Daily Current Affairs 25th September -2021
Topics
- Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021
- India Endorses Objectives of Global Covid-19 Summit
- Bharath Net Project
- Arctic sea ice hits its minimum extent for the year
- Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records (FASTER) System
1) Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021
#GS2 #Government policies and Interventions #GS3 #Issues Relating to Intellectual Property Rights #IPR Regime in India
Context: Recently, the union government has introduced Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021 which amended the Patents Rules 2003.
Key Details:
- By amending the rules, Union Government has reduced the patent filing and processing fees that are charged on educational institutions.
- These changes is in line with similar concession available to start-ups under the Start-up India initiative.
- Patents Rules have been amended in 2016, 2017, 2019 and 2020 to achieve the objective of removing procedural inconsistencies and unnecessary steps in processing of applications thereby speedup grant/registration and final disposal.
- By amending the Rules, the procedures are made more compact, time-bound, user- friendly and compatible for e-transactions.
Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021:
- Patent Fees for Educational Institutions Reduced:
- To facilitate commercialization of research undertaken in educational institutions, the patent fees have been reduced.
- While applying for patents, innovators had to apply for these in the name of institutions that were required to pay exorbitant patenting fees.
- The high patenting fee was a hindrance for educational institutions in getting newer research and technologies patented.
- However, now the official fees payable by them in reference to the Patents Rules, 2003, have been reduced through the Patents (Amendment) Rules, 2021.
- Benefits related to 80% reduced fee for patent filing & prosecution have been extended to all educational institutions.
- This benefit was earlier available to all recognised educational institutions owned by the government.
- Extension of Expedited Examination System:
- Historically, grant of a patent was a rigorously time-consuming process from its provisional application to the grant of the patent.
- However, with amendments in 2016 and 2019 to the Patents Rules, 2003, the time for grant of a patent has been reduced to six months “depending on the promptness of the applicants in cooperating with the Controller”.
- The amendment has been done to reduce the time period of grant of a patent, clear pendency of cases and encourage more filings of patent claims to eventually promote technological advancement and innovation.
- The fastest granted patent is the one which was granted in 41 days after filing of such request.
- This facility of Expedited Examination system was initially provided for patent applications filed by Start-ups.
- It has been now extended to 8 more categories of Patent Applicants:
- SME (Small and Medium Enterprises), Female applicants, Government Departments, Institutions established by a Central, Provincial or State Act, Government Company, an Institution wholly or substantially financed by the Government and applicants under Patents Prosecution Highway.
- The Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) is a set of initiatives for providing accelerated patent prosecution procedures by sharing information between some patent offices.
Other Key Initiatives regarding this:
- Augmentation of manpower by recruiting new examiners;
- Making the patenting process completely online;
- Hearing of patenting cases through video-conferencing for speedy and contact-less proceedings;
- Dynamic redesigning of the website and real-time based hassle-free dissemination of IP information to stakeholders.
- The mechanism of lodging feedback and complaints regarding the functioning of IP offices has been set up on the IPO website.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade in collaboration with the office of Controller General of Patents, Designs & Trade Marks (CGPDTM) is regularly engaged in the dissemination of information to IP stakeholders through awareness activities in IPR which are conducted for schools, universities, industries, legal and enforcement agencies and other stakeholders.
About Patents:
- A patent is a form of preservation of intellectual property.
- It is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a product or a process that provides, in general, a new way of doing something, or offers a new technical solution to a problem.
- To get a patent, technical information about the invention must be disclosed to the public in a patent application.
- Patents in India are governed by “The patent Act 1970” which was amended in 2005 to make it compliant with TRIPS.
What kind of protection does a patent offer?
- A patent is an exclusive right granted for an invention, which is a new product or process that meets conditions of
- novelty,
- non-obviousness, &
- industrial use.
- In principle, the patent owner has the exclusive right to prevent or stop others from commercially exploiting the patented invention.
- In other words, patent protection means that the invention cannot be commercially made, used, distributed, imported or sold by others without the patent owner’s consent.
- Patents are territorial rights. In general, the exclusive rights are only applicable in the country or region in which a patent has been filed and granted, in accordance with the law of that country or region.
- The term of every patent in India is twenty years from the date of filing the patent application, irrespective of whether it is filled with provisional or complete specification.
2) India Endorses Objectives of Global Covid-19 Summit
#GS2 #Effect of Policies & Politics of Developed & Developing Countries on India’s Interests #Agreements Involving India and/or Affecting India’s Interests
Context: Summit, organized by US, aims to align aroundthe global targets andtaking associated required actions to endCOVID-19 pandemic and build back better.
Key Details:
- Global leaders attending the Summit have again underlined their commitment to ensuring equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines for all countries through COVAX.
- Building on the momentum and global solidarity generated over the past eighteen months by various commitments including at summits organised by the European Commission, the G20, the G7, Summit saw further pledges made to COVAX and equitable access.
- As the host of the Summit, the United States and as part of its commitment, pledged an additional 500 million doses of Pfizer vaccine to be delivered to low- and lower-middle-income countries through COVAX.
- These doses are in addition the deal for 500 million Pfizer doses facilitated by the United States, announced in June, bringing the US total doses to be provided through COVAX to nearly 1.1 billion doses.
- Emphasising the close partnership between the African Union and COVAX in delivering doses to African countries, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa called on higher-income countries to trade places in production queues and to support COVAX in their shared goal of increasing coverage across the African continent.
Key targets that would be covered:
- Vaccinate the world by Supporting G20.
- 40% global vaccination by end of 2021, WHO goal of at least 70% globa lvaccination by 2022 and manufacturing doses for adequate supplies to all countries by 2022.
- India’s Bharat Biotech has committed to deliver 5.5 crore doses of its Covid-19 vaccine, Covaxin, in October.
- Save lives now by solving oxygen crisis,eliminating testing gaps, building surge PPE manufacturing capacity along with timely access to therapeutics and better detection,monitoring and mitigation of new COVID-19 variants.
- Build Back Better by creating sustainable health security financing, catalysing political leadership (set up of Global Health Threats Council in 2021) and supporting G20’s call for a Global Ministerial Health and Finance Board.
Prime Minister Modi while addressing the summit stated that:
- PM Modi emphasised the need to focus on addressing the Covid-19 Pandemic’s economic effects.
- Supply chains of raw materials needed for vaccine production must be kept open.
- Previously, India and the South Africa have proposed a TRIPS waiver at the WTO for COVID vaccines, diagnostics and medicines.
- Mutual recognition of vaccine certificates to make international travel easier thereby addressing the pandemic’s economic effects.
- This statement comes amid a controversy over the UK’s revised travel guidelines for fully vaccinated Indians.
About COVAX:
- COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access (COVAX), is co-convened by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI),Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance Gavi) and the World Health Organization (WHO) – working in partnership with UNICEF as key implementing partner, developed and developing country vaccine manufacturers, the World Bank, and others.
- It is the only global initiative that is working with governments and manufacturers to ensure COVID-19 vaccines are available worldwide to both higher-income and lower-income countries.
- So far COVAX has delivered more than 300 million doses to 142 economies, and according to the latest forecast, a total of approximately 1.2 billion doses will be available for the lower income economies supported by the COVAX Advance Market Commitment (AMC) by the end of 2021.
- The key COVAX milestone of two billion doses released for delivery is now expected to be reached in the first quarter of 2022.
3) Bharath Net Project
#GS2 #Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
#GS3 #Indigenization of Technology & Developing New Technology
Context: Recently,The Meghalaya Cabinet cleared amendments to a tripartite agreement for the implementation of BharatNet project in Meghalaya.
- Main objective is to facilitate the delivery of e-governance, e-health, e-education, e-banking, Internet and other services to the rural parts of the state.
Background:
- The tripartite agreement was first signed in 2013 between DOT, Meghalaya government’s IT Department and BharatBroadband Network Limited (BBNL).
- Union Cabinet, in July 2021, accorded approval for the revised implementation strategy of BharatNet through Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode in 16 States of the country.
Key Details:
- It will now extend up to all inhabited villages beyond Gram Panchayats (GPs), in the said States.
- The revised strategy also includes creation, upgradation, operation, maintenance and utilization of BharatNet by the concessionaire who will be selected by a competitive international bidding process.
- The estimated maximum viability gap funding approved for the above PPP model is Rs. 19,041 crores.
Significance of Phase 02:
- An estimated 3.61 lakh villages including GPs in 16 states will be covered.
- The PPP model will leverage private sector efficiency for operation, maintenance, utilisation and revenue generation, and is expected to result in a faster roll out of BharatNet.
- Extension of reach of BharatNet to all inhabited villages with reliable, quality, high speed broadband will enable better access of e-services offered by various central and state government agencies.
- It will also enable online education, tele medicine, skill development, e-commerce and other applications of broadband.
- It is expected that revenue will be generated from different sources including proliferation of broadband connections to individuals & institutions, sale of dark fibre, Fiberization of mobile towers, e-commerce etc.
- Proliferation of broadband in rural areas will bridge the rural-urban divide of digital access and accelerate the achievement of Digital India.
- The penetration and proliferation of broadband is also expected to increase direct and indirect employment and income generation.
- The States where PPP Model is envisaged, will facilitate free Right of Way.
About BharatNet:
- BharatNet Project was originally launched in 2011 as the National Optical Fibre Network(NOFN) and renamed as Bharat-Net in 2015.
- It seeks to provide connectivity to 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs) through optical fibre.
- It is a flagship mission implemented by Bharat Broadband Network Ltd. (BBNL).
- The objective is to facilitate the delivery of e-governance, e-health, e-education, e-banking, Internet and other services to rural India.
- The project is a Centre-State collaborative project, with the States contributing free Rights of Way for establishing the Optical Fibre Network.
- The entire project is being funded by Universal service Obligation Fund (USOF), which was set up for improving telecom services in rural and remote areas of the country.
Bharat Net PPP Model will bring in following consumer friendly advantages:
(a) Use of innovative technology by the Private Sector Provider for the consumers;
(b) High quality of service and Service Level to consumers;
(c) Faster deployment of network and quick connectivity to consumers;
(d) Competitive tariffs for services;
(e) Variety of services on high-speed broadband including Over the top (OTT) services and multi-media services as part of packages offered to consumers, and
(f) Access to all online services.
Significance of PPP in Telecom Sector:
- PPP Model in this critical infrastructure of Telecom is a novel initiative.
- The selected Private Sector Partner is expected to provide reliable, high speed broadband services as per pre-defined Services Level Agreement (SLA).
- The Private Sector Partner is also expected to bring an equity investment and raise resources towards capital expenditure and for operation and maintenance of the network.
- Hence, the PPP Model for BharatNet will enhance efficiency, quality of service, consumer experience and leverage private sector expertise, entrepreneurship and capacities for accelerating achievement of digital India.
- This will be in addition to substantial savings of public money.
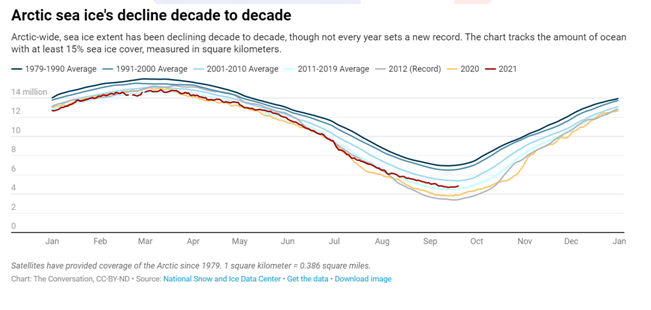
4) Arctic sea ice hits its minimum extent for the year
#GS3 #Environmental Pollution & Degradation #Prevention & Control of Pollution & Degradation
Context:September marks the end of the summer sea ice melt season and the Arctic Sea ice minimum, when sea ice over the Northern Hemisphere Ocean reaches its lowest extent of the year.
- The Arctic Sea ice reached its minimum extent, coming in at 4.72 million square miles. It is the 12th lowest on record and the record minimum melting of the ice occurred in 2012.
- The Arctic Ocean is the mass of water positioned approximately above latitude 65° N. Arctic Sea Ice refers to the area of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice.
Key Details:
- Sea ice cover has dropped by roughly half since the 1980s as a direct result of increased carbon dioxide from human activities.
- As per Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Arctic Sea ice levels in recent years have been at their lowest since at least 1850 for the annual mean and in at least 1,000 years for late summer.
- It concluded that the Arctic is likely to be practically sea ice free in September at least once before 2050.
- At this stage of the melt season, the sea ice pack is at its weakest and is highly responsive to the weather conditions of a given day or week. Subtle shifts can have big impacts.
- Summer melt began in earnest in May, a month that also featured multiple cyclones entering the Arctic.
- This increased sea ice drift but also kept temperatures relatively low, limiting the amount of melt.
- The extent and pace of melting increased significantly in June, which featured a predominant low-pressure system and temperatures that were a few degrees higher than average.
- In August, sea ice decline slowed considerably, with warm conditions prevailing along the Siberian coast, but cooler temperatures north of Alaska.
Reasons behind Rapid Melting of Ice:
- Counter clockwise Ice Circulation:
- Cyclones entering the Arctic from Siberia generated counter clockwise winds and ice drifts.
- This counter clockwise ice circulation pattern generally reduces the amount of sea ice moving out of the Arctic through the Fram Strait, east of Greenland.
- This likely contributed to the record low summer sea ice conditions observed in the Greenland Sea.
- This ice circulation pattern also increased ice export out of the Laptev Sea, off Siberia, helping create a new record low for early summer ice area in that region.
- Albedo:
- Ice has a higher albedo than land or water surfaces, this is one of several reasons for the Arctic’s warming about three times faster than the planet as a whole.
- Therefore, as global ice cover decreases, the reflectivity of Earth’s surface decreases, more incoming solar radiation is absorbed by the surface, and the surface warms.
- Darke Deep Ocean Surface.
- The Arctic’s bright ice is replaced by a darker open ocean surface, less of the sun’s radiation is reflected back to space, driving additional heating and ice loss.
- Low Pressure System:
- The low-pressure system also increases cloudiness over the Arctic.
- Clouds generally block incoming solar radiation, reducing sea ice melt, but they can also trap heat lost from the surface, so their impact on sea ice melt can be a mixed bag.
- Local Feedback Loops:
- Weather events can also trigger local feedback loops.
- A freak heat wave, for example, can trigger ice melt and further warming.
- Winds and ocean currents also break up and spread ice out across the ocean, where it can be more prone to melt.
Impact of Arctic Sea minimum:
- Threatening Coastal Communities:
- Humans in the Arctic have become more vulnerable to coastal erosion and face having to relocate their communities away from coastlines.
- Rising seas endanger coastal cities and small island nations by exacerbating Coastal Flooding and storm surge.
- Shipping:
- Melting Arctic Sea ice is likely to increase traffic through the Arctic Ocean.
- A 2016 study concludes that Arctic warming and sea ice decline will lead to “remarkable shifts in trade flows between Asia and Europe, diversion of trade within Europe, heavy shipping traffic in the Arctic and a substantial drop in Suez traffic.
- Temperature
- The Arctic and Antarctic are the world’s refrigerator. Since they are covered in white snow and ice that reflect heat back into space, they balance out other parts of the world that absorb heat.
- Less ice means less reflected heat, meaning more intense heatwaves worldwide. But it also means more extreme winters: as the polar jet stream—a high-pressure wind that circles the Arctic region—is destabilized by warmer air, it can dip south, bringing bitter cold with it.
- Food Security:
- Polar vortexes, increased heat waves, and unpredictability of weather caused by ice loss are already causing significant damage to crops on which global food systems depend.
- This instability will continue to mean higher prices for you and growing crises for the world’s most vulnerable.
- Permafrost:
- Permafrost in the Arctic region (ground that is permanently frozen) stores large amounts of methane.
- When it thaws, that methane is released, increasing the rate of warming.
- This, in turn, causes more ice and permafrost to thaw or melt, releasing more methane, causing more melting.
- As we lose more ice more quickly and see more rapid permafrost melt, we will start seeing the worst climate change predictions come true.
- Threat to Biodiversity:
- Sea ice decline has been linked to boreal forest decline in North America and is assumed to culminate with an intensifying wildfire regime in this region.
- The annual net primary production of the Eastern Bering Sea was enhanced by 40–50% through phytoplankton blooms during warm years of early sea ice retreat.
- Polar bears are turning to alternative food sources because Arctic Sea ice melts earlier and freezes later each year.
Way Forward
- Arctic sea ice is part of a complex global system, and as a result it affects communities at all latitudes.
- There is a lot that can be done around the world to slow the loss of Arctic Sea ice, largely in the form of reducing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions.
- Maintaining the balance between anthropological activities and carrying capacity of the environment is one of the foremost steps that can be taken at this point of time.
- Also, preserving important carbon sinks and fragile ecosystems like mangroves and marshescan hold back the greenhouse gas build-up that contributes to sea ice loss.
5) Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records (FASTER) System
#GS2 #Judiciary #Fundamental Rights #E-Governance
Context: Recently, the Supreme Court has given its approval to implement a system for electronic transmission of its orders.
- It will ensure effective implementation of Article 21 (right to life).
- The process to develop the FASTER system began with the Chief Justice of India’s observations in court on July 16 this year.
About the FASTER System:
- FASTER is an acronym form Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records.
- The system offers sending e-authenticated copies of interim orders, stay orders, bail orders and record of proceedings to the duty-holders for compliance and due execution, through a secured electronic communication channel.
- In relation to the implementation of FASTER system, the Supreme Court has directed all states to ensure the availability of internet facility with adequate speed in each and every jail and take necessary steps to arrange for internet facility.
Significance of the system:
- It will address the issue of communication delay which is one of leading cause of jail inmates locked up despite bail orders passed by the courts.
- This will reduce the burden of overcrowding of jails by facilitating faster release of Undertrials.
- Undertrials are the people who are yet to be found guilty of the crimes they have been accused of.
- It would also prevent unnecessary arrests and custody of people even after the court had already granted them its protection.
- It may even communicate a stay on an execution ordered by the final court on time.
- This will reduce the burden of overcrowding of jails by facilitating faster release of Undertrials.
Daily Current Affairs 25th September -2021
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube

