Accountability
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions gave the info on key Administrative Reforms which were initialised in recent years and highlighted the importance of these reforms in making governance more accessible.
- Intention of these reforms is to reassure greater efficiency, transparent and corruption free governance, accountability.
Key Details:
- Mission Karmayogi:
- It is a National Architecture for Civil Services Capacity Building.
- It is also a Comprehensive reform of the capacity building tool at individual, institutional and process levels for effective public service delivery.
- It is meant to build a future-ready civil service with the right attitude, skills and knowledge, allied to the idea of New India.
- The capacity building will be carried out through iGOT-Karmayogi digital platform, with content drawn from best practices from various countries and organisations.
- Lateral Entry into an administrative position:
- This is important because modern times require highly skilled and driven individuals at the helm of administrative affairs, without which public service delivery mechanisms do not work efficiently.
- Lateral Entry aids in bringing the ideals of economy, efficiency, and effectiveness in the Government sector.
- It will help in developing a culture of performance within the Government sector.
- e-Samiksha:
- A real time online scheme for monitoring and follow through action on the choices taken by the Government at the top level in respect of implementation of important Government projects.
- Also, the government has been taking a rigorous review for clearing out inefficient and Officers of doubtful integrity by premature retirement.
- e-Office:
- e-Office Mission Mode Project (MMP) has been reinforced for allowing Ministries/Departments to swap to paperless office and competent decision making.
- Citizen Charters:
- Union Government has mandated Citizen Charters for all Ministries/Departments which are updated and revised on a regular basis.
- It is a written document that elucidates the service provider’s efforts taken to focus on their commitment towards fulfilling the needs of the citizens/customers.
- Good Governance Index 2019:
- It evaluates the Status of Governance and effects of various interferences taken up by the State Government and Union Territories.
- The main objectives of the index are to provide quantifiable data to compare the state of governance in all States and UTs, empower States and UTs to frame and implement appropriate strategies for improving governance and move to result oriented approaches and administration.
- It has been launched by the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions.
- National Conference on e-Governance:
- It provides a stage for the government to engage with experts, intellectuals from industry and academic institutions to talk about experiences concerning various e-Governance initiatives.
- In 2020, Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG) along with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology organised the 23rd National Conference on e-Governance was organised by the (MeitY) in Mumbai.
- Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS):
- It is an online web-enabled scheme developed by National Informatics Centre (Ministry of Electronics & IT [MeitY]), along with Directorate of Public Grievances (DPG) and Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG).
- The CPGRAMS offers the facility to lodge a grievance online from any location. It allows the citizen to track online the grievance being followed up with concerned Departments and also enables DARPG to monitor the grievance.
- Increasing proficiency in decision making in Central Secretariat by reducing the channel of submission to 4, adoption of e-Office version 7.0, digitization of central registration units, greater delegation of virtual private networks under the Central Secretariat Manual of Office Procedure 2019, and adoption of desk officer system.
Road Ahead:
- Reforms are an obvious answer to the novel challenges confronting the state institution handling public affairs; what lies at the root of such an exercise is the effort to augment administrative competence in the changed scenario.
- Since the civil servants are answerable to political executives and that results in politicisation of civil services, the attention must be on external accountability tools like citizen charters, social audits and stimulating outcome orientation among civil servants.
- Civil servants should provide impartial, coherent and commendable suggestions to the political executive in policy formulation.
- It requires an unbiased Civil Services Board to take care of all the aspects regarding promotions, transfers, posting and suspensions.
- Report by Standing Committee on Water Resource management
#GS3 # Disaster Management # Management of Disasters #GS2 # India and its Neighbourhood – Relations
Context: Recently, a report titled “Flood Management in the Country including International Water Treaties in the field of Water Resource Management with particular reference to Treaty/Agreement entered into with China, Pakistan and Bhutan” was tabled in Parliament by the Standing Committee on Water Resources.
- The committee is headed by BJP member Dr Sanjay Jaiswal,
Key recommendations of the committee:
- On Flood Management:
- The committee suggested the creation of a permanent institutional structure in the form of National Integrated Flood Management Group which should be headed by Minister of Jal Shakthi with concerned Ministers of the State Governments as the members of it “immediately” for control and management of floods in India.
- This group should assume the complete responsibility of coordination as well as building cooperation between all agencies in charge of flood management and their consequences on life and property.
- As per the recommendation, group should meet at least once a year and the first meeting should be held within three months of the submission of this report to the Parliament.
- The panel has also proposed that “flood control and management” should be brought under the concurrent list of the Constitution.
- As per National Commission on Floods, the total area liable to flood in the country is 40 million hectares.
- The total damage to crops, houses and public utilities from the year 1953 to 2018 has been projected to be about ?4,00,097 crore.
- The huge losses and indemnities because of floods every year is an indication of poor planning, failure of the flood control policy, inadequate preparedness and poor disaster management.
- Findings on Indus Water Treaty:
- Committee highlighted the impact of Climate Change:
- There are cases of more high-intensity rainfall as well as long stretches where there is little rainfall.
- The influence of glaciers in the Indus basin is higher than in the Ganges or Brahmaputra basins.
- Because of fragility of Himalayan region, there is greater risk and frequency of landslides and flash floods
- Utilisation of the Waters of the Indus:
- India was able to make proper use of the ‘Eastern Rivers’ (Ravi, Beas and Satluj) through the dams such as Ranjit Sagar on the Ravi, Pong on the Beas and Bhakra Nangal on the Satluj.
- However, poor maintenance of canals in Punjab and Rajasthan has resulted in lowering their water carrying capacity.
- So, the water from the Harike Barrage on the confluence of the Beas and Satluj in Punjab was generally released downstream into Pakistan.
- Committee advised the union government to accelerate new projects to utilise the full potential of the rivers for irrigation and other purposes.
- Re-negotiate the Indus Treaty:
- The report emphasised on renegotiating the Indus water Treaty signed in 1960 to address the effect of climate change and other issues which are not covered under the Treaty.
- River Interlinking:
- The panel expressed its displeasure over the progress in river interlinking projects.
- Even with a National Perspective Plan (NPP) in 1980 itself, no project for interlinking of rivers has been implemented so far.
- The National Perspective Plan (NPP) was prepared by the then Ministry of Irrigation in August 1980 for transferring water from water surplus basins to water-deficit basins.
- As per the panel, growing consensus among the States is the biggest hindrance in the implementation of river interlinking, but urged the union government to take required steps to resolve the roadblocks quickly taking into account of enormous damages caused by floods every year and benefits arising out of the river interlinking.
- Even with a National Perspective Plan (NPP) in 1980 itself, no project for interlinking of rivers has been implemented so far.
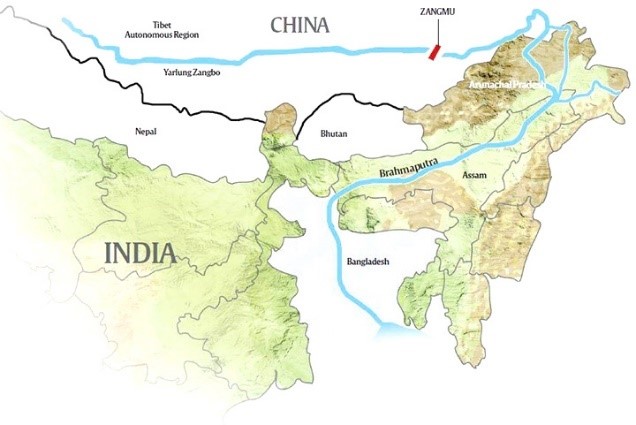
- Monitoring Brahmaputra:
- Panel advised the government to keep an eye on “Chinese actions” to ensure that they do not pursue any major interventions on the Brahmaputra that would adversely affect the country’s “national interests”.
- Report also voiced committee’s apprehensions regarding Chinese projects in upstream areas.
- 3 hydropower projects on the main stream of Brahmaputra River in Tibet Autonomous Region have been permitted by China and a hydropower project at Zangmu was declared fully operational by China in October 2015.
- The panel expressed its displeasure over the progress in river interlinking projects.
- Committee highlighted the impact of Climate Change:
4.Status of the E-Prisons Project
#GS2 #Government policies and implementation #Judiciary #Good Governance and E-Governance
Context: As per ministry of Home Affairs written reply to question in the Rajya Sabha recently, the e-Prisons project, which aims at computerization of the functioning of prisons in the country, has been operationalised in all States and Union Territories.
Highlights of the Project:
- It has 3 major components:
- e-Prison Management Information System (MIS) which is used at the prisons for their day-to-day regular activities.
- National Prisons Information Portal: It is a citizen centric portal giving statistical data of several prisons in India.
- Kara Bazaar: Portal for showcasing and selling the products created in various prisons of the country by prisoners.
- e-Prisons application suite has been developed by National Informatics Centre (NIC), Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY).
- e-Prisons data has been combined with the Police and Court system under the Inter-operable Criminal Justice System.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has provided financial assistance of Rs. 99.49 crores to the States and Union Territories (UTs) for the E-Prisons Project.
- Also, acting on the request of the Home ministry, NIMHANS, an Institute of National Importance, has recently issued a set of rules on the management of mental health issues of the prisoners and prison staff.
Inter-operable Criminal Justice System:
- It is a mutual platform for information exchange and analytics of all the pillars of the criminal justice system comprising Police, Forensics, Prosecution, Courts, Prisons.
- Main objective is to minimise the errors and time taken in sharing of essential information between the pillars, which frequently lead to greater challenges like longer period of trials, poorer convictions, transit losses of documents etc.
- Some other crucial benefits are usable analytics products like the National Database on Sexual Offenders (NDSO) to identify & track repeat and habitual sexual offenders.
- The Limited Liability Partnership (Amendment) Bill 2021
#GS3 # Government policies and interventions # Inclusive Growth & Issues Arising from It # Effects of Liberalization on the Economy
Context: Recently Rajya Sabha passes the Bill to amend the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act, 2008.
- The Act provides for regulation of limited liability partnerships (LLP).
- LLP is an alternative corporate body form to traditional partnership firms.
- Under LLP, a partner’s liabilities are limited to their investment in the business.
- Every LLP shall have minimum of two designated partners being individuals, at least one of them being resident in India and all the partners shall be the agent of the Limited Liability Partnership but not of other partners.
Key Provisions of the amendment:
- Main objective of the amendment is to facilitate the Ease of Doing Business and encourage start-ups across the country.
- Certain offences decriminalised: The present law has 24 penal provisions, 21 compoundable offences and 3 non-compoundable ones. The amendment bill seeks to decriminalise 12 of these offences.
- The Bill converts certain felonies into civil defaults and changes the nature of punishment for these offences.
- Change of name of LLP: The current Act states that the union government may direct an LLP to change its name on certain grounds and failing to obey such direction is punishable with a fine ranging from Rs 10,000 to five lakh rupees.
- The Bill discards some of these grounds, and empowers the union government to assign a new name to such an LLP instead of levying a fine.
- Non-compliance of orders of Tribunal: Under the Act, non-compliance with an order of the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) is punishable with imprisonment up to six months and fine up to Rs 50,000. The Bill discards this offence.
- Adjudicating Officers: Under the Bill, the union government may appoint adjudicating officers for awarding penalties under the Act.
- These will be central government officers not below the rank of Registrar.
- Appeals against orders of the Adjudicating Officers will lie with the Regional Director.
- Special courts: The Bill allows the union government to create special courts for guaranteeing speedy trial of wrongdoings under the Act.
- Appeals to Appellate Tribunal: Under the Act, appeals against orders of the NCLT lie with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT).
- The Bill adds that appeals cannot be made against an order that has been passed with the consensus of the parties.
- Appeals must be filed within 60 days (extendable by another 60 days) of the order.
- Small LLP: The Bill provides for formation of a small LLP where: (i) the contribution from partners is up to Rs 25 lakh (may be increased up to five crore rupees), (ii) turnover for the preceding financial year is up to Rs 40 lakh (may be increased up to Rs 50 crore).
- Start-up LLPs: The union government may also notify certain LLPs as start-up LLPs.
- Standards of accounting: The union government may recommend the standards of accounting and auditing for classes of LLPs, in consultation with the National Financial Reporting Authority.
- Sunscreens and Corals
#GS3 #Conservation #Environment pollution and degradation
Context: Recently, Thailand has banned sunscreens containing chemicals that harms coral from all of its marine national parks.
Key Details:
- Concerns are growing that lotions tourists use for sun protection are harming slow-growing corals.
- As per the Thai Department of Conservation, 04 components (oxybenzone, octinoxate, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor or butylparaben) commonly found in sun creams were shown to destroy coral larvae, thwart coral reproduction resulting in reef bleaching.
- Anyone breaking the rule will be penalised.
- Similar restrictions have been introduced by the Pacific Island of Palau and the US state of Hawaii.
- This is the latest attempt by the Thai government to protect its coral from the tourism industry.
How bad is the problem of Sunscreens?
- As per the National Geographic magazine: About 14,000 tonnes of sunscreen are estimated to be released into the oceans annually.
- Almost 82,000 chemicals from personal care products are expected to be contaminating the sea bodies.
- This has led to the depreciation of 80% of the corals in the Caribbean in the last 50 years.
- Sunscreens do not dissolve in the water quickly. When released into the ocean water, it makes a coating on surface of the corals and impacts zooxanthellae (symbiotic algae within coral tissue) and the polyp movement, which directly influences the growth and photosynthesis process of the reefs.
