Sarat Chandra IAS Academy brings to you the daily current affairs keeping in mind the changing pattern of the UPSC civil services exam. UPSC Prelims and Mains exams mix the current affairs with static core concepts. So, we give the background explanation for every current topic.
TOPICS OF THE DAY:
- G20: PM calls for a new global index in post-pandemic world
- FPI’s Inflow Surge
- The Copernicus Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite
- Exercise SITMEX-20
- Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System or IRNSS
1) G20: PM calls for a new global index in post-pandemic world:
Relevant to: GS 2- Global groupings involving India and affecting India’s interests
Context: 15th G20 Summit was virtually convened by Saudi Arabia, on 21-22 November, 2020.
Theme of 15th G20 Summit “Realizing Opportunities of 21st Century for All”.
India @ 15th G20 Summit Call for a New Global Index for the Post-Corona World India called for a new Global Index for the Post-Corona
World comprising of four key elements –
1) Creation of a vast Talent Pool
- For the past few decades, while there has been an emphasis on Capital and Finance, the time has come to focus on Multi-Skilling and Re-skilling to create a vast Human Talent Pool.
- This would not only enhance dignity of citizens but would make our citizens more resilient to face crises.
2) Technology reaches all segments of the society
- Any assessment of new technology should be based on its impact on Ease of Living and Quality of Life.
3) Transparency in systems of governance
- Greater Transparency in governance systems which will inspire our citizens to deal with shared challenges and enhance their confidence.
4) Dealing with Mother Earth with a spirit of Trusteeship
- Dealing with environment and nature as trustees rather than owners to inspire us towards a Holistic and Healthy Life Style, a principle whose benchmark could be a Per Capita Carbon Footprint.
India’s suggestion for creation of a G20 Virtual Secretariat:
- Noting that ‘Work from Anywhere’ is a new normal in the post-COVID world, India also suggested creation of a G20 Virtual Secretariat as a follow up and documentation repository.
What is the G20?
- The Group of Twenty, or the G20, is the premier forum for international economic co operation.
- The G20 brings together the leaders of both developed and developing countries from every continent.
- Collectively, G20 members represent around 80% of the world’s economic output, two- thirds of global population and three-quarters of international trade.
- Throughout the year, representatives from G20 countries gather to discuss financial and socioeconomic issues.
History of the G20
- Originated in 1999 at the level of Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors, the G20 gathered for high-level discussions on macro-financial issues.
- In the wake of the 2008 global financial crisis, the G20 was elevated to include the leaders of member countries.
- The first G20 Leaders’ Summit took place in Washington D.C. in November 2008.
- Consequently, the G20 agenda expanded beyond macro-financial issues, to include socio-economic and development issues.
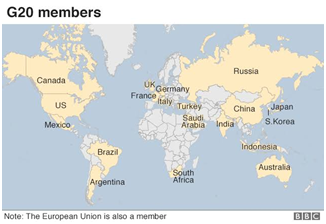
G20 Participants:
- The G20 members are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, South Korea, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union (EU).
- In addition to the G20 members, other countries are invited to participate.
- Spain is a permanent guest invitee to the G20 meetings.

2) FPI’s Inflow Surge Despite India Being Hardest Hit Due to Covid-19:
Relevant to : GS3- Effects of Liberalization, Inclusive Growth
Context : FPI inflows in India have been highest ever, over Rs 1.4 lakh crore in eight months. Foreign Portfolio Investors
Definition: When an international investor, invests in the passive holdings of an enterprise of another country, i.e., investment in the financial asset, it is known as FPI.
Purpose: Getting short term financial gain and not for obtaining significant control over managerial operations of the enterprise.
Passive Holdings: The investment is made in the securities of the company, i.e., stock, bonds, etc.
Foreign portfolio investors include both foreign individuals and foreign institutional investors (FIIs).
Benefits
- Portfolio diversification
- International credit
- Access to bigger market
- Benefit from exchange rate
- Easy to withdraw
Disadvantages:
- They do not have direct control over the assets or the businesses.
- Very volatile i.e., can be pulled out very quickly.
- Can lead to crises if relied too much upon e.g., East Asian Crises of 1990’s.
- Do not bring technologies with them unlike FDI.
- May or may not create jobs.
Reasons for FPI Inflows Picking Up:
- Unlock in Phases: Inflows started picking up in August with more liberal unlock guidelines, and a faster and wider reopening of the economy.
- US Elections: Outcome of US Presidential elections fueled FPI inflows into emerging markets and led to a sharp rally in equity markets worldwide, including India.
- Vaccine Development: Covid-19 vaccine by Pfizer and BioNTech, Moderna and Russia,
- provided comfort and buoyed market sentiments over the last 10 days
Domestic Investors Staying Cautious:
- Waiting Out the Storm: Domestic institutional investors (DIIs) pulled out a net Rs 32,649 crore in November alone.
- Total outflow by DIIs over the last four months between August and November till date amounts to Rs 60,903 crore.
3) The Copernicus Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite:
Relevant to: Prelims GS
Sentinel-6 Satellite
- This is a part of the next mission dedicated to measuring changes in the global sea level.
- It has been named after Dr Michael Freilich, who was the Director of NASA’s Earth Science Division from 2006-2019 and passed away in August this year.
What is the mission?
- The mission, called the Jason Continuity of Service (Jason-CS) mission, is designed to measure the height of the ocean, which is a key component in understanding how the Earth’s climate is changing.
- The spacecraft consists of two satellites, the other, called Sentinel-6B, to be launched in 2025.
- It has been developed jointly by the European Space Agency (ESA), NASA, and France’s National Centre for Space Studies (CNES).
What will the satellite do?
- The satellite will ensure the continuity of sea-level observations into the fourth decade and will provide measurements of global sea-level rise.
- Since 1992, high-precision satellite altimeters have helped scientists understand how the ocean stores and distributes heat, water and carbon in the climate system.
- Essentially, the satellite will send pulses to the Earth’s surface and measure how long they take to return to it, which will help scientists measure the sea surface height.
- It will also measure water vapour along this path and find its position using GPS and ground-based lasers.

Significance of the mission:
- As per NASA, it is possible to observe the height of the oceans on a global scale and monitor critical changes in ocean currents and heat storage only from space.
- Data from satellites such as Sentinel-6 help scientists foresee the effects of the changing oceans on the climate.
- Further, in order to measure and track changes in the oceanic heat budget, scientists need to know the ocean currents and heat storage of the oceans, which can be determined from the height of the sea surface.
4) Exercise SITMEX-20:
Relevant to: Prelims GS
- The SITMEX series of exercises are conducted to enhance mutual inter-operability and imbibing best practices between IN, Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and Royal Thai Navy (RTN).
- The first edition of SITMEX, hosted by Indian Navy, was conducted off Port Blair in September 2019.
- The 2020 edition of the exercise is being hosted by RSN.
- The maritime drill witnessed a variety of exercises including naval manoeuvres, surface warfare exercises and weapon firings.
- Besides improving inter-operability, SITMEX series of exercise also aims to strengthen mutual confidence and develop common understanding and procedures towards enhancing the overall maritime security in the region
5) Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System or IRNSS:
Relevant to: GS3- Science and Technology, GS1- Geographical Application of Space
Context: India became the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system. IRNSS has been recognized by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as a part of the World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
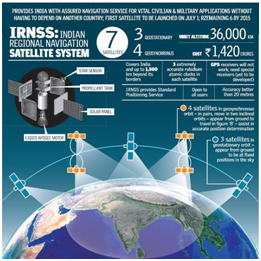
About Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System:
- IRNSS is an independent regional navigation satellite system developed by India.
- It is designed to provide accurate position information service to users in India as well as the region extending up to 1500 km from its boundary, which is its primary service are
- IRNSS will provide two types of services, namely, Standard Positioning Service (SPS) to all the users and Restricted Service (RS), provided only to the authorized users.
- The IRNSS System is expected to provide a position accuracy of better than 20 m in the primary service area.
Components of IRNSS:
- IRNSS Comprises of Space and Ground Segments.
- The space segment consists of seven satellites, with three in geostationary orbit and four in inclined geosynchronous orbit.
- IRNSS ground segment is responsible for navigation parameter generation and transmission, satellite control, ranging and integrity monitoring as well as time keeping.
Applications of IRNSS are:
- Terrestrial, Aerial and Marine Navigation-
-All merchant vessels including small fishing vessels are authorized to use the system.
-Vessels that have transponders will be tracked by satellite navigation showing accurate position in the Indian Ocean region. - Disaster Management. –
-Provide latest pictures of developing Cyclones and weather disturbances. - Vehicle Tracking and Fleet Management-
-Any given time, there are at least 2,500 merchant vessels in Indian waters that can all use the IRNSS. - Integration with Mobile Phones-
-Could replace GPS in offering location-based services. - Precise Timing.
- Mapping and Geodetic Data Capture.
- Terrestrial Navigation Aid for Hikers and Travelers.
- Visual and Voice Navigation for Drivers.
Meaning of International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) Recognition of the IRNSS:
- IMO – It is the United Nations’ specialized agency responsible for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine and atmospheric pollution by ships.
- Maritime Safety Committee: MSC of the IMO recognized the IRNSS as a component of the World-wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS).
- Importance of This Recognition: With the recognition as a component of the of the WWRNS, the Indian navigation system is similarly placed as GPS, or the Russian Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS).
- The Nation to Have Such A Service: After the US, Russia and China; India has become the fourth country to have its independent regional navigation system.
India needed an indigenously built navigational satellite as this will-
- Reduce Dependence on Foreign Satellites:
-An overdependence on one system (GPS) cannot be safe.
-Also, foreign constellations can’t be relied upon during war scenarios.
-There is also a threat of data theft and misuse. - Boon for The Military:
-In Kargil in 1999, one of the first things Indian military sought was the global positioning system (GPS) data for the region; but the US denied it to India.
-Help the Indian Navy track vessels in the IOR.
Sarat Chandra IAS Academy provides civil services coaching not only for graduates but also for students pursuing their graduation. You can visit our website, telegram channel, facebook account, instagram for regular current affairs, daily questions on UPSC prelims and Mains for practice. Also we provide test series for prelims and mains, both Online classes and Offline classes (Vijayawada)