Daily Current Affairs 27th August-Topics
- Enhanced Access and Service Excellence (EASE 4.0)
- Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane
- ‘Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2021’ by Asian Development Bank
- Forum for Decarbonisation of Transport Sector
- Nano-Robots
1.Enhanced Access and Service Excellence (EASE 4.0)
#GS3 #Mobilisation of Resources #Banking Sector & NBFCs
Context: Union Finance Minister recently launched the EASE 4.0 and undertook the annual performance review of the public sector banks (PSBs).
About Ease 4.0:
- It is a unique reform agenda for PSBs designed at institutionalising clean and smart banking.
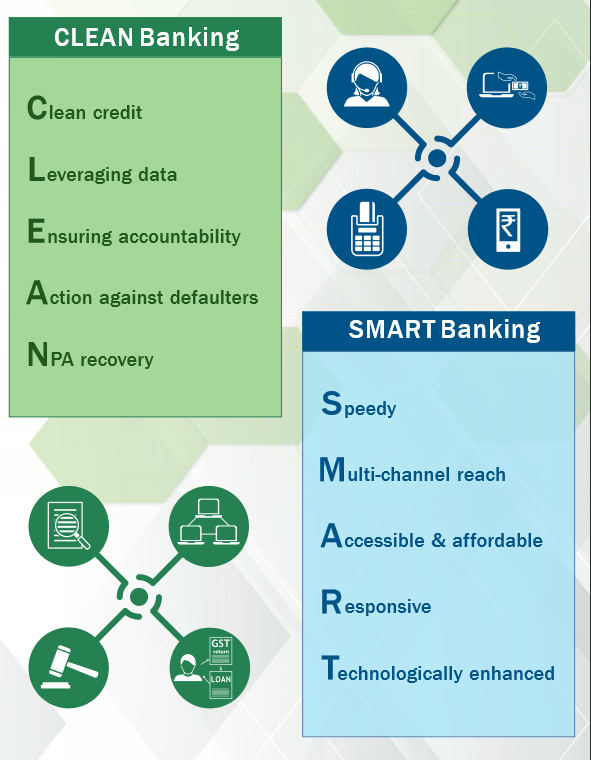
- This commits PSBs to technology-enabled, simplified and collaborative banking to further the agenda of customer-centric digital transformation.
- Major themes proposed under EASE 4.0:
- 24×7 Banking with robust technology to guarantee uninterrupted availability of banking services.
- PSBs have also been asked to come up with detailed schemes specific for the North-Eastern states.
- Bad Bank: The proposed bad bank is very close to getting a licence.
- Industries now have option to raise funds outside the banking sector.
- Banks themselves are raising funds through various avenues.
- These new aspects need to be studied to target credit where it is needed.
- Fintech (Financial technology) should be used effectively by the Banking sector to further these agendas.
- Export Promotion: Banks will be urged to work with state governments to push the ‘one district, one export’ agenda.

About EASE Agenda:
- EASE launched in January 2018 together by the government and PSBs.
- It was commissioned through Indian Banks’ Association and authored by Boston Consulting Group.
- Various Stages under EASE Reforms Agenda:
- EASE 1.0: The EASE 1.0 report exhibited substantial improvement in PSB performance in resolution of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) transparently.
- EASE 2.0: 06 themes of EASE 2.0 to make reforms of 1st version irreversible, strengthen processes and systems, and drive outcomes.
- Responsible Banking;
- Customer Responsiveness;
- Credit Off-take,
- PSBs as UdyamiMitra (SIDBI portal for credit management of MSMEs);
- Financial Inclusion & Digitalisation;
- Governance and Human Resource (HR).
- Ease 3.0 seeks to improve experiences of banking in all customer fields, using tech viz.
- Dial-a-loan and PSBloansin59 minutes.com.
- Partnerships with FinTechs and E-commerce companies,
- Credit@click,
- Tech-enabled agriculture lending,
- EASE Banking Outlets etc.
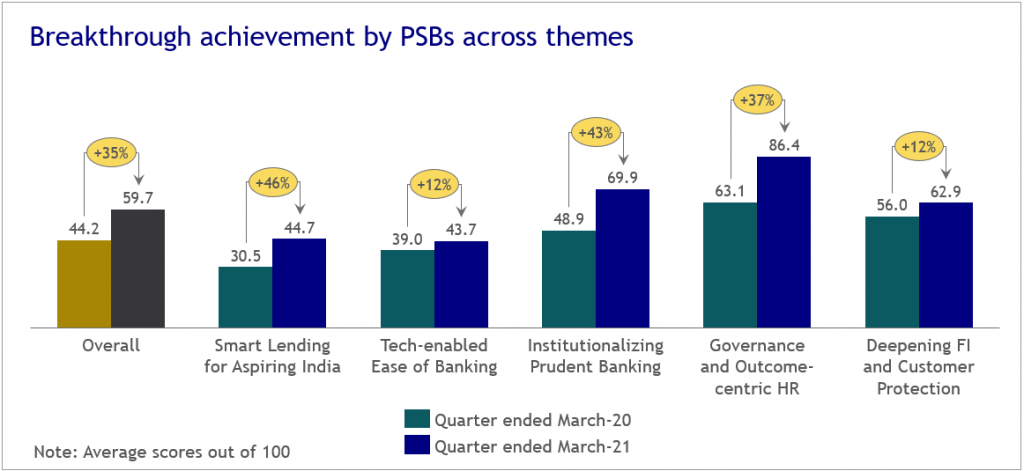
Performance Under EASE Reforms Agenda:
- EASE Reforms Index: With the aim of encouraging healthy competition among banks to drive change, this index is introduced to measure performance of each PSB on 120+ objective metrics.
- Public sector Banks have done well and come out of Prompt Corrective Action in spite of service extended during the Covid19 disruption.
- PSBs have recorded remarkable growth over 04 quarters since the launch of EASE 3.0 Reforms Agenda in February 2020.
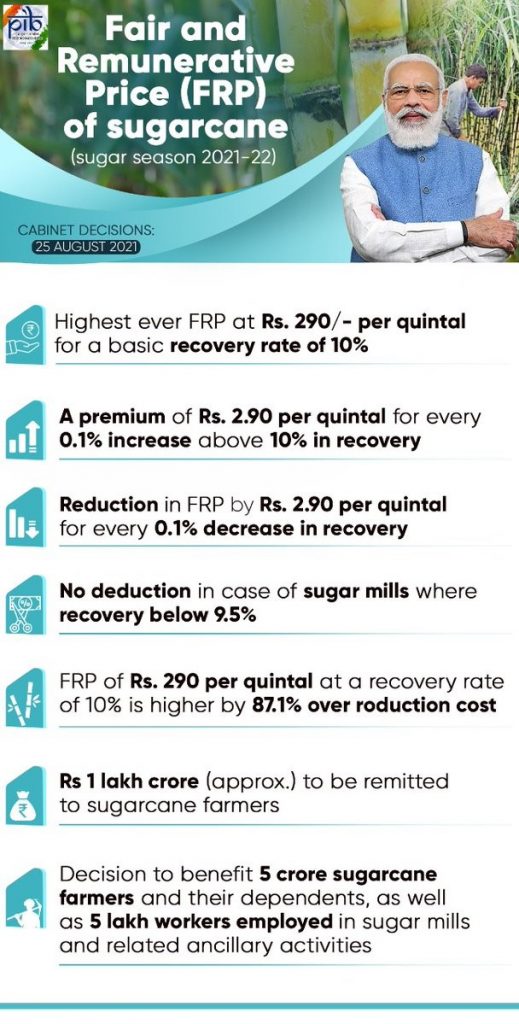
2.Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane
#GS3 # Major Crops Cropping Patterns in Various Parts of the Country # Agricultural Pricing Policy #GS2 #Government policies and intervention
Context: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs recently approved the rise in the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for sugar season 2021-22.
Sugarcane Pricing policy:
- Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966 was amended in 2009 to replace the concept of Statutory Minimum Price (SMP) with the ‘Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP)’ of sugarcane.
- The FRP is based on the Rangarajan Committee report on reorganizing the sugarcane industry.
- The cane price announced by the Union Government is determined on the basis of the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) in consultation with the State Governments and after taking feedback from associations of sugar industry.
- FRP is fixed considering the following factors:
- a) cost of production of sugarcane;
- b) return to the growers from alternative crops and the general trend of prices of agricultural commodities;
- c) availability of sugar to consumers at a fair price;
- d) price at which sugar produced from sugarcane is sold by sugar producers;
- e) recovery of sugar from sugarcane;
- f) the realization made from sale of by-products viz. molasses, bagasse and press mud or their imputed value;
- g) reasonable margins for the growers of sugarcane on account of risk and profits.
- State Government: State Advised Prices (SAP)
- The SAP are announced by the Governments of key sugarcane producing states.
- SAP is generally higher than FRP.
- The Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) is an attached office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It is an advisory body whose recommendations are not binding on the Government.
Key Policy Decisions for Sugar Season 2021-22

Sugar Pricing Policy:
- Sugar prices are determined by the market & depends on demand & supply of sugar.
- However, in 2018, government has introduced Minimum selling price (MSP) for sugar to protect the interest of farmers, so that industry may get at least the minimum cost of production of sugar, so as to enable them to clear cane price dues of farmers.
- MSP of sugar is determined by considering the components of Fair & Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane and minimum conversion cost of the most efficient mills.
Minimum Support Price:
- MSP is a “minimum price” for any crop that the government considers as remunerative for farmers and hence deserving of “support”.
- It is also the price that government agencies pay whenever they procure the particular crop.
- MSP for total of 20 crops (14 Kharif and 6 rabi crops) is now being recommended by the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
- MSP is an obligatory, not a statutory exercise as there is no statutory backing for MSP or any law mandating their implementation.
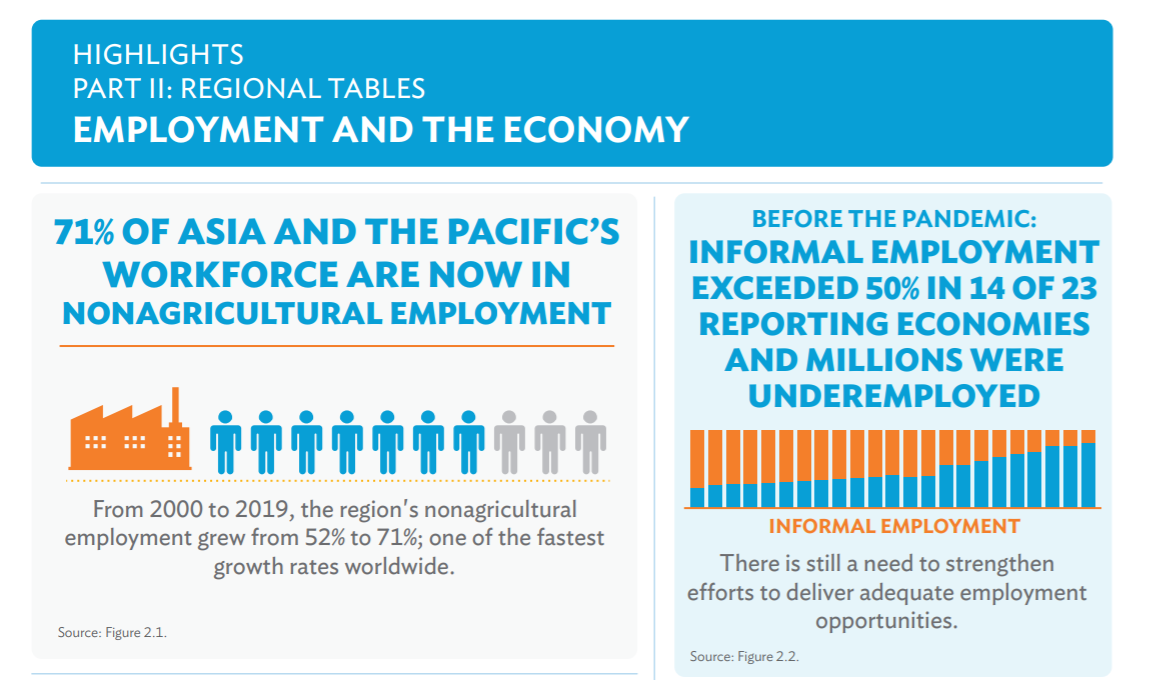
3.‘Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2021’ by Asian Development Bank
#GS2 # Issues Relating to Poverty & Hunger #Employment # Important International Institutions
Context: Asian Development Bank (ADB) recently released a report titled as the Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2021.
About the report:
- This report showed that the region made considerable progress in the last 20 years with respect to numerous development targets.
- The ADB Institute in 2020 conducted household surveys across many economies that are members of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
- It presents comprehensive economic, financial, social and environmental statistics for ADB’s 49 regional members.
Highlights of the report:
- Poverty:
- Concept of poverty is multidimensional which encompasses deprivations in income, health, education, and living standards.
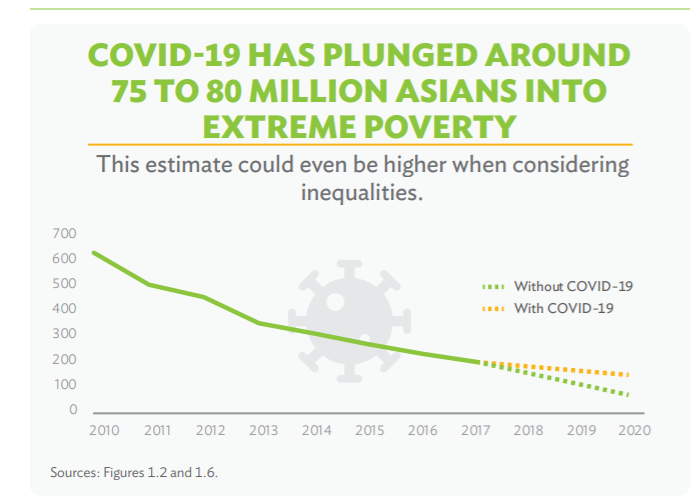
- Covid-19 pushed 75-80 million people in the developing Asia-Pacific into extreme poverty in 2020.
- About 203 million people — 5.2% of developing Asia’s population — lived in extreme poverty as of 2017.
- Without the pandemic, that number would have declined to an estimated 2.6% in 2020.
- Skills and regional inequality: In some Asian economies, rural poverty rates are 5 to 8 times higher than urban poverty rates. Poverty is also higher among those lacking in higher education.
- Contribution to Global GDP:
- Asia and the Pacific’s economy has grown at a healthy pace in recent years and contributed as much as 35% to global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in present US dollars in 2019.
- Increased economic linkages with the rest of the world and strong consumption contributed to this growth.
- But the pandemic took a toll just when weaker domestic investment and slowing global trade and economic activity started to challenge this momentum.
- Household Income:
- A substantial number of households involved in business were severely affected by the pandemic.
- Among households engaged in agriculture or depending on wages and salary, more than 50% reported an increase in income, no change or a decrease of less than 26%.
- Unemployment:
- As unemployment rates increased by at least 20% in 2020 due to the covid19 in more than 1/3rd of the reporting economies, the Asia-Pacific region lost an estimated 8% of working hours.
- As businesses were interrupted, many workers lost their jobs, leading to higher unemployment and underemployment rates.
- Labour Force Participation:
- From 2019 to 2020, labour force participation rates among women, on average, declined by 1.4%, while labour force participation rates among men declined by 0.8%.
- Sustainable Development:
- The pandemic is threatening Asia-Pacific’s progress toward critical targets under the United Nations-mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).
- In some economies where food insecurity and undernourishment were already a concern prior to COVID-19, millions had to reduce food consumption due to financial difficulties caused by the pandemic.
- This threatens the regions progress on SDG 02.
- Children Related Data:
- The incidence of undernourishment reduced from more than 521 million people in 2001 to 316 million in 2019.
- Almost all learners in the region were affected by closure of schools during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- In spite of efforts to continue school activities through remote learning, poorer students suffered greater disruption to their education during the pandemic.
Way Forward:
- Asia and the Pacific has made remarkable strides, but Covid-19 has exposed social and economic fault lines that may weaken the region’s sustainable and inclusive development.
- To achieve the United Nation’s SDG 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, policy makers need to utilise high-quality and timely data as a guide for actions to ensure that the recovery leaves no one behind – especially the poor and vulnerable.
Asian Development Bank:
- It is a regional development bank established in 1966. It has 68 members.
- 49 are from within Asia and the Pacific and 19 outside.
- ADB’s 05 largest shareholders are Japan and the United States (each with 15.6% of total shares), the People’s Republic of China (6.4%), India (6.3%), and Australia (5.8%).
- Main objective of ADB is to promote social and economic development in Asia and the Pacific.
- India is a founding member of ADB.
- Its headquarters is located in Manila, Philippines.
- Forum for Decarbonisation of Transport Sector
#GS3 # Environmental Pollution & Degradation #National Environment Agencies, Policies #Niti Aayog
Context: Recently, NITI Aayog and World Resources Institute (WRI), India jointly launched the Forum for Decarbonizing Transport.
- World Resources Institute, India is an independent charity lawfully registered as the India Resources Trust which offers objective information and practical proposals to foster environmentally sound and socially equitable development.
About the forum:
- It is a part of the Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC)-Transport Initiative for Asia (NDC-TIA) project, which concentrates on developing a clear strategy of effective policies and the development of a multi-stakeholder platform for decarbonising transport in the region.
- The NDC-TIA project works to bring down the peak level of GHG emissions (transport sector) in Asia (in line with a well below 2-degree pathway), resulting in problems like congestion and air pollution.
- The International Climate Initiative (IKI) is a key element of Germany’s climate financing and the funding commitments in the framework of the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- It will act as the conduit for bringing diverse voices and needs to adopt an integrated approach for greening the transport sector in India.
Expected advantages of the forum:
- It will aid in the creation of innovative business models for targeted results and the all-inclusive growth of the electric mobility space in India.
- It will also offer a platform to start dialogues for the creation of uniform policies and help realize specific outcomes in reducing emissions from the transport sector.
Need of the forum:
- India has an enormous and diverse transport sector, which is also the 03rd most Carbon dioxide emitting sector.
- Statistics from the International Energy Agency (IEA), 2020 and Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change, 2018 shows that within the transport sector, road transport contributes to more than 90% of the total CO2 emissions.
- With swelling urbanisation, the number of sales of vehicles is growing swiftly.
- It is projected that the total number of vehicles will be doubled by 2030.
- Thus, the transition to a decarbonisation path for the transport sector in India is indispensable to achieve the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement for 2050.
Way Forward:
- India has a great prospect for decarbonize its urban transport sector.
- Encouragement of walking, cycling and public transport coupled with electrification of motor vehicles should be the right strategy for the country.
- To properly use and streamline EVs across the country, there is a need to create a conducive ecosystem for different stakeholders.
- A harmonized effort between these stakeholders will help bringing in more investment, encourage adoption, and guarantee fair operation in the industry.
5.Nano-Robots
#GS3 #Science and technology – Developments & their Applications & Effects in Everyday Life # Awareness in Different Fields- Nanotechnology
Context: Recently, scientists has found a way to overcome issues relating to root canal treatments and other dental procedures using nanosized robots.
- Root canal treatment is intended at eliminating bacteria from the infected root canal, prevent reinfection of the tooth and save the natural tooth.
About the Research:
- A substantial proportion of root canal treatments be unsuccessful, because the process leaves out some bacteria that are lodged deep within the dentinal tubules.
- In the research the scientist has found a way to address this using nanosized robots that will move through the tubules and target the bacteria.
- In this method, spiral silica nanobots with a jiff of iron embedded in them are inserted in the central canal of the tooth.
- Then a spinning magnetic field is applied. This makes the nanorobot to move – like screws move into a wall.
- Once the bacterial colony is reached, the nanorobot can deploy various antibacterial strategies one of which is localised heating.
Nanorobots:
- Nanorobotics defines the technology of creating machines or robots at the nanoscale.
- ‘Nanobot’ is an informal term to refer to engineered nano machines.
- Nanobots are robots that carry out a very specific function and are ~50–100 nm wide.
- They can be used very efficiently for drug delivery.
- Usually, drugs work through the entire body before they reach the disease-affected area.
- Using nanotechnology, the drug can be targeted to a exact location which would make the drug much more effective and reduce the chances of possible side effects.
Uses of Nanotechnology in Health Care:
- Nanotech detectors for heart attack.
- Nanocarriers for eye surgery, chemotherapy etc.
- Diabetic pads for regulating blood sugar levels.
- Nano sponges are polymer nanoparticles coated with a red blood cell membrane, and can be used for absorbing toxins and removing them from the bloodstream.
- Nanoflares are used for detection of cancer cells in the bloodstream.
- Nanopores are used in making DNA sequencing more efficient.
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube