CURRENT AFFAIRS 07-09-2021
Topics
- Greater devolution of autonomy to the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council
- Nipah Virus in Kerala
- Global warming impact on El Nino and La Nina events
- Account Aggregator (AA) network
- Eat Right Station
-
Greater devolution of autonomy to the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council
#GS2 #Issues & Challenges Pertaining to the Federal Structure #Devolution of Powers & Finances to Local Levels & Challenges Therein #Welfare Schemes for Vulnerable Sections
Context: Recently, Union government signed a tripartite agreement with five insurgent groups from the Karbi Anglong region and Assam government.
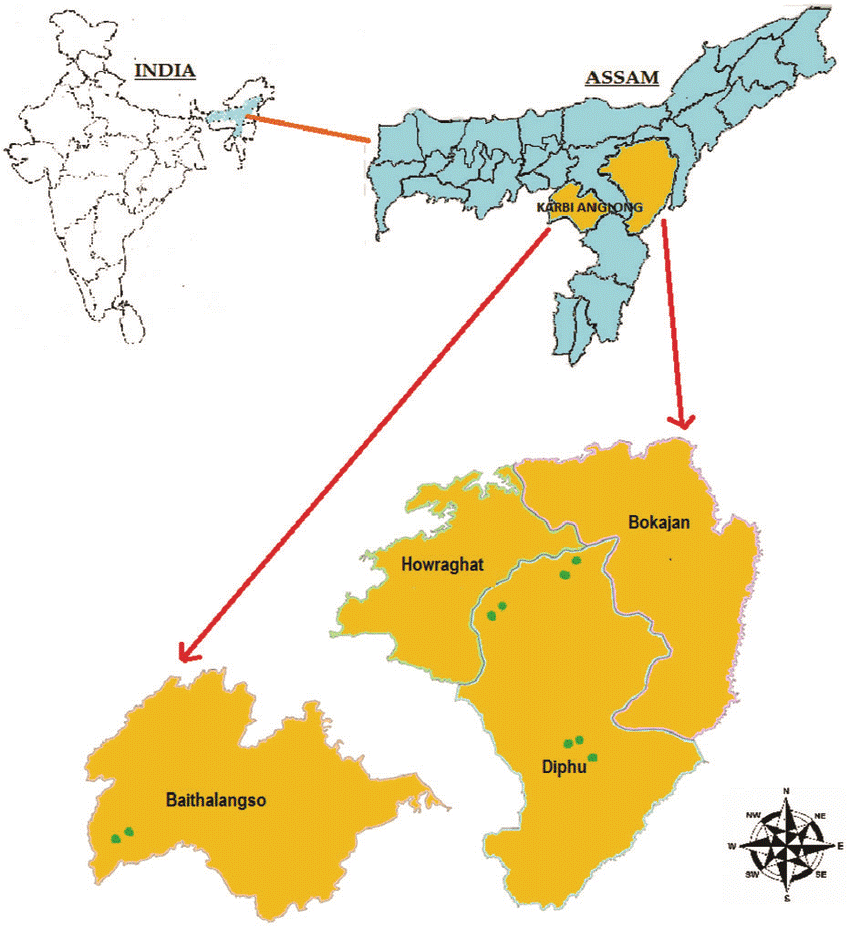
Background:
- Karbi Anglong is the Assam’s largest district and a melting pot of ethnicities and tribal groups — Karbi, Dimasa, Bodo, Kuki, Hmar, Tiwa, Garo, Man (Tai speakers), Rengma Naga.
- Its diversity also produced different outfits and fuelled an insurgency which became a roadblock for region’s development.
- The Karbi have been demanding a separate state since 1946.
- With time, their movement took the shape of an insurgency which became stronger in the 1990s.
- The Union signed various ceasefire agreements with several groups but there were always breakaway factions that continued armed struggle.
- In February 2021, 1,040 militants of five Karbi outfits surrendered before then Chief Minister Sonowal.
- The current accord is a result of negotiations with the five groups since then.
- The militant outfits are also demanding more powers to the council along with a financial package of Rs 1,500 crore and inclusion of Karbi language in the 08th
Highlights of the agreement:
- The agreement was signed by the representatives of the Karbi Longri North Cachar Hills Liberation Front (KLNLF), People’s Democratic Council of Karbi Longri (PDCK), United People’s Liberation Army (UPLA), Karbi People’s Liberation Tigers (KPLT) and the Kuki Liberation Front (KLF).
- The agreement grants greater devolution of autonomy to the Karbi Anglong Autonomous Council (KAAC)
- It also provides for the protection to the language, culture and identity of the region and reservation to the Karbi people.
- Militant organizations laid down arms and more than 1000 of their armed cadres have given up violence and joined the mainstream of society.
- Union government will provide a Special Development Package of Rs 1000 crore over 05 years to Assam Government to undertake specific projects for the development of Karbi areas.
- As per the Accord, the Assam government shall set up a Karbi Welfare Council for focused development of Karbi people living outside the KAAC area.
- The Consolidated Fund of the State will be amended to meet the resources of the KAAC.
- In this, for the first time, Karbi and Scheduled Tribes people will get reservation.
- In no Sixth Schedule region, there is provision for reservation to a Scheduled Tribe.
- This accord will grant Scheduled Tribe status to Karbi staying in the plains as well.
Other significant agreements in Assam:
- Bodo Peace Accord: In 2020, Union government, Government of Assam and representatives of Bodo groups signed an agreement, wherein the Bodoland Territorial Area District (BTAD) was redrawn and renamed as the Bodoland Territorial Region (BTR), in Assam.
- Bodos are the single largest community among the notified Scheduled Tribes in Assam. They have been demanding a Bodo state since 1967-68.
2.Nipah Virus in Kerala
#GS3 #Issues related to health #GS3 #Disaster management
Context: Kerala and neighbouring states has been put on high alert following the death of a 12-year-old boy due to Nipah virus.
- After a gap of over 03 years, a case of the zoonotic Nipah virus infection has been reported in Kozhikode district of Kerala.
- Two health workers, who were in contact with the minor, have been quarantined after they showed symptoms of the infection. The state has also identified 158 people who have come in contact with the child, with at least 20 being primary contacts.
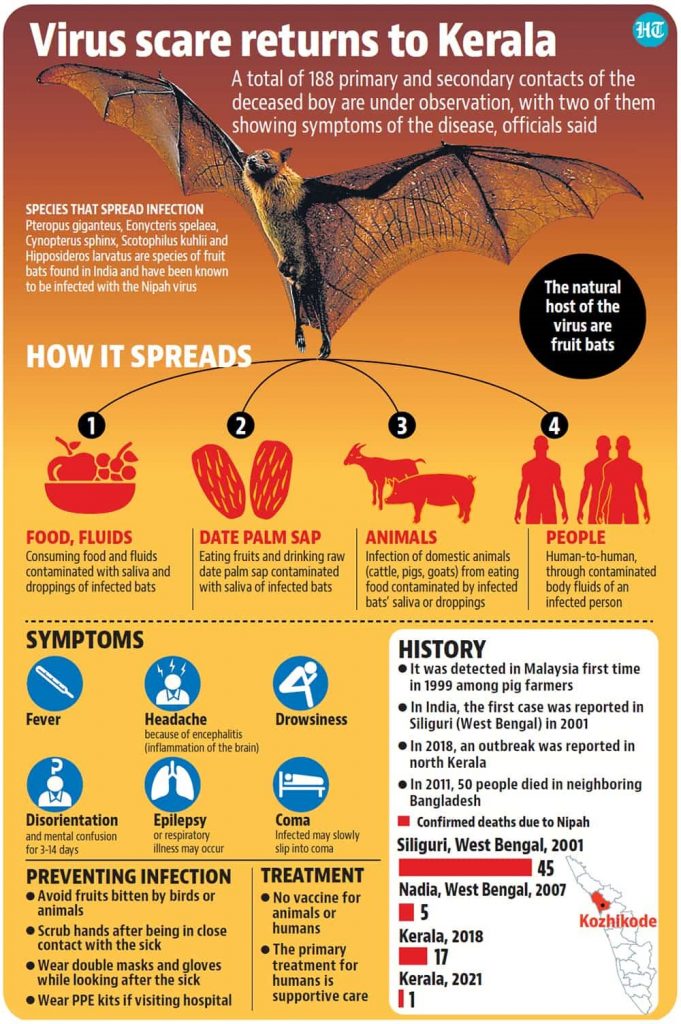
About the virus:
- It is a zoonotic virus (it is transmitted from animals to humans.
- Symptoms include acute encephalitis and respiratory illnesses.
- The first outbreaks of the Nipah virus among humans was reported from Malaysia (1998) and Singapore (1999).
- The virus takes its name from the village in Malaysia where the person in whom the virus was first isolated died of the disease.
- There have been multiple outbreaks of the Nipah virus, all of them in South and Southeast Asian nations.
- Since 2001 Bangladesh has seen at least 10 outbreaks.
- In India, West Bengal had seen an outbreak in 2001 and 2007, while Kerala had reported several cases in 2018.
How does it spread?
- The transmission happens primarily through consumption of contaminated food.
- But human-to-human transmission is also considered possible.
- The animal host reservoir for this virus is known to be the fruit bat, commonly known as flying fox.
- Fruit bats are known to transmit this virus to other animals like pigs, and also dogs, cats, goats, horses and sheep.
- Humans get infected mainly through direct contact with these animals, or through consumption of food contaminated by saliva or urine of these infected animals.
- Person-to-person transmission is not fully established, but a recent study, suggested “that respiratory droplets of an infected person can transmit the virus”.
- During previous outbreaks, people in close contact with the infected person, primarily hospital staff and caregivers, have contracted the disease.
Nipah v/s Covid 19:
- The Nipah virus is known to spread far more slowly than SARS-CoV-2.
- However, the mortality rate of Nipah is the biggest concern.
- During the first outbreak in Siliguri, 45 of the 66 people confirmed to have been infected died. That is a mortality rate of 68%.
- During 2018 outbreak in Kerala, 17 of the 18 patients confirmed to have been infected died.
- In comparison, the mortality rate of Covid-19 epidemic is expected to be around one per cent.
- So far, all outbreaks of the Nipah virus have been localised and contained quickly, compared to the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic.
- Nipah virus is far less infective than SARS-CoV-2.
- Human-to-human transmission is not as easy, or as fast, as seen in the case of SARS-CoV-
- Reproductive number (R0) in the previous outbreaks of Nipah virus was about 0.48.
- The R-value is a measure of how quickly the virus spreads in the population.
- A value less than one means less than one person is being infected by an already infected person.
- Very high death rates also contribute to low transmission
Is the infection curable?
- According to World Health Organisation, there is no treatment or vaccine available for the infection, either for people or animals.
- The only way for people to recover is through supportive care, which includes rest, hydration, and treatment of symptoms as they arise.
What should be done: Precautions and Roadmap
- The absence of a vaccine suggests awareness is the only key to curb the infection.
- Precautions:
- Wash hands with soap and water frequently
- Avoid intake of raw date palm
- Do not consume fruits that have fallen from trees or show indications of being bitten by an animal.
- Avoid contact with NiV-infected people
- Avoid contact with pigs or bats
- Avoid places where bats are known to or could roost
- Coordinated efforts should be taken by both union and state government with mutual trust regarding containment and other protocols.
- There are urgent steps that need to be taken together, including contact tracing, quarantine, isolation, collection, and transportation of samples for lab testing and a detailed study of the surrounding areas by the National Centre for Disease Control from an epidemiological standpoint.
-
Global warming impact on El Nino and La Nina events
#GS1 # Salient Features of World’s Physical Geography # Atmospheric Circulation & Weather Systems #World Climate
Context: A recent study shows that with climate change becoming more and more severe, it could impact the El Nino and La Nina events, causing them to become more extreme and frequent.
Key Details on the study:
- The impact of climate change on the weather events was calculated using one of the fastest supercomputers in South Korea – Aleph.
- The supercomputer took 01 second for the calculation for which a single human would take 45 million years.
- It completed century-long simulations that cover present-day climate as well as two different levels of global warming.
Highlights of the finding:
- The study focused on events that would happen to ENSO (El Nino and the Southern Oscillation) when the level of carbon dioxide doubled and quadrupled.
- It also studied the atmospheric heat and its movement.
- El Nino events in future would most likely lose heat to the atmosphere at a quicker rate due to evaporation of water.
- It also found that there could be a reduced difference between temperatures in eastern and western tropical Pacific in the future, which could inhibit the temperature extremes that are developed during the ENSO cycle.
- Apart from this, the team also looked at the tropical instability waves, and found that they might also weaken, thereby disrupting the La Nina event.
- The study said that while year-to-year fluctuations in the temperatures in eastern Pacific equatorial region could weaken due to human impact on the environment, the rainfall extremes related to El Nino and La Nina would continue to increase.
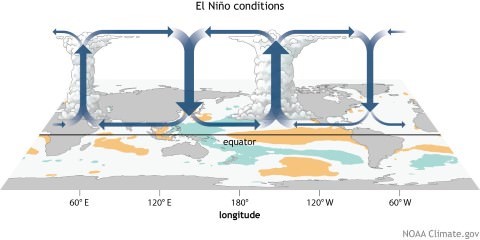
EL-Nino and ENSO:
- El Nino and the Southern Oscillation, also known as ENSO is a periodic fluctuation in sea surface temperature (El Niño) and the air pressure of the overlying atmosphere (Southern Oscillation) across the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino is the event where there is an occasional development of warm ocean surface waters along the coast of Ecuador and Peru.
- When this warming occurs the usual upwelling of cold, nutrient rich deep ocean water is significantly reduced.
- El Niño normally occurs around Christmas and usually lasts for a few weeks to a few months and sometimes lasts longer.
- Climatically, El Niño development brings drought to the western Pacific, rains to the equatorial coast of South America, and convective storms and hurricanes to the central Pacific.
La Nina
- After an El Niño event weather conditions usually return back to normal.
- Event where there is an abnormal accumulation of cold water in the central and eastern Pacific because of strong trade winds is called a La Niña.
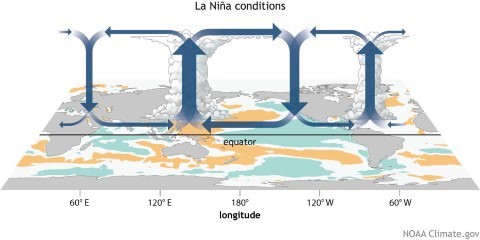
Effects of La Niña include:
- Drought over central North America.
- Abnormally heavy monsoons in India and Southeast Asia,
- Cool and wet winter weather in south-eastern Africa, wet weather in eastern Australia,
- Cold winter in western Canada and north-western United States, winter drought in the southern United States.
-
Account Aggregator (AA) network
#GS3 #Government policies and interventions #Banking sector and NBFCs
Context: Recently, 08 of India’s major banks — State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, IDFC First Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC Bank, IndusInd Bank and Federal Bank — joined the Account Aggregator (AA) network.
Key Details:
Who is an Account Aggregator?
- As per the Reserve Bank of India, an Account Aggregator is a non-banking financial company engaged in the business of providing, under a contract, the service of recovering or collecting financial information relating to its customer.
- It is also involved in consolidating, organising and presenting such information to the customer or any other financial information user as may be specified by the bank.
- It was created through an inter-regulatory decision by RBI and other regulators including SEBI, IRDA, and PFRDA through an initiative of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC)
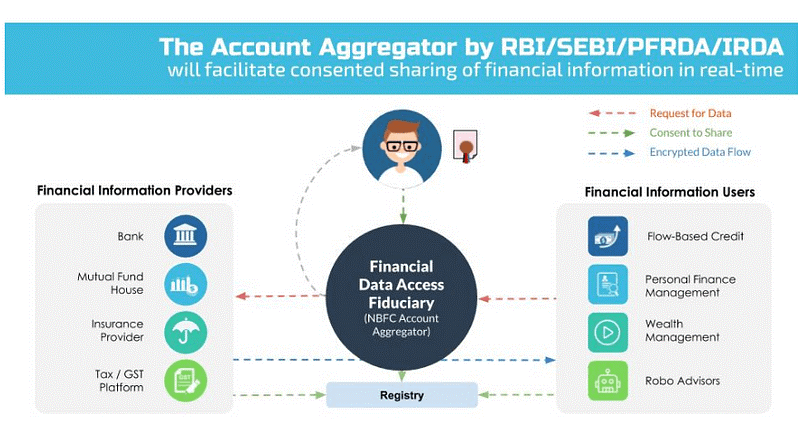
- In an AA network, Banks act as financial data providers, lenders act as financial data seekers, NBFC-AAs act as mediums of communication between banks and lenders, and third-party service providers work with AAs.
- The AA framework allows customers to avail various financial services from a host of providers on a single portal based on a consent method, under which the consumers can choose what financial data to share and with which entity.
- An Account Aggregator allows a customer to transfer his financial information pertaining to various accounts such as banks deposits, equity, mutual fund and pension funds to any entity requiring access to such information.
- There are 19 categories of information that fall under ‘financial information’, besides various other categories relating to banking and investments.
Significance of AA’s:
- Improved access to data helps in addressing important financial needs such as small-size loans for MSMEs and affordable micro-insurance.
- For MSMEs, which collectively face a credit gap, providing improved access to their financial data can help bring more visibility towards their creditworthiness.
- As a majority of MSMEs are largely outside the scope of formal credit due to the lack of transparent and accessible financial records, the AA framework can help regulate, digitise, and simplify the process of opening up access to financial data.
- Consequently, this improved access can help lenders better meet the MSMEs’ financial needs.
- AA reduces the fraud associated with physical data by introducing secure digital signatures and end-to-end encryption for data sharing.
5.Eat Right Station
#GS2 #Issues Relating to Development & Management of Social Sector/Services – Health
Context: Recently, Chandigarh Railway Station was awarded a 5- star ‘Eat Right Station’ certification for providing high-quality, nutritious food to passengers.
Key Details:
- Chandigarh railway station is the 05th station in India to get this recognition.
- The other 04 stations are Anand Vihar Terminal Railway Station (Delhi), Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (Mumbai), Mumbai Central Railway Station (Mumbai) and Vadodara Railway Station. The certification is part of the ‘Eat Right India’ movement.
- The Indian Railway Stations Development Corporation (IRSDC) looks after food supply along with upgradation of railway stations.
- The certification was issued by Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) to railway stations upon the conclusion of an FSSAI-empanelled third-party audit agency with ratings from 1 to 5.
- The 5-star rating indicates exemplary efforts by stations to ensure safe and hygienic food is available to passengers.
- The certification is part of the ‘Eat Right India’ movement- a large-scale effort by FSSAI to transform the country’s food system to ensure safe, healthy and sustainable food for all Indians.
Eat Right Movement:
- To improve public health in India and combat negative nutritional trends to fight lifestyle diseases, FSSAI launched ‘The Eat Right Movement’ on 10th July, 2018.
- Its tagline is ‘Sahi Bhojan, Behtar Jeevan’.
- It is aligned to the National Health Policy 2017 with its focus on preventive and promotive healthcare and flagship programmes like Ayushman Bharat, POSHAN Abhiyaan, Anaemia Mukt Bharat and Swachh Bharat Mission.
- It adopts a judicious mix of regulatory, capacity building, collaborative and empowerment approaches to ensure that our food is good both for the people and the planet.
- Further, it builds on the collective action of all stakeholders – the government, food businesses, civil society organizations, experts and professionals, development agencies and citizens at large.

Food Safety and Standards Authority of India:
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is a statutory body established under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The FSSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, which is a consolidating statute related to food safety and regulation in India.
- FSSAI is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.
- The FSSAI is headed by a non-executive Chairperson, appointed by the Union Government.
- The FSSAI has its headquarters at New Delhi.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 07th September -2021
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube

