CURRENT AFFAIRS 13-11-2021
Topics
- The National Education Day
- The Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) Report on Political Fundings
- The 11th Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) Group meeting
- What is Cord blood banking?
- Nutrition Smart Villages
1. The National Education Day
#GS1-Modern Indian History
Context
- Since 2008, November 11 has been observed as National Education Day to commemorate the birth anniversary of Abul Kalam Ghulam Muhiyuddin, commonly known as Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, India’s first Education Minister.
In depth information

Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad, who was he?
- Maulana Abdul Kalam Azad was born in the Saudi Arabian city of Mecca in the year 1888.
- His mother was an Arab, the daughter of Sheikh Mohammad Zaher Watri, while Azad’s father, Maulana Khairuddin, was an Afghan-born Bengali Muslim who moved to Arab after the Sepoy Mutiny and lived in Mecca.
- In 1890, when Abul Kalam was two years old, he returned to Calcutta with his family.
Azad received a typical Islamic education.
- He was educated at home, initially by his father and then by specially designated teachers who were experts in their subjects.
- Azad studied Arabic and Persian first, followed by philosophy, geometry, arithmetic, and algebra.
- Through self-study, he also learnt English, international history, and politics.
- Azad was also fluent in Hindustani, Hindi, and English.
Weekly Journals:
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad founded the Al-Hilal weekly publication in Urdu in 1912 in order to gain Muslim revolutionary recruits.
- Al-Hilal was instrumental in fostering Hindu-Muslim harmony following the Morley-Minto reforms, which resulted in ill blood between the two populations.
- Al-Hilal evolved became a revolutionary mouthpiece for radical ideas.
- Al-Balagh is a weekly publication with the same goal of preaching Indian nationalism and revolutionary ideologies based on Hindu-Muslim solidarity.
- The government outlawed this paper in 1916 and evicted Maulana Abul Kalam Azad from Calcutta, exiling him to Bihar, where he was liberated after World War I in 1920.
Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, a member of the Indian National Congress, supported Gandhiji’s Non-Cooperation Movement and joined the party in 1920.
- He was elected president of the Congress’s special session in Delhi (1923).
- He became the youngest President of the Indian National Congress when he was 35 years old.
Pre-Independence Contributions: He was a supporter of Hindu-Muslim unity and opposed Partition.
- In 1912, he founded the Al-Hilal weekly publication in Urdu, which was instrumental in establishing Hindu-Muslim cooperation following the Morley-Minto reforms, which resulted in ill blood between the two populations (1909)..
- In 1914, the government outlawed Al- Hilal because it was seen as a propagator of secessionist ideas.
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad went on to start another weekly, Al-Balagh, with the same goal of spreading Indian nationalism and revolutionary principles based on Hindu-Muslim harmony.
- The government outlawed this paper in 1916 and evicted Maulana Abul Kalam Azad from Calcutta, exiling him to Bihar, where he was liberated after World War I in 1920.
- Azad joined the Indian National Congress in 1920 after supporting Gandhiji’s Non-Cooperation Movement (1920-22).
- Azad joined the Indian National Congress in 1920 after supporting Gandhiji’s Non-Cooperation Movement (1920-22).
- He was elected president of the Indian National Congress in 1923. He became the youngest President of the Indian National Congress when he was 35 years old.
- As part of Gandhiji’s Salt Satyagraha, Maulana Azad was jailed in 1930 for violating the salt rules. He was imprisoned for a year and a half at Meerut.
- In 1940, he was elected president of Congress for the second time, and he served until 1946.
- Maulana Azad was an ardent proponent of universalism, a truly liberal and humanistic educational system, in the sphere of education.
- Azad’s objective was to build a fully integrated personality by fusing Eastern and Western notions of man. The Eastern perspective placed a greater emphasis on spiritual excellence and individual salvation, whereas the Western concept placed a greater emphasis on worldly accomplishments and social advancement.
- He was one of the founder members of the Jamia Milia Islamia University, which was founded in 1920 in Aligarh, United Provinces.
- His works include Ghubar-eKhatir, Dars-e-Wafa, India Wins Freedom, and others.
Post-Independence Contributions:
- He became the first education minister of independent India in 1947 and continued in that position until his death in 1958. During his time in office, he made significant contributions to the country’s development.
- During his time as education minister, he built the first IIT, IISc, School of Planning and Architecture, and the University Grants Commission.
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations promotes Indian culture to foreign countries.
- Three academic institutions were established: Sahitya Academy for Literature Development, Sangeet Natak Academy for Indian Music and Dance Development, and Lalit Kala Academy for Painting Development.
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad was posthumously awarded India’s highest civilian honour, Bharat Ratna in 1992.
2. The Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) Report on Political Fundings
#GS2- Polity and Governance
Context
- According to a survey by the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR), over 55 percent of funds collected by regional parties in FY 2019-20 originated from “unknown” sources.
In depth information
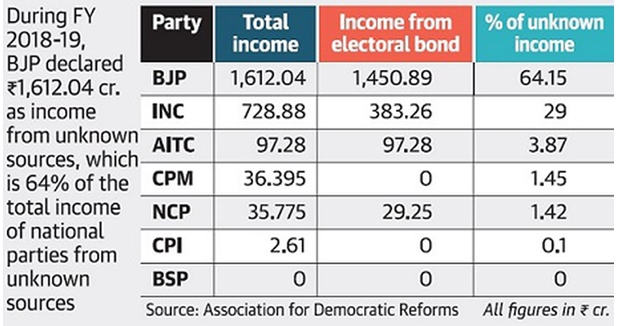
Key findings of the report
- A significant portion comes from “unknown” sources: Nearly all of the donations from “unknown” sources came in the form of electoral bonds.
- According to the study, donations from “unknown” sources accounted for 70.98 percent of national parties’ income.
- The list was topped by southern parties: TRS, TDP, YSR Congress Party, DMK, and JD(S), all from the south, topped the list of regional parties with the largest income from “unknown” sources.
- Donors who are “well-known”: Regional parties earn 22.98 percent of their total income in donations from “known” donors.
- TRS had the highest earnings: Telangana Rashtra Samithi (TRS) recorded the greatest income from undisclosed sources among regional parties.
ADR Recommendations:
- In 2016, 255 parties were removed from the list of registered unrecognised parties because they were no longer active.
- This exercise should be continued in order to weed out all political parties that have not run for office in more than five years, as well as to tighten the registration procedure.
- The registration of political parties must be regulated in order to prevent money laundering, corrupt election tactics, and the misuse of money power.
- As a result, the ECI should enforce tight standards for registering a group of people as a political party, as well as taking the drastic step of delisting parties that do not follow the rules.
- Unrecognized parties should be subjected to IT examination, particularly those that do not run for office but record the receipt of voluntary funds.
About Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR)
- A group of professors from the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad founded the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) in 1999. They filed a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) with the Delhi High Court in 1999, seeking for [or requesting] the disclosure of candidates’ criminal, financial, and educational backgrounds.
- Based on this, the Supreme Court mandated that all candidates contesting elections file an affidavit with the Election Commission disclosing their criminal, financial, and educational backgrounds before to the election.
- The first election watch was undertaken by ADR in 2002 for the Gujarat Assembly Elections, in which the electorate was given a full analysis of the backgrounds of candidates contesting elections in order to enable them make an informed choice during the polls.
- Since then, ADR has worked with the National Election Watch to organise Election Watches for practically all state and parliament elections. It works on a number of programmes aiming at improving the country’s political and electoral systems’ transparency and accountability.
3. The 11th Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) Group meeting
#GS2- Agreements Involving India &/or Affecting India’s Interests
Context
- The 11th Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) Group meeting between India and the United States of America (US) took place virtually recently.
- The DTTI Group meets twice a year, rotating between India and the United States.
In depth information
Important Points to Remember
- The co-chairs agree on a revised Statement of Intent to improve defence technology cooperation conversation.
- Under the Joint Working Group Air Systems, the first project agreement for an air-launched unmanned aerial vehicle was inked.
- Forum for Defense Industry Collaboration
- The goal of the Virtual Expo was to foster the development of specialist technology.
- The goal of the DTTI Group is to offer chances for defence equipment co-production and development.
About Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI)
- The meetings are usually held twice a year, with the locations rotating between India and the United States.
- The group’s goal was to provide the bilateral defence trade relationship a sustained leadership focus and to open up chances for co-production and co-development of defence equipment.
- This forum allows Indian and American businesses to participate directly in DTTI and encourages conversation between government and business on problems that affect industrial collaboration.
India and the United States have a strong defence relationship.
- With increased defence trade, joint exercises, personnel exchanges, and cooperation in maritime security and counter-piracy, the defence connection has evolved as a fundamental pillar of the India-US strategic partnership.
- More bilateral exercises are conducted between India and the United States than with any other country. Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar, Tarkash, Tiger Triumph, and Cope India are some of the most prominent bilateral exercises.
- The total value of defense-related procurement from the United States exceeds $15 billion.
- The Defence Technology and Trade Initiative (DTTI) between India and the United States aims to promote co-development and co-production initiatives.
- The United States designated India as a “Major Defense Partner” in June 2016, committing the US to enable technology sharing with India on a par with its closest friends and partners.
- The elevation of India to Tier I of the Strategic Trade Authorization (STA)license exception will help to facilitate cooperation in sophisticated and sensitive technologies even further.
- Other key conversation platforms on defence cooperation, in addition to the 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, are the Defence Policy Group, Military Cooperation Group, Defense Technology and Trade Initiative, and so on.
What are the most important outcomes of the 11th DTII?
- To begin, the DTTI formed four Joint Working Groups focused on land, marine, aviation, and aircraft carrier technology to advance mutually approved initiatives. Ongoing initiatives and cooperation opportunities were reported to the co-chairs by these groups.
- Second, India and the United States have agreed to collaborate on the development of air-launched unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).
- Finally, there was a virtual expo of the Defence Industry Collaboration Forum. The forum allows Indian and American businesses to participate directly in DTTI and encourages conversation between government and business on problems that affect industrial collaboration.
Challenges
- The United States wants India to abandon Russian equipment and platforms, fearing that this could expose its technology and information to Moscow.
- So far, India has moved on with the purchase of Russia’s S-400 air defence missile system, which has been a source of contention for American diplomats.
Ahead of Schedule
- Senior officials from both countries must maintain a continuous level of engagement in order to improve defence opportunities.
- Strengthening India’s defence industrial foundation, developing new areas of technical growth, and expanding US-India business connections should be the priority.
4.What is Cord blood banking?
#GS3-Biotechnology related issues.
Context:
- The Cord Blood Banking Services Market was worth $1,126 million in 2016 and is expected to reach $2,772 million by 2023, with a CAGR of 13.8% from 2017 to 2023.
- The increased awareness of the benefits of using cord blood stem cells for the treatment of chronic diseases like cancer has resulted in a government initiative that has resulted in an increase in the number of cord blood banks, which is expected to fuel the market growth of cord blood banking services.
In depth information
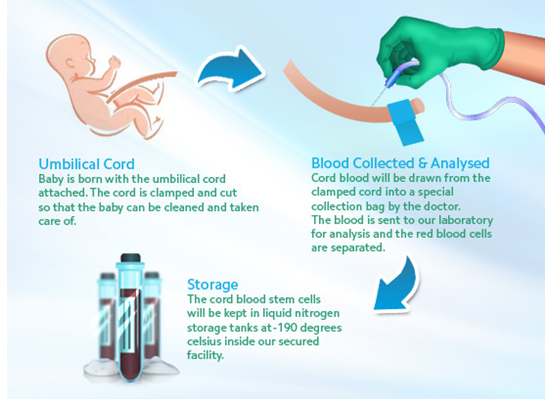
What is Cord Blood and How Does It Work?
- The blood that stays in the umbilical cord and placenta after delivery is known as cord blood (short for umbilical cord blood).
- It contains hematopoietic stem cells, which are special cells that can be used to treat certain disorders.
- The blood from the newborn that is left in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth is known as cord blood. Cord blood banking is the process of conserving umbilical cord blood, which is a rich source of stem cells, for future use.
- It contains hematopoietic stem cells, which are special cells that can be used to treat certain disorders.
- Hematopoietic stem cells can develop into a variety of blood cells throughout the body.
- Cord blood banking is suggested around the world as a source of hematopoietic stem cells (derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood) transplantation for haematological malignancies and diseases.
- The use of cord blood as a source of stem cells for all other disorders has yet to be established.
What Can You Do With It?
- Stem cells abound in the umbilical cord fluid.
- They can be used to treat cancer, blood problems such as anaemia, and immune system disorders that interfere with your body’s capacity to fight itself.
- The fluid is simple to collect and contains 10 times the number of stem cells seen in bone marrow.
- Cord blood stem cells are rarely infected and are just half as likely to be rejected as adult stem cells.
Stem Cells
- Stem cells are unique human cells with the ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types, ranging from muscle cells to brain cells.
- Adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells are the two types of stem cells.
- Embryonic stem cells are derived from unused embryos that have been submitted to research following an in vitro fertilisation treatment.
- These embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means they can differentiate into a variety of cell types.
Cord blood has numerous advantages.
- It protects a baby from any disorders that can be treated with stem cells (own & donor).
- It provides unrelated donor stem cells to the baby’s siblings, parents, and grandparents (maternal and paternal).
Concerns about stem cell banking:
- Despite the fact that its application is still experimental, stem cell banking has been intensively marketed over the last decade. However, these companies charge parents exorbitant money to save their children’s cells.
- The danger here is that corporations are just using emotional marketing to get parents to bank their children’s cells for several years in the hopes of future therapeutic usage.
5. Nutrition Smart Villages
#GS2- Government Policies & Interventions Issues Relating to Poverty & Hunger
Context
- The Union Agriculture Minister recently unveiled the “Nutrition Smart Village” initiative, which will benefit 75 communities across India.
In depth information
The initiative’s goals are as follows:
- Educating people about nutrition.
- Farm women and school children are involved in education and behavioural transformation in rural communities.
- To tackle malnutrition and poverty, traditional wisdom is being harnessed through a local recipe.
- Using homestead agriculture and Nutri-garden to implement nutrition-sensitive agriculture.
- To strengthen the Poshan Abhiyan and attain the aim of malnutrition-free villages, intense awareness campaigns and field operations will be conducted, emphasising on the concepts of Nutri-village, Nutri-food, Nutri-diet, Nutri-thali, and so on.
- The All India Coordinated Research Project (AICRP) on Women in Agriculture helps to attain the goals. The initiative is currently operational in 13 centres across the country, spread over 12 states. Five communities will be adopted by each AICRP centre. The ICAR will take over the rest of the villages (Indian Council of Agricultural Research).

