UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 27th January 2022
Topics
- Negative Ion Technology
- The Republic
- Najafgarh Jheel
- Ukraine crisis- NATO sent ships and fighter jets
- Trade Defence Wing (TDW) Operations
1.Negative Ion Technology
#GS2-Health
Context
- The Netherlands’ Authority for Nuclear Safety and Radiation Protection (ANVS) recently released a statement naming a number of negative ion wearable goods that contain more radioactivity than is legally allowed.
In depth information
- Negative ion technology incorporates negative ions into personal products and is currently being promoted as a way to improve health, energy balance, and well-being.
- Silicone wristbands, quantum or scalar-energy pendants, and kinesthesiology tape all utilise this technology.
- Negative ions are also produced when oxygen is broken down by sunshine, radiation, air, or water.
- Natural radioactive elements like uranium and thorium are frequently found in the minerals that form negative ions.
- Negative ions are said to boost mood and create pleasant emotions. They provide a variety of mental and physical health benefits, such as stress reduction, improved sleeping, and breathing, among others; nevertheless, these ions may also act on pollutants, negatively charging them and causing them to collect on surfaces.
Related Issues:
- Certain of these goods included levels of radiation that were higher than the background level, and in some cases, high enough to necessitate licencing.
- The radioactivity of the minerals used in products varies, making it impossible for the user to tell how radioactive these items are.
- The act of producing radiation spontaneously is known as radioactivity.
- The goods were discovered to contain radioactive ingredients, which produce ionising radiation continuously, exposing the wearer.
- Exposure to ionising radiation can have negative health consequences, and using the goods for long periods of time can cause tissue and DNA damage.
- Skin burns, acute radiation illness that causes cancer and hair loss, temporary reduction in white blood cells, possible chromosomal damage, and reduced resistance to infection are all possible side effects of exposure.
- Researchers from the International Atomic Energy Agency discovered that the undergarment sector in Malaysia and elsewhere sold “negative ion undergarments” that contained tourmaline, monazite, and zircon, all of which are known to contain uranium and thorium.
Efforts:
- The IAEA considers the frivolous use of radiation or radioactive chemicals in toys and personal jewellery or adornments, which result in an increase in activity, to be unreasonable in “Radiation Protection and Safety of Radiation Sources: International Basic Safety Standards” (2014).
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) developed a special safety advisory titled “Radiation Safety for Consumer Products” (2016).
- The Atomic Energy (Radiation Protection) Rules, 2004, in India, have provisions that are similar to those of the IAEA.
2.The Republic
#GS2-Indian Constitution
Context
- People make a republic strong and keep it alive. The Indian republic has been maintaining a dynamic equilibrium for 73 years in its current form.
In depth information
Representatives who are directly elected
- Our people deserve credit for the pyramidal three-layered elected representative system that governs us now.
- Today, this system has over 3 million elected representatives (one million of them are women), over 4,000 members of state legislatures, and over 500 members of Parliament.
- Perhaps no other country in the world has such a large degree of directly elected representatives.
The Constitution’s moral and spiritual foundation
- “Our Constitution has a moral underpinning — to achieve justice for all part of our society; as well as a spiritual basis — to preserve and safeguard all religions in the execution of their functions,” argues K M Munshi in Pilgrimage to Freedom.
- The struggle to ensure fairness for all members of our society continues.
- The impoverished of all categories, including the Backward Classes, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes, demand improved chances and affordable justice.
- The spiritual basis of our Constitution, which requires us to conserve and safeguard all religions, is also under threat, according to Munshi.
- When one’s right to practise one’s religion is denied or threatened, the public’s or media’s silence diminishes that constitutionally protected right.
The difficulties faced by social media
- An otherwise valuable tool, social media, has become a challenge and occasionally a threat to one or more of the rights established in our Constitution, thanks to the power of technology and its ability to broadcast on a large scale.
- Limiting them to preserve citizens’ rights is considered as a violation of the right to free speech.
- Without intervention, the harm caused by widespread false news to social cohesion could lead to people losing faith in the Constitution itself.
Constitution as a dynamic, living process
- Our Constitution has been altered more than any other in the world.
- If the Constitution has been amended more than 100 times, more than 1,500 statutes have been scrapped because they have outlived their usefulness.
- By remaining on paper, these deadwood regulations occasionally became a weapon in the hands of rent-seekers.
- As part of administrative reform, they were removed, making the executive’s function more visible and responsible.
- The 101st amendment, which established the Goods and Services Tax, is the best example of the Constitution’s constant evolution.
- His amendment created a single indirect tax framework by combining the majority of the Centre’s and states’ indirect levies.
- Even though it has only been in existence for five years, the GST Council has proven to be resilient in the face of adversity.
- It’s a positive sign for cooperative federalism.
Conclusion
- In nearly seven decades, our Constitution has served us well. Several post-imperial republics have discarded their previous constitutions in favour of new ones. The people are the only ones who can maintain the republic strong and vibrant.
3. Najafgarh Jheel
#GS3-Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Context
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) recently ordered Delhi and Haryana to implement an Environment Management Plan (EMP) for the restoration and protection of the Najafgarh Jheel, a transboundary wetland.
- The National Wetland Authority will oversee the implementation of these action plans through the individual State Wetland Authorities.
- The Union Environment Ministry has previously established a three-member committee to develop an integrated EMP.
In depth information

- The primary objective for the Environment Management Plan would be to notify the Najafgarh jheel and its area of influence under the Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules of 2017.
- Certain activities are prohibited and regulated within wetlands and their ‘zone of impact.’
- It outlines immediate actions such as demarcating the wetland’s boundaries with geo-tagged pillars and commissioning a hydrological assessment and species inventory.
- In-situ treatment of major drains that meet the Najafgarh jheel, regular monitoring of the waterbird population, and eliminating flow impediments such as power substations are among the medium-term interventions that will be undertaken in two to three years.
- The jheel is well-known as a migratory and resident waterbird habitat.
- It also suggests a detailed estimate of sewage generation in the area based on predicted population for the next 15 years, as well as the identification of all drains that contribute to pollution in the jheel.
Najafgarh Jheel:
- It’s in a natural depression at the Gurugram-Rajokri border on National Highway-48 in southwest Delhi.
- The lake is mostly filled with sewage from Gurugram and the Delhi suburbs. Haryana is home to a section of the lake.
- At the lake, 281 bird species have been recorded, including numerous endangered species such as the Egyptian vulture, Sarus Crane, Steppe Eagle, Greater Spotted Eagle, Imperial Eagle, and those migrating through the Central Asian Flyway.
Related Issues:
- Due to massive encroachment, the water body bordering Delhi and Gurugram has shrunk to only seven square kilometres.
- The restoration of the jheel, according to the Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH), would produce roughly 20 million gallons of water each day, enough to support a population of 3.5 lakh people.
- The Societies Registration Act of 1860 established INTACH as a non-profit charitable organisation.
- Najafgarh Jheel has been greatly fragmented and changed, built upon, exploited as a trash receptacle, and infested with exotic species, despite providing a variety of benefits and sustaining homes for diverse species.
- The Sahibi river, whose natural floodplain was Najafgarh Jheel, has been transformed into a drain. Because of the destruction of wetlands, nearby towns in Haryana and Delhi are at risk of pluvial floods and low groundwater levels.
- Recent wetlands projects, despite inhibiting natural wetland functions, are precarious due to the region’s strong seismicity and liquefaction.
Significance:
- The Najafgarh Jheel is a vital piece of natural infrastructure for the region, buffering floods, cleaning wastewater, recharging groundwater (with a high potential for water supply to a large population), and providing habitat for a variety of plant, animal, and bird species.
- Because it is a heat and carbon sink, it can control the microclimate. In fact, if the EMPs are properly and fully deployed, the jheel has the potential to become a key component of the National Capital Region’s ability to offset local climate change consequences.
4.Ukraine crisis- NATO sent ships and fighter jets
#GS2-Important International institutions
Context
- NATO partners have put personnel on standby and sent ships and fighter jets to reinforce Europe’s eastern defences amid escalating tensions over Russia’s military buildup near Ukraine.
In depth information
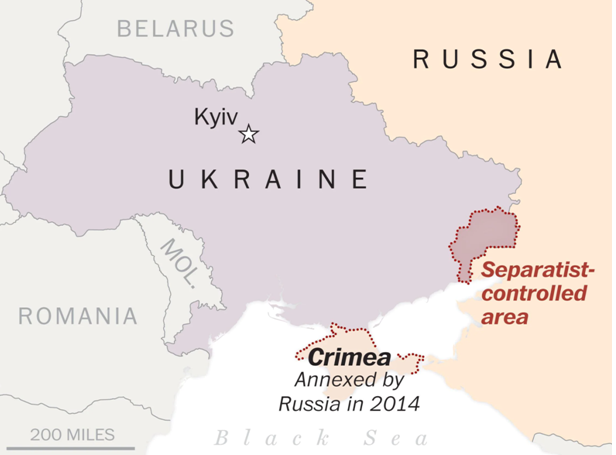
What exactly is the source of the conflict?
- Tensions between Ukraine and Russia, both former Soviet republics, rose in late 2013 as a result of a historic political and trade agreement with the European Union. Weeks of protests in Kiev exploded into bloodshed after the pro-Russian then-President, Viktor Yanukovych, cancelled the talks.
- Then, in March 2014, Russia annexed Crimea, a self-governing peninsula in southern Ukraine with significant Russian ties, ostensibly to protect its and Russian-speaking inhabitants’ interests.
- Pro-Russian separatists in Ukraine’s Donetsk and Luhansk regions declared independence from Kiev shortly after, sparking months of bloodshed. Despite the fact that Kiev and Moscow signed a peace pact in Minsk in 2015, sponsored by France and Germany, ceasefire violations have occurred on several occasions.
Recent advancements include:
- For nearly two weeks, US, NATO, and Ukrainian officials have been issuing statements in response to what they claim are extraordinary Russian army moves near Ukraine.
- More than a million Russian troops are stationed along Russia’s border with Ukraine, a potential NATO member.
What exactly is the problem? What are Russia’s requirements?
- Russia claimed that the military build-up would be de-escalated only if NATO withdraws its forces from all European countries that joined the alliance after May 1997.
- NATO would practically be unable to operate in any of the Baltic countries bordering Russia (Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania), central European countries like Poland, Hungary, and the Czech Republic, and Balkan countries like Croatia and Slovenia.
- Russia also wants NATO to abandon plans for further ‘enlargement,’ implying that it will refuse to admit Ukraine and Georgia as members. Another demand is that NATO not conduct manoeuvres in eastern Europe, Ukraine, or Georgia without first obtaining Russia’s agreement.
International attention is required:
- In the east of the country, a fight between Kiev and pro-Russian insurgents has claimed the lives of 14,000 people. According to the UN Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights’ October 2021 report, 3,393 of those killed were civilians.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- It is a military partnership between governments.
- The Washington Treaty established it.
- On April 4, 1949, a treaty was signed.
- Brussels, Belgium is where the company’s headquarters are located.
- Mons, Belgium, was the headquarters of the Allied Command Operations.
Composition:
- The alliance has grown from 12 to 30 countries since its inception, thanks to the admission of new member states. North Macedonia was the most recent member state to join NATO on March 27, 2020.
- “Any additional European state in a position to further the principles of this Treaty and contribute to the security of the North Atlantic area” is welcome to join NATO.
Minsk Agreements:
- Minsk I: In September 2014, Ukraine and separatists supported by Russia reached a 12-point ceasefire agreement in Belarus’ capital.
- It includes provisions for prisoner exchanges, humanitarian relief delivery, and the removal of heavy armaments.
- The arrangement immediately fell apart, with both parties breaking it.
- Minsk II: In 2015, an open confrontation was averted thanks to the signing of the ‘Minsk II’ peace deal, which was mediated by France and Germany.
- Its goal was to put an end to the combat in the rebel-held areas and hand over the border to Ukrainian soldiers.
5.Trade Defence Wing (TDW) Operations
#GS3- Indian Economy
Context
- The efforts of the Department of Commerce’s Trade Defence Wing (TDW) have provided assistance to Indian exporters.
In depth information
Concerning the Trade Defense Wing (TDW)
- In the year 2016, it was founded.
- It has served as a focal point for offering support to Indian exporters and defending their interests in inquiries conducted by other countries against India.
- It coordinates with various ministries of the Central and State Governments, as well as presenting India’s defence talks with other nations’ investigating authorities, primarily the US and EU authorities.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 27th January 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

