UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 20th January 2022
- World Economic Forum’s Davos Agenda ’22
- Houthis attack on UAE
- Global Cyber security Outlook 2022: WEF
- 2021 Sixth Warmest Year
- Artificial Moon
1.World Economic Forum’s Davos Agenda ’22
#GS2-Polity
Context
- The World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Agenda on the ‘State of the World’ will feature government and industry leaders discussing major global concerns, including a special address by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau prior of the Davos gathering.
In depth information
- The World Economic Forum (WEF), located in Geneva, Switzerland, is an international organisation.
- Every year, it brings together its membership of political and business leaders to discuss major global economic issues.
- Political, economic, social, and environmental concerns are just a few examples.
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) is most known for its annual World Economic Forum Meeting in Davos, Switzerland.
- The event attracts business and political figures from all over the world for a series of roundtable conversations on global challenges.
- The World Economic Forum (WEF) does not have autonomous decision-making power; instead, it tries to persuade powerful people to make decisions that benefit the global community.
- The organisation is self-funded, with several significant corporate and political personalities among its members.
Issues
- While the WEF attracts enormous numbers of industrial leaders, corporate leaders, civil society leaders, and international organisations each year, it has been accused for being more of a networking hub than an intellectual nebula or a platform for discovering practical answers to global challenges.
- Lack of representation: The platform, which enables collaboration through debate, has been chastised for failing to represent all segments of civil society and for failing to deliver effective answers.
Significance
- It has an impact on governmental and private sector decision-making, notably on global concerns like poverty, social challenges, climate change, and global economic recovery.
- Closing the vaccination gap, strengthening global trade chains, and bolstering economies in weak markets through humanitarian investment are all examples of growing economies.
- Data solutions will also be discussed in order to prepare for the next epidemic.
- The environment and related challenges, such as biodiversity loss and man-made disasters, are at the top of the World Economic Forum’s current priority list.
- Other WEF projects will be launched, including one targeted at speeding up the mission on the economic possibility of nature-positive solutions and another on cyber-resilience.
2. Houthis attack on UAE
#GS3- Organized Crime & Terrorism
Context
- The Houthi rebels in Yemen, who are backed by Iran, have claimed responsibility for a drone strike on three oil tankers in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
In depth information
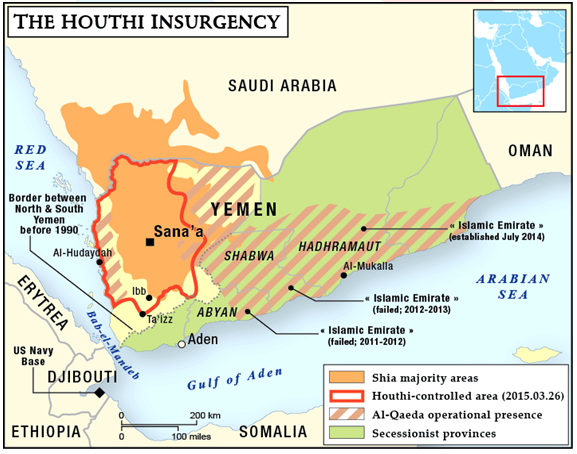
Why did the Houthis choose the UAE as a target?
- Despite promising the formal departure of its forces in 2019 and 2020, the UAE joined the Saudi campaign in 2015 and has been firmly involved in the battle ever since.
- This isn’t the first time the Houthis have launched an attack against the UAE.
- The Houthis claimed assaults against the UAE in 2018, when UAE-backed forces were making progress in Yemen.
- In recent months, the Houthis have been targeted by the Giants Brigades, a paramilitary group mostly made up of Southern Yemenis (supported by the UAE), and the Joint Forces (a militia led by a nephew of the murdered former President Saleh).
- They have pushed into Houthi territory in al-Bayda and Marib with government troops, inflicting major damage on the Houthis on the Arabian coast.
Concerning the Yemeni Crisis
- Yemen has been devastated by a nearly seven-year civil war that began when the Houthis took control of the capital, Sana’a, and Saudi-led forces intervened to fight the rebels in order to stop Iranian influence in the region and restore the former government.
- The battle is also considered as part of a regional power struggle between Iran, which is dominated by Shias, and Saudi Arabia, which is ruled by Sunnis.
What was Saudi Arabia’s role in all of this?
- In March 2015, the Saudi-led coalition intervened in Yemen after the Houthis deposed the internationally recognised government in Sanaa.
- The US, UK, and France provided logistical and intelligence support to the coalition.
- The coalition forces were able to push the Houthis out of the south of Yemen, but they were unable to do so in the majority of the northwest.
- In the process, tens of thousands of people have been slaughtered in what is largely regarded as one of the world’s worst humanitarian catastrophes.
- Both sides have been accused of committing a slew of war crimes including civilian killings.
Houthi retaliation
- In reprisal, the Houthis have attacked a number of Saudi Arabian sites, including airports and oil facilities.
- In retaliation for Saudi airstrikes, the Houthis have conducted repeated attacks on Saudi cities from northern Yemen over the last six years.
- In north Yemen, the Houthis have established a government.
Ceasefire
- At talks in Sweden, the warring parties agreed to a ceasefire after six months of fighting.
- They were required to redeploy their forces from Hudaydah, establish a prisoner exchange mechanism, and address the situation in Taiz under the Stockholm agreement.
- The UN hoped that the agreement would pave the way for a political settlement to end the civil war, but fighting between the Houthis and coalition-led forces erupted in January 2020, with fighting on multiple front lines, missile strikes, and air raids.
- Due to a coronavirus pandemic, Saudi Arabia announced a unilateral ceasefire in April 2020, but the Houthis rejected it, demanding the lifting of air and sea blockades in Sanaa and Hudaydah.
Incidences on
- Yemen: The collapse of the city could result in a humanitarian crisis, since large numbers of civilians fleeing conflict elsewhere have sought safety in the vicinity.
- Around 140 camps have sprouted up in the adjacent desert to provide rudimentary shelter for up to two million people.
- World: It has the potential to escalate regional tensions significantly. It also concerns the West because of the danger of attacks emerging from the country as it becomes more unstable, such as those carried out by al-Qaeda or IS affiliates.
- Yemen is also strategically important because it sits on a strait connecting the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, which carries a large portion of the world’s oil shipments.
- India: The Gulf of Aden is one of India’s most important shipping routes, accounting for $50 billion in annual imports and $60 billion in annual exports.
- Since the mid-1880s, Indian nationals have lived in Aden, including Hindus, Muslims, and Parsis.
- There are more than 8 million ex-pats in the region, bringing home more than $80 billion in remittances each year.
- As a result, the Yemeni turmoil might disrupt remittances and disrupt shipping routes.
India has taken steps to help Yemen.
- During Saudi Arabia’s and its allies’ 2015 military intervention in Yemen, the Indian Armed Forces undertook Operation Rahat to evacuate around 4,000 Indian citizens and other foreign people. The 11-day marine evacuation from Aden port began on April 1, 2015.
- Yemen has already received food and medical aid from India, and hundreds of Yemeni nationals have sought medical care in India in recent years.
| Houthis
Origin ? The Houthi movement can be traced back to Hussein al-Houthi and his father, Badr al-Din al-Houthi, who created “Believing Youth” (Muntada al-Shahabal-Mu’min), a Zaydi revivalist organisation in the early 1990s. ? Zayd Bin Ali, the great grandson of Imam Ali, Prophet Mohammed’s cousin and son-in-law, is revered by Shias, Sunnis, and Zaydis. ? In the eighth century, Zayd Bin Ali launched a revolution against the Ummayad Caliphate. He was assassinated, but his martyrdom spawned the Zaydi cult. ? The Zaydis were a strong group in Yemen for centuries. The Zaydis would establish a monarchy (the Mutawakkilite Kingdom) in the country after the Ottoman Empire fell apart in 1918. ? Their reign of terror came to an end in 1962, when the monarchy was overthrown by Egypt-backed revolutionaries. ? The Houthis, also known as Ansar Allah (God’s Partisans), are a Shiite Muslim military and political movement in Yemen that is backed by Iran. ? Its members, who belong to the Shiite minority Zaidi sect, seek for Zaidis in northern Yemen to have regional autonomy. ? During the preceding decade, they fought a series of rebellions against Saleh, and took advantage of the new president’s weakness by seizing control of Saada province’s northern core and surrounding areas. |
3. Global Cyber security Outlook 2022: WEF
#GS3- Internal Security
Context
- According to the World Economic Forum’s ‘Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2022,’ cyberattacks have increased as a result of growing Covid-driven digitalisation.
In depth information
The Report’s Main Points
- Rising cyber-attacks:
- The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the speed of digitalisation, resulting in a record-breaking year for cybercrime in 2021, with ransomware attacks up 151% and an average of 270 cyberattacks per organisation.
- Last year, each successful cyber breach cost a corporation USD 3.6 million (about Rs 27 crore), and the average share price of the hacked company lagged NASDAQ by nearly 3% even six months after the event in the event that the breach became public.
Ransomware is extremely dangerous.
- According to the World Economic Forum, the global digital economy grew as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, but criminality also grew, with nearly 80% of cyber leaders now considering ransomware a “risk” and “threat” to public safety.
- Cyber-strength:
- Cyber resilience is integrated into enterprise risk management plans, according to 92 percent of business executives questioned, but only 55 percent of cyber leaders concur.
- As a result of incompatible security priorities and policies, this leadership gap can expose companies to assaults.
- Only around a fifth of cyber leaders are confident that their companies are cyber-resilient.
- The weakest link is:
- SMEs are viewed as the weakest link in the supply chain by nearly nine out of 10 people.
Challenges
- Time to reply: It takes an average of 280 days for a company to detect and respond to a cyberattack.
- Lack of skill set: Nearly two-thirds of respondents said it would be difficult to respond to a cybersecurity incident because their team lacked the necessary skills.
- Retaining competent personnel: A scarcity of security personnel poses a serious threat to corporate continuity and potentially national security.
- According to the survey, 50 percent of all respondents would find it difficult to respond to and recover from a cyberattack due to a skills gap within their team, and only about a quarter of businesses with 5,000 to 50,000 employees have the people and skills they require now.
Prioritization issues:
- According to the survey, while about 85 percent of cyber executives agree that cyber resilience is a business priority for their firm, one of the most significant obstacles they face is gaining decision-makers’ support when prioritising cyber risks above a variety of other risks.
- These contradictory findings suggest that emphasising cyber resilience as a corporate strategy is necessary but insufficient.
Ahead of Schedule
- In a world where digital technology has made us so interconnected, cybersecurity and global security are synonymous.
- No single public or private organisation can have a complete picture of the entire cyber landscape.
- To put the pieces of the puzzle together, senior leadership must require that organisations exchange information.
- To be resilient and promote customer trust, businesses must collaborate more closely with ecosystem partners and other third parties to make cybersecurity part of their ecosystem DNA.
4.2021 Sixth Warmest Year
#GS3-Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Context
- Two American agencies recently revealed statistics indicating that 2021 was the sixth warmest year on record for the world.
- And the last ten years have been the warmest on record since records began in 1880.
- NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the United States gathered the data (NOAA).
In depth information
- Earth in 2021: In 2021, the Earth was roughly 1.1 degrees Celsius warmer than it was during the onset of the industrial revolution in the late 1800s.
The Northern Hemispheres and Southern Hemispheres:
- The land surface temperature in the Northern Hemisphere was the third hottest on record, with 2016 (second) and 2020 (first) being even higher.
- The surface temperature in the Southern Hemisphere in 2021 was the ninth highest on record.
Temperatures at the Sea’s Surface:
- Sea surface temperatures have reached new highs in sections of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
- In 2021, the upper ocean heat content hit a new record, topping the previous high recorded in 2020.
- The seven years with the highest ocean heat content all happened in the last seven years (2015-2021).
- In December 2021, the extent of Antarctic sea ice was 3.55 million square miles.
- This was the third-smallest December extent on record, at 11.6 percent below average.
- Only December 2016 and December 2018 had a smaller magnitude.
La Nia’s effects: La Nia’s effects kept global temperatures lower.
- La Nia is a weather pattern that occurs in the Pacific Ocean and has an impact on weather all over the globe.
- When ocean surface waters along the Pacific coast of the South American tropics cool, a La Nia event occurs. This happens every two to seven years on average.
- The following are some of the reasons for the current warming trend:
- Human activities have boosted emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, resulting in this global warming trend.
- The repercussions of global warming are already being felt on the planet: Arctic sea ice is melting, sea levels are increasing, wildfires are growing more intense, and animal migration patterns are shifting.
In India, the temperature is rising.
- The first portion of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCCSixth )’s Assessment Report (AR6), titled Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis, was issued in August of 2021.
Findings from the Indian Subcontinent:
- Heatwaves: Heatwaves and humid heat stress will become increasingly extreme and frequent in South Asia in the twenty-first century.
- Monsoon precipitation is also likely to change, with both yearly and summer monsoon precipitation expected to rise.
- The West Coast The monsoon has been declining in recent decades due to an increase in aerosols, but if this decreases, the country will see heavy monsoon rains.
- The Indian Ocean, which encompasses the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, has warmed more rapidly than the global average.
- When global warming is 1.5°C to 2°C, the sea surface temperature across the Indian Ocean is likely to rise by 1 to 2°C.
India’s Recent Climate-Related Measures:
- At the UNFCCC COP26, an ambitious climate action vision with five aspects was announced.
- By 2030, non-fossil energy capacity will have reached 500 GW.
- By 2030, renewable energy will account for 50% of total energy consumption.
- By 2030, overall anticipated carbon emissions will be reduced by one billion tonnes.
- By 2030, the economy’s carbon intensity will be less than 45 percent.
- By 2070, we will have achieved our goal of “net zero” emissions.
- India is now ranked fourth in the world in terms of installed renewable energy capacity, with non-fossil energy accounting for more than 25% of the entire energy mix in the last seven years.
- India has also led programmes such as the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and the Coalition for Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) (CDRI).
5. Artificial Moon
#GS3-Space
Context
- China recently completed the construction of an artificial moon facility to imitate lunar conditions and the environment for scientists testing new technology and future expeditions.
- The facility will open to the public later this year.
In depth information
- The research facility for artificial moons
- It’s in the Chinese province of Jiangsu, in the eastern city of Xuzhou.
- It will make gravity “disappear” by using intense magnetic fields within a vacuum container with a diameter of 2 feet (60 cm).
- To simulate the lunar surface, the room will be filled with pebbles and dust.
- It’s the “first of its sort in the world,” and it can keep its low-gravity state for as long as it wishes.
Objectives:
- To put instruments and technologies through their paces in a low-gravity environment similar to that of the moon, and to see if their experiments will work on the surface.
- The research facility will also aid in assessing whether or not human settlement on the moon is possible.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 20th January 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

