CURRENT AFFAIRS 03-11-2021
Topics
- Bhasha Sangam Initiative
- The River Festival- Ganga Utsav 2021
- India targets net-zero carbon emissions by 2070
- Mandakini River
- World Bank Loan for Strengthening Health System: Meghalaya
1. Bhasha Sangam Initiative
#GS2-Education, Issues Related to Children Growth & Development, Government Policies & Interventions
Context
- To mark Rashtriya Ekta Diwas, the Ministry of Education has launched numerous programmes under Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat (EBSB).
- The Prime Minister launched the Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat in 2015 on the occasion of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel’s 140th birthday.
- The Rashtriya Ekta Diwas commemorates Shri Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel’s birth anniversary.
In-depth Information on the Initiatives:
What is the Bhasha Sangam School Initiative?
- The Ministry of Education’s Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat project includes Bhasha Sangam.
- The goal is to teach school kids fundamental sentences in 22 Indian languages.
- The importance of this is that it will assist pupils in learning fundamental conversational skills in an Indian language different than their mother tongue.
What is the Bhasha Sangam App?
- It is a cooperation between the Department of Higher Education (DoHE) and MyGov.
- The app comes with 100 daily words in 22 Indian languages at first. These sentences are available in both Roman and the chosen language’s script, as well as in audio format.
- Quiz App Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat
- It’s a quiz game aimed at kids and teens to help them learn more about our various regions, states, cultures, national heroes, monuments, traditions, tourism destinations, and languages,geography, history, and topography are all topics covered in this course.
Shreshtha Bharat: Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat:
- It was established in 2015 to promote participation among the people of various States/UTs in order to improve mutual understanding and bonding amongst people of various cultures, hence ensuring India’s unity and integrity.
- It is the Ministry of Education’s initiative.
- Every state and territory in the country would be paired with another for a set length of time, during which they would engage in structured exchanges in areas such as language, literature, cuisine, festivals, cultural events, tourism, and so on.
2.The River Festival- Ganga Utsav 2021
#GS1-Physical Geography,Water Resources,
#GS2-Government Policies & Interventions,
#GS3-Environmental Pollution &DegradationConservation
Context
- The 5th edition of Ganga Utsav-The River Festival 2021, which honours the glory of the national river Ganga, has just begun.
- On November 4, 2008, the Ganga was designated as India’s National River.
- The event will also include the introduction of the Ganga Tarang Portal, as well as a curtain raiser for the Ganga Knowledge Portal.
In depth information
- Every year on November 4th, the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) holds a Ganga Utsav to commemorate the proclamation of River Ganga as the “National River.” This year’s Ganga Utsav will take place from November 1 to 3, 2021.
- The Union Minister for Jal Shakti, is in charge of organising the 2021 event.Union Minister for Jal Shakti, was present on the first day of the event. The “Ganga Utsav 2021 – The River Festival” will not only honour the glory of the Ganga, but also all of the country’s rivers, in order to promote the observance of “Nadi Utsav” (River Festival).
- The National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) set a Guinness World Record for the maximum number of images of handwritten notes shared on Facebook in an hour on the first day of the event.
Ganga Action Plan:
- Government Initiatives on the River Ganga It was the first river action plan to improve water quality through sewage interception, diversion, and treatment.
- The National River Conservation Plan is a follow-up to this plan, and it attempts to clean up the Ganga river as part of Ganga Action Plan phase 2.
- National Ganga Basin Authority (NRGBA): It was established in 2009 under Section 3 of the 1986 Environmental Protection Act.
- The Clean Ganga Fund was established in 2014 with the goal of cleaning up the Ganga, establishing sewage treatment plants, and preserving the river’s biotic diversity.
- Web App for Bhuvan-Ganga: It guarantees that the public is involved in the monitoring of pollution entering the Ganga.
- Rubbish Discharge is Prohibited: In 2017, the National Green Tribunal (NGT) issued an order prohibiting the disposal of any waste in the Ganga.
3.India targets net-zero carbon emissions by 2070
#GS3- Environmental Pollution & Degradation
Context
- Glashow held the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP 26).
- India has committed to achieving net-zero emissions by the year 2070.
In details
Why was it necessary to take this step?
- According to scientists, achieving net-zero by 2050 is the best chance the world has of keeping temperatures below 1.5 degrees Celsius over pre-industrial levels.
- India is the third-largest annual emitter of carbon emissions, but the sixth-largest when historical emissions are taken into account, and it is one of the lowest per capita emitters when population size is taken into consideration.
- India had not committed to a date by which it would reach net-zero emissions, or to a year by which it would ensure that its net carbon dioxide emissions were zero.
- By 2070, India will have achieved net-zero carbon emissions.
- In contrast, India had resisted calls from wealthier countries to adopt net-zero targets in the run-up to the COP.
India’s 5 Commitments

What countries have declared net-zero goals?
- New Zealand’s government approved the Zero Carbon Act in 2019, committing the country to a carbon-free future by 2050.
- The UK parliament enacted laws mandating the government to cut the country’s net greenhouse gas emissions by 100%.
- President Joe Biden of the United States promised that by 2030, the country’s greenhouse gas emissions will be reduced by at least 50% from 2005 levels.
- World War Zero was begun in 2019 with the purpose of bringing together unusual allies on climate change and achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050 in the country.
- The European Commission’s “Fit for 55” initiative asks all of the EU’s 27 member countries to reduce emissions by 55% below 1990 levels by 2030.
- China stated that it would achieve net-zero emissions by 2060 and that it would not allow emissions to exceed those of 2030.
The COP26
- The Conference of Parties (COP) is part of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), which was established in 1994.
- The 26th Conference of Parties (known as COP26) will be held in Glasgow’s Scottish Event Campus in 2021.
- The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was founded to aim toward “stabilisation of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.”
- The member states were given a set of tasks, which included:
- Developing climate change mitigation strategies
- Working together to prepare for the effects of climate change
- Promoting climate change education, training, and public awareness
- The seventh COP was held in New Delhi from October 23 to November 1, 2002.
- COP21, one of the most important conferences, was held in Paris, France, in 2015. Member countries agreed to collaborate to “keep global warming well below 2 degrees Celsius, ideally 1.5 degrees Celsius, in comparison to pre-industrial levels.”
4. Mandakini River
#GS1 -Geographical Features & their Location
Context
- Every day, the Mandakini River becomes more and more filthy.
In depth information
Mandakini River Information
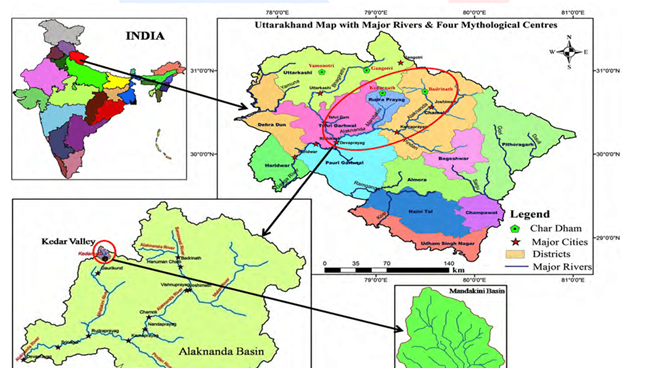
- In government records and on maps, the river is referred to as Paisuani.
- It begins in the hills of Khillora near Pindra village in the region of Majhagawan in Madhya Pradesh and proceeds 39 kilometres to the Sati Anusuiya Ashram location. This 35-kilometer stretch is a seasonal stream that only flows during the monsoon season.
- Sati Anusuiya is a perennial stretch of the Mandakini River that receives a considerable number of small and large springs.
- It empties into the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh’s Chitrakoot district’s Karwi tehsil.
Significance:
- The river is the lifeblood of Chitrakoot and its environs, with about 70% of Chitrakoot residents relying on it for drinking and household uses.
- Chitrakoot is well-known for its connection to the Hindu epic Ramayana. On full moon, new moon, and Diwali nights, hundreds of people flock to the town to bathe in the river.
Pollution in the Mandakini:
- In February 2020, the Union Ministry of Jal Shakti (Water Resources) produced a list of Madhya Pradesh’s 22 most polluted rivers. One of Madhya Pradesh’s most polluted rivers has been recognised as the Mandakini.
- Based on population trends, the current expected sewage generation in the river’s watershed is around 5 million litres per day (MLD).
- By 2030, sewage generation is predicted to reach 5.5 MLD.
- Food waste, plastic bags, and other trash were thrown directly into the river by several tourists.
Government Efforts:
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change approved a project for the abatement and conservation of the Mandakini River in Chitrakoot under the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP) (M.P.). The project was approved with the Central and State governments sharing 70 percent and 30 percent of the costs, respectively.
- The Government of Madhya Pradesh’s Public Health Engineering Department completed Phase 1 of the Chitrakoot town’s sewerage system.
5.World Bank Loan for Strengthening Health System: Meghalaya
#GS 2-Government Policies &Interventions,Important International Institutions
#GS3-Mobilization of Resources,Inclusive Growth
Context
- The World Bank and India recently signed a USD 40 million agreement for the Meghalaya Health Systems Strengthening Project.
In depth information
Focus areas of Meghalaya Health Systems Strengthening Project (MHSSP):
- Assist in expanding the design and coverage of Meghalaya’s health insurance program,
- Improving the quality of health services through certification and better human resource systems,
- Enabling efficient access to medicines and diagnostics to the poor and vulnerable in the state,
- Merge with PMJAY to cover 100 per cent of the households in Meghalaya,
- Invest in infection prevention and management of bio-medical waste (both solid and liquid waste).
Significance
- The Meghalaya Health Systems Project will aid in the improvement of the effectiveness of Meghalaya’s health insurance scheme, the Megha Health Insurance Scheme (MHIS). In Meghalaya, the MHIS currently covers 56 percent of households.
- With the merger of the Meghalaya Health Insurance Scheme (MHIS) with the national Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojna (PMJAY), the scheme now aspires to provide a more complete package and cover 100% of Meghalayan households. The combination will also aid in removing barriers to receiving hospital care for low-income families and avoiding costly out-of-pocket expenses.
- The MHSSP will also aid in the transition of the health-care sector to a performance-based financing system, with Internal Performance Agreements (IPAs) between the Department of Health and Family Welfare (DoHFW) and its subsidiaries fostering greater responsibility at all levels. This, in turn, is expected to improve the system’s management and delivery of high-quality health care.
- The MHSSP would also help to promote synergy among various schemes and expand the state insurance agency’s capacity.
Benefits
- Eleven districts in Meghalaya will benefit from the Meghalaya Health Systems Strengthening Project. It will improve the health sector at both the primary and secondary levels by improving clinical skills and planning and management capacities. The MHSSP will assist women and individuals living in rural regions in making greater use of community-based healthcare services.
- For a more resilient response to health emergencies, pandemics, and future outbreaks, the Project will also invest in infection prevention and control.
- It should be noted that increased healthcare services may result in an exponential increase in bio-medical waste, and that inappropriate disposal of bio-medical waste or other hazardous wastes poses environmental dangers.
- As a result, the Meghalaya Health Systems Strengthening Project would also invest in improving the broader ecosystem for bio-medical waste disposal management (both solid and liquid waste). This will encompass collection, segregation, and disinfection, all while enhancing health-care quality, patient safety, and environmental protection.

