Daily Current Affairs 30th September -2021
Topics
- Build Back Better World (B3W) Initiative
- Action Plan for Rabies Elimination
- Global strategy to defeat meningitis
- Aapada Mitra Programme
- Landsat 09
1) Build Back Better World (B3W) Initiative
#GS2 #Important International Institutions #Effect of Policies & Politics of Developed & Developing Countries on India’s Interests
Context: U.S. officials are set to tour Latin America to scout infrastructure projects as a part of Build Back Better World (B3W) Initiative.
Key Details:
- Build Back Better World (B3W) is an initiative undertaken by G7 countries.
- Launched in June 2021, the initiative is led by USA designed to counter China’s strategic influence of the BRI Project (Belt and Road Initiative) by providing an alternative to the Belt and Road Initiative for the infrastructure development of the low- and middle-income countries
Guiding Principles of B3W:
- The ultimate goal is to narrow down the infrastructure deficit in the developing world, further exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The G7 countries will work to address the $40 trillion worth of infrastructure needed by developing countries by 2035.
- The initiative aims to catalyse funding for quality infrastructure from the private sector and will encourage private-sector investments that support “climate, health and health security, digital technology, and gender equity and equality”.
- The initiative builds on the Blue Dot Network, a collaboration that aims to build a global network through lending-based financing to build roads, bridges, airports, ports, power plants.
- The B3W efforts are in line with the standards and principles of the Blue Dot Network, relating to the environment and climate, labour and social safeguards, financing, construction, anti corruption, and other areas.
- Infrastructure development carried out in a transparent and sustainable manner – financially, environmentally, and socially – will lead to a better outcome for recipient countries and communities.
- B3W will envisage to establish a more inclusive model of global development.
- Once implemented, B3W is aimed to become possibly one of the largest infrastructure-focused initiatives by the democratic world, extending from “Latin America and the Caribbean to Africa to the Indo-Pacific”
B3W in Indo- Pacific:
- B3W may emerge more as a complement than an alternative to BRI. Although they may be clearly in competition in terms of goals for certain sectors (particularly technology), the two initiatives could very well operate as complementary to each other.
- Like BRI, B3W expects to harvest cross-national cooperation, cross-continental connectivity and regional synergy between the countries in question while working on large-scale projects in the developing world.
- For both G7 and regional like-minded powers, building B3W in a systematic, planned and effective manner must be a priority and tie-ups with national programmes can help achieve this progress.
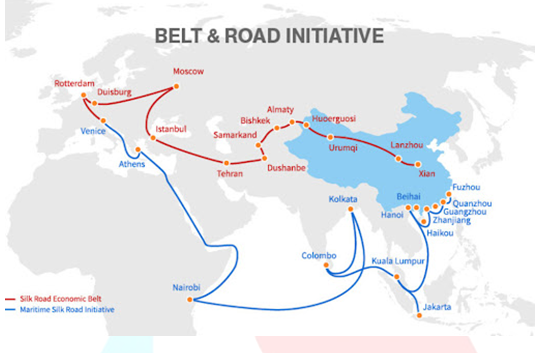
About Belt and Road Initiative:
- The BRI project was launched in 2013, it broadly aims to facilitate cross-border transportation of goods, access to energy, creating demand for existing excess capacity in Chinese industries.
- China had an overall exposure of investment of around $750 billion between 2013 to mid-2020.
- To date, Chinese companies have secured more than $340bn in construction contracts along the Belt and Road.
What are the risks for countries involved?
- BRI is also being seen as a part of China’s debt trap policy, wherein China intentionally extends excessive credit to another country with the intention of extracting economic or political concessions from the debtor country.
- Earlier this year, the Center for Global Development found eight more Belt and Road countries at serious risk of not being able to repay their loans.
- The affected nations – Djibouti, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, the Maldives, Mongolia, Montenegro, Pakistan and Tajikistan – are among the poorest in their respective regions and will owe more than half of all their foreign debt to China.
- China’s “maritime silk road” also pushes its strategic advantage at sea.
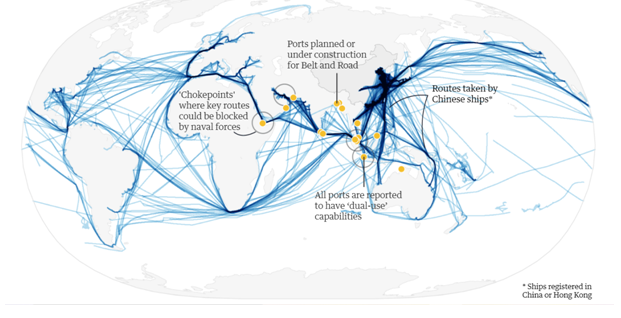
- Also, projects like China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), building of Colombo Port City Project in Sri Lanka are not only commercial in nature but have strategic implications too.
2) Action Plan for Rabies Elimination
#GS2 #Government policies and interventions #Issues related to health
Context: Recently, the Union Government, on the occasion of World Rabies Day launched a national action plan (NAPRE) for the elimination of dog mediated rabies by 2030
- The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has drafted the action plan in consultation with the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
Key Details:
- The NAP-RE is a guidance document for the states/ stakeholders to develop their own action plan, specific to their needs and aims at systematic reduction of rabies risk through sustained mass dog vaccinations, pre and post exposure prophylaxis and public education until the country is completely free of dog-mediated rabies. This document will help in the following: –
- To prepare an action plan that centre on the elimination of human rabies transmitted by dogs,
- To Strengthen State’s commitment on implementation of NAP-RE
- To ensure, for as long as possible, continuity of prevention of human rabies with effective, quality assured and vaccinations accessible to all who need them
- To strengthen capacities of the public Health Services, Veterinary Services and the local governing bodies.
- To Identify and support activities that when strategically used would eliminate dog mediated rabies.
- To strengthen Inter-ministerial, Inter department coordination and supporting mechanisms among all stakeholders
- To obtain and sustain high-level political commitment at the central and state level.
- To encourage community participation in urban and rural areas.
About Rabies?
- Rabies is one of the most fatal zoonotic diseases.
- It is transmitted after bite of rabid animal, and is 100 % fatal if the timely intervention in terms of appropriate management of wound and Anti Rabies Prophylaxis is not given to the animal bite victims.
- Rabies is mostly found in wild animals like bats, raccoons, skunks, and foxes, dogs.
- About 96% of the mortality and morbidity is associated with dog bites.
- The rabies virus infects the central nervous system.
- If a person does not receive the appropriate medical care after a potential rabies exposure, the virus can cause disease in the brain, ultimately resulting in death.
- Rabies can be prevented by vaccinating pets, staying away from wildlife, and seeking medical care after potential exposures before symptoms start.
- Rabies affects only mammals.
Rabies in India:
- In India, rabies is transmitted commonly by dogs and cats (~97%), followed by wild animals(2%) such as mongoose, foxes, jackals, and wild dogs, and occasionally by horses, donkeys, monkeys, cows, goats, sheep, and pigs.
- Rodents, rats and bandicoots, squirrel, rabbits, birds, and bats are generally not known to transmit rabies.
- The presence of un vaccinated free roaming dogs (FRD) or street dogs, amidst human settlements is a major contributor to the high incidence of rabies in India, as the disease is endemic.
- With the exception of Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep Islands, human cases of rabies are reported from all over the country. The cases occur throughout the year.
- Hence estimating such street dog’s population size is crucial to the planning and evaluation of any interventions, such as mass immunization against rabies. Apart from human, rabies also causes mortality among bovine and cattle.

3) Global strategy to defeat meningitis
#GS2 #Government policies and Interventions #Issues related to Health
Context: Recently,The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched the first-ever global strategy to defeat meningitis – ‘Global Roadmap to Defeat Meningitis by 2030’.
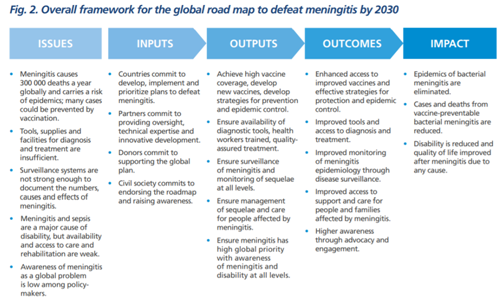
Highlights of the Roadmap:
- While the road map addresses all meningitis regardless of the cause, it primarily focuses on the main causes of acute bacterial meningitis (meningococcus, pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae and group B streptococcus), that were responsible for over 50% of the 250 000 deaths from all-cause meningitis in 2019, cause other invasive disease such as sepsis and pneumonia, and against which effective vaccines are available (or will be in a near future).
- The road map sets a comprehensive vision for 2030 “Towards a world free of meningitis”, with three visionary goals:
- Elimination of bacterial meningitis epidemics;
- Reduction of cases of vaccine-preventable bacterial meningitis by 50% and deaths by 70%;
- Reduction of disability and improvement of quality of life after meningitis due to any cause.
- It sets a path to achieve goals, through concerted actions across five interconnected pillars:
- Prevention and epidemic control focused on the development of new affordable vaccines, achievement of high immunization coverage, improvement of prevention strategies and response to epidemics;
- Diagnosis and treatment, focused on speedy confirmation of meningitis and optimal management;
- Disease surveillance to guide meningitis prevention and control;
- Care and support of those affected by meningitis, focusing on early recognition and improved access care and support for after-effects from meningitis, and
- Advocacy and engagement, to ensure high awareness of meningitis, consideration into countries plans, and increase the right to prevention, care and after-care services.
About Meningitis:
- About: Meningitis is an inflammation (swelling) of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
- A bacterial or viral infection of the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord usually causes the swelling. However, injuries, cancer, certain drugs, and other types of infections also can cause meningitis.
- Early meningitis symptoms may mimic the flu (influenza). Symptoms may develop over several hours or over a few days.
- Sudden high fever, Stiff neck, Severe headache, Headache with nausea or vomiting, Confusion or difficulty concentrating, Seizures, Sleepiness or difficulty waking, Sensitivity to light, No appetite or thirst, Skin rash (sometimes, such as in meningococcal meningitis)
- How it spreads:
- Bacterial Meningitis
- Generally, the germs that cause bacterial meningitis spread from one person to another. Certain germs can spread through food.
- How people spread the germs often depends on the type of bacteria.
- Viral Meningitis
- People can spread the viruses that cause viral meningitis to other people. If you have close contact with someone who has viral meningitis, they may spread the virus to you. However, you are not likely to develop meningitis. That’s because most people infected with these viruses will not develop meningitis.
- Impact: Meningitis is fatal and debilitating, striking fast with serious health, economic and social consequences, including life-long disabilities, and affecting people of all ages in all countries.
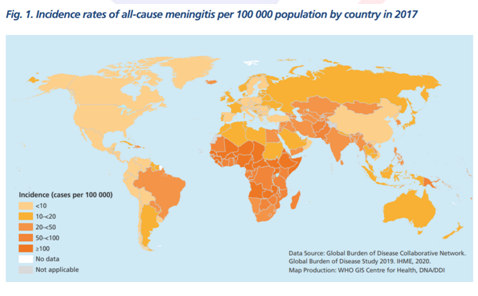
- Meningitis caused by bacterial infection causes around 2,50,000 deaths a year and can lead to fast-spreading epidemics.
- Treatment: A range of antibiotics is used to treat meningitis, including penicillin, ampicillin, and ceftriaxone.
- Available Vaccines: Meningococcal, Haemophilus influenzae type b and Pneumococcal vaccines.
- Bacterial Meningitis
Spread:
- Meningitis epidemics have occurred in the last decade in all regions of the world. But it is most common in the ‘Meningitis Belt,’ which spans 26 countries across sub-Saharan Africa.
4) Aapada Mitra Programme
#GS3 #Disaster management #Government Initiatives on Disaster Management
Context: Union government recently released the training manual of Aapda Mitra Scheme on September 29, 2021, on the occasion of 17th foundation day celebrations of “National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)”.
- Foundation Day of NDMA was celebrated under the theme- ‘Stopping Impact of Disaster Incidents in the Himalayan Region’.
About Aapda Mitra Scheme:
- NDMA has been implementing a central sector scheme namely Aapda Mitra since May 2016 with a focus on training of 6000 community volunteers (200 volunteers per district).
- The scheme aims to provide the community volunteers with the skills that they would need to respond to their community’s immediate needs in the aftermath of a disaster thereby enabling them to undertake basic relief and rescue tasks during emergency situations such as floods, flash-floods and urban flooding.
The objectives of the scheme:
- Development and Standardization of training modules at National Level;
- Development of Information Knowledge Management System at National level linked to States/UTs;
- Training institutions to be empanelled by respective States/UTs at the State/UT level;
- To train 6000 community volunteers in life saving skills of disaster response (flood relief and rescue), coordination, assistance, and provide personal protective equipment and emergency responder kits;
- To create a Community Emergency Stockpile/Reserve at the district/block level containing essential light search and rescue equipment, medical first aid kits, etc;
- To disseminate training and education tools developed under the project to more number of flood prone districts in subsequent phases of the scheme.
Disaster Related Initiatives:
- National Disaster Response Fund.
- Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030.
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR).
National Disaster Management Authority
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), is the apex statutory body for Disaster Management in India.
- It was constituted on 27th September 2006, under the Disaster Management Act, 2005.
- It is headed by the Prime Minister of India.
- NDMA, as the apex body, is mandated to lay down the policies, plans and guidelines for Disaster Management to ensure timely and effective response to disasters. Towards this, it has the following responsibilities:
- Lay down policies on disaster management;
- Approves the National Plan;
- Approve plans prepared by the Ministries or Departments of the Government of India in accordance with the National Plan
- Lay down guidelines to be followed by the State Authorities in drawing up the State Plan;
- Lay down guidelines to be followed by the different Ministries or Departments of the Government of India for the purpose of integrating the measures for prevention of disaster or the mitigation of its effects in their development plans and projects;
- Coordinate the enforcement and implementation of the policy and plans for disaster management
- Recommend provision of funds for the purpose of mitigation;
- Provide such support to other countries affected by major disasters as may be determined by the Central Government;
- Take such other measures for the prevention of disaster, or the mitigation, or preparedness and capacity building for dealing with threatening disaster situations or disasters as it may consider necessary;
- Lay down broad policies and guidelines for the functioning of the National Institute of Disaster Management.
5) Landsat 09
#GS3 #Issues related to space #Developments & their Applications & Effects in Everyday Life
Context: Recently, NASA has launched an earth monitoring satellite called Landsat 9 from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on an Atlas V 401 launch vehicle.
- The satellite is a joint mission of NASA and the US Geological Survey (USGS).
- NASA is in charge of building, launching, and testing the satellite, while the United States Geological Survey (USGS) operates the satellite, and manages and distributes the data archive
- This satellite is referred to as NASA’s’ new eye in the sky’ that will help study climate change.
Landsat Program:
- It will be the ninth satellite in the Landsat program stretching back almost 50 years.
- The first Landsat satellite was launched in 1972 and since then, Landsat satellites have collected images of earth and helped understand how land usage has changed over the decades.
- In 2008, it was decided that all Landsat images will be free and publicly available and the policy has helped scores of researchers, farmers, policy analysts, glaciologists, and seismologists.
- Landsat images have proved invaluable to the International Charter: Space and Major Disasters, supporting emergency response and disaster relief to save lives.
- With the addition of Landsat 9, the Landsat program’s record of land imaging will be extended to over half a century.
Significance:
- Remote sensing provides information about geographic spaces, like ecosystems that allows scientists to predict the distribution of species, as well as detecting both natural occurring and anthropogenic generated changes in a greater scale than traditional data provided by field work.
- It also presents data more accurately than models that are derived from field work.
- The different bands in Landsat, with diverse spectral range provide highly differentiated applications.
- There are big and diverse applications of Landsat imagery and satellite date in general, ranging from ecology to geopolitical matters.
- Land cover determination has become a very common use of Landsat imagery and remotely sensing generated images all around the world.
About Landsat 9:
- To reduce the build time and a risk of a gap in observations, Landsat 9 largely replicates its predecessor Landsat 8.
- Landsat 9 will extend our ability to measure changes on the global land surface at a scale where we can separate human and natural causes of change. When land use and resource availability issues arise, Landsat 9 will help decision makers make informed management decisions.
- The Landsat 9 joins Landsat 8 that was launched in 2013 and the satellites together will collect images of Earth’s surface.
- The instruments aboard Landsat 9 are the Operational Land Imager 2 (OLI-2) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2).
- OLI-2:The OLI–2 will capture observations of the Earth’s surface in visible,near-infrared, and shortwave-infra red bands with an improved radio- metric precision slightly improving overall signal to noise ratio.
- TIRS-2:It will measure the thermal infrared radiation, or heat, of the Earth’s surface with two bands that have improved performance over Landsat 8’s thermal bands.
- Both OLI–2 and TIRS–2 have a 5-year mission design life, although the spacecraft has 10+ years of consumables.
Landsat 9 will enable informed decision support for key areas such as:
- Tropical deforestation and global forest dynamics: the Landsat archive provides an impartial and unbiased record of Earth’s forests for world governments and resource organizations to verify claims of environmental protection and carbon storage.
- Urban expansion: the Landsat record helps us visualize the impact of humankind’s convergence on urban centres and to understand the environmental consequences.
- Water use: Landsat 9 will be an invaluable tool for managing water in areas such as the Western U.S. where water is scarce and water usage between agriculture, industry, and residential needs is very competitive.
- Coral reef degradation: Landsat has helped enable global monitoring of Earth’s reefs.
- Glacier and ice-shelf retreat: the Landsat archive chronicles changes to 98 percent of Earth’s glaciers, and Landsat 9 will continue monitoring them into the future.
- Natural and man-made disasters: Landsat data are regularly used as part of the International Disaster Charter, mapping disaster impacts to save lives.
- Climate change: Landsat data provide a direct view of how almost five decades of climate change have affected Earth’s surface and biology.
Daily Current Affairs 30th September -2021
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube

