UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 28th January 2022
- Election – irrational freebies
- Integrity Pact
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)
- Spot-billed Pelicans
- Lithium mining
1. Election – irrational freebies
#GS2-Government Policies & Interventions
Context
- A lawsuit has just been filed in the Supreme Court asking the Electoral Commission of India (ECI) to take an election symbol or deregister a political party that promises or distributes “irrational freebies” from public monies before elections.
In depth information
- The petition said that political parties’ recent habit of influencing voters by offering freebies in the run-up to elections is not only the greatest threat to democratic ideals, but also violates the Constitution’s spirit.
About Freebies in Indian Politics:
- In order to guarantee the people’s support, political parties promise to provide free power and water, as well as monthly allowances for unemployed, daily wage workers, and women, as well as electronics such as computers and smartphones.
Concerning the Petition:
- The ECI’s mandate for free and fair elections, according to the petitioner, is violated by arbitrary offers of nonsensical gifts.
- Articles 14 (equality before the law), 162 (executive power of a State), 266(3) (expenditure from the Consolidated Fund of India), and 282 (discretionary grants) of the Constitution plainly prohibit the distribution of private goods and services from public monies.
- The appeal also asked the Supreme Court to order the Union to enact legislation in this area.
- It asked the ECI to amend the relevant paragraphs of the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order 1968 to include an additional criterion.
- It specifies that a “political party shall not promise/distribute unreasonable freebies from the public fund before the election” in order to be recognised as a state party.
Arguments in Favor of Freebies include the following:
- Essential for Fulfilling Expectations:
- In a country like India, where states have (or don’t have) a particular amount of development, people have expectations that are met by such promises of freebies when elections come around.
- Furthermore, when residents of neighboring/other states (with different ruling parties) receive freebies, there are comparable expectations.
- Helps Lesser Developed States:
- In states with a lower degree of development and a higher proportion of the population living in poverty, such freebies become a necessity, and it becomes necessary to provide such subsidies to the people for their own upliftment.
Issues Associated With ‘Freebies’:
- Economic Cost: This imposes a significant financial burden on the state and federal budgets.
- Against a Free and Fair Electoral: The promise of irrational freebies from public monies before elections swayes people, disrupts the level playing field, and taints the election process.
- It amounts to unethical behaviour akin to bribing the electorate.
- Against the Equality Principle:
- Using public funds to distribute private products or services that are not for public use before an election breaches numerous provisions of the Constitution, notably Article 14. (equality before law).
- SC Decision:
- In the case of S Subramaniam Balaji vs. Government of Tamil Nadu, the Supreme Court ruled that unrealistic political promises and giveaways are a major issue that disrupts election fairness.
- The court also held that promises made in an election manifesto cannot be construed as “corrupt practise” under the Representation of People Act or any other applicable law, and that thus, the distribution of freebies cannot be stopped when the ruling party uses public funds for this purpose by passing Appropriation Acts in the state legislature.
- At the same time, the court pointed out that there is no law directly governing the contents of election manifestos, and ordered ECI to draught guidelines in conjunction with all recognised political parties.
Next Steps
- Better Policy Reach:
- The economic policies or development models that the parties intend to execute must be expressed clearly and effectively.
- Furthermore, the parties should have (and offer) a thorough understanding of the economics and costs associated with such measures.
- Demand-Based Freebies:
- India is a large country, and there are still a great number of people living in poverty.
- It is also critical that all people are included in the country’s development agenda.
- Offering reasonable and practical freebies or subsidies that can be easily accommodated in a state’s budget does little harm and can be leveraged.
- Differentiating Subsidies from Freebies:
- There is a need to understand the economic implications of freebies and how they relate to public money.
- It’s also important to distinguish between subsidies and freebies, because subsidies are justified and explicitly targeted benefits that result from demand.
- People’s Perceptions:
- People should learn that selling their votes for goodies is a bad idea. They cannot expect competent leaders if they do not oppose.
2. Integrity Pact
#GS2-Government Policies
Context
- The Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) recently changed the criteria for appointing Independent External Monitors (IEM) to government agencies.
- It made the change months after issuing a revised standard operating procedure for the adoption and execution of the ‘Integrity Pact’ provision, which is intended to combat corruption in public procurement.
In depth information
- Integrity Pact:
- The ‘Integrity Pact’ is a contract between prospective vendors/bidders and the buyer in which both parties commit to not engaging in any corrupt acts in any aspect or stage of the transaction.
- Any infringement of the clause will result in bidders being disqualified and being barred from future business interactions.
- The accord also ensures that public procurement is transparent, equitable, and competitive.
Independent External Monitors:
- The IEMs conduct an independent and objective evaluation of the documents to evaluate whether the parties have met their contractual responsibilities.
- After reviewing any contract-related complaints, they provide recommendations to the appropriate authorities.
- If they discover major anomalies that fall under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988, they may file a report to the top executive of the organisation or immediately to the Chief Vigilance Officer (CVO) and the CVC.
Modifications to the IEM Rules: The zone of eligibility for IEM empanelment has been updated. It now includes the following:
- Officers who have served as Additional Secretaries to the Government of India, as well as those who have served as Chairman-cum-Managing Directors (CMD) of Schedule ‘A’ public sector businesses.
- Persons who, at the time of retirement, were equivalent to or higher than the position of Additional Secretary to the Central Government.
- Officers of the armed services who were in a pay bracket equivalent to or greater than that of an Additional Secretary at the time of retirement; CMDs/MDs and Chief Executive Officers (CEOs) of public sector banks, insurance companies, and other financial organisations are also eligible.
3.The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)
#GS3- S&T,Space
Context
- The Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) recently declared that the indigenous Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) will fly for the first time in April 2022.
- In April 2022, the SSLV-D1 Micro SAT will be released.
About
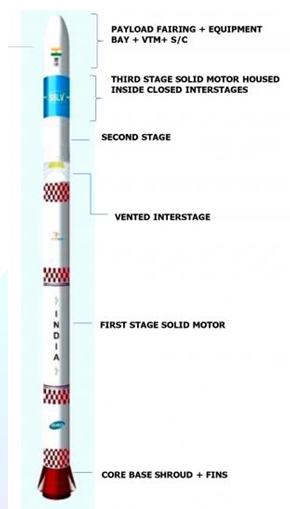
- During his time as director of the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre in Thiruvananthapuram, Dr S Somanath (New Chairman of ISRO) is credited with designing and constructing the SSLV.
- The SSLV’s first flight was supposed to take place in July 2019, but it has been postponed due to difficulties from Covid-19 and other issues.
- The Department of Space’s NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) will be the exclusive nodal agency for delivering end-to-end SSLV launch services for the customer satellite.
- SSLV was created to satisfy the needs of “Launch on Demand” in a cost-effective manner.
- It is a three-stage all-solid vehicle with a mass of 110 tonnes, making it ISRO’s smallest vehicle.
- It can launch satellites weighing up to 500 kilogrammes into low earth orbit, while the tried-and-true PSLV can launch payloads weighing up to 1000 kilogrammes.
- It will only take 72 hours to integrate, as opposed to the 70 days it now takes for a launch vehicle.
- Instead of 60 employees, just six will be needed to complete the task.
- The entire project would be completed in a short period of time and will cost roughly Rs 30 crore. It will be a vehicle that can be summoned at any time.
- SSLV is ideal for simultaneously launching several microsatellites and allowing for multiple orbital drop-offs.
Aims:
- The project’s main goal is to produce a cost-effective launch vehicle with a high launch frequency and quick turnaround capabilities to meet the growing demand for small satellite launch services in the global market.
- To increase the level of collaboration between the space sector and private Indian enterprises.
Agreements and commercial bookings
- In 2019, the SSLV secured a commercial booking from Spaceflight Inc, a US space launch services middleman.
- Between 2021 and 2023, ISRO signed six agreements with four countries for the launch of foreign satellites.
- The launch of these satellites would bring in €132 million.
4.Spot-billed Pelicans
#GS1-Species
Context
- Spot-billed pelicans (Pelicanusphilippensis) have died in large numbers in Telineelapuram Important Bird Area (IBA) in Srikakulam district, Andhra Pradesh, due to a nematode infestation.
- Hundreds of painted storks and thousands of spot-billed pelicans migrate from Siberia to breed in the Telineelapuram IBA.
In depth information

- According to preliminary findings, nematode infestation is to blame for the death of spot-billed pelicans that feed on neighbouring water bodies.
- The parasite is thought to have originated via aquaculture management practises near the habitat.
- The infestation of nematodes would not transmit from one species to another.
- The transmission of the infestation from fish, snails, and invertebrates is complicated. It has nothing to do with water or aqua ponds.
About Spot-billed pelicans
- Pelecanusphilippensis is the scientific name for this species.
- Physical Characteristics: They are little pelicans. Mature pre-breeding spot-billed pelicans have a brownish-grey crest and a grey dorsal coloration that fades to white ventrally. Although the skin in front of each eye is brilliant purple, the eye-ring and most face skin is an orange-yellow colour.
- It is a sociable animal that lives and travels primarily in flocks. On land, spot-billed pelicans are not graceful, but they can fly and swim well.
- It is capable of hunting large fish from bodies of water and wetlands, making it susceptible to infestation.
- Spot-billed pelicans are carnivorous and eat primarily fish, though tiny reptiles, amphibians, and aquatic crustaceans are occasionally added to their diet.
- It forages actively food in both freshwater and marine habitats, occasionally diving just beneath the surface but never to significant depths.
- Habitat: Found in Southeast Asia’s lowland freshwater, brackish, and marine wetland environments, primarily near open water.
- India, Sri Lanka, southern Cambodia, and Sumatra, as well as coastal areas, have the largest remaining populations.
- It is classified as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
5.Lithium mining
#GS3-Science and technology
Context:
- Serbians have taken to the streets to protest Rio Tinto’s intentions to mine lithium in the Jadar valley near Lozinca town, blocking important roads and bridges and disrupting traffic.
In depth information
Potential:
- According to Reuters, the mine would have produced enough lithium, boric acid, and sodium sulphate to power one million electric vehicles.
- The mine, when fully operational, would have produced “58,000 tonnes of refined battery-grade lithium carbonate” per year, making it Europe’s largest lithium producer.
What is the source of your concern?
- While the country already suffers from industrial pollution, a new mine will exacerbate the problem by damaging the surrounding land and water.
- Serbia is the fifth most polluted country in Europe and the 32nd most polluted country in the world, according to a list of 98 countries.
- Serbia is one of the top ten countries with the most pollution-related mortality, according to a 2019 research by the Global Alliance on Health and Pollution, with 175 deaths per 100,000.
Lithium Facts:
- It’s a silvery-white metal with a delicate texture. It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element under normal conditions.
- It must be stored in mineral oil because it is very reactive and combustible. It’s an alkali metal that’s also quite rare.
- The following are some of the most important characteristics and properties:
- It is the solid element with the largest specific heat capacity.
- Lithium’s single balancing electron makes it a good electrical conductor.
- When exposed to air and water, it is combustible and can even explode
Uses:
- Lithium is a critical component of modern technologies, with applications in ceramics, glass, telecommunications, and aircraft.
- Lithium is widely utilised in Lithium ion batteries, lubricating grease, high-energy rocket propellants, optical modulators for mobile phones, and as a convertor to tritium, which is used as a raw material in thermonuclear reactions such as fusion.
Substance to be used:
- Because of the thermonuclear use, Lithium is now classified as a “prescribed substance” under the Atomic Energy Act of 1962, allowing AMD to explore Lithium in various geological domains around the country.
- “Prescribed Substance” means any substance, including any mineral, that the Central Government may prescribe by notification as a substance that is or may be used for the production or use of atomic energy or research into matters related thereto, and includes uranium, plutonium, thorium, beryllium, deuterium, or any of their respective derivatives or compounds, as well as any other materials containing any of the aforesaid elements.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 28th January 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

