Sarat Chandra IAS Academy brings to you the daily current affairs keeping in mind the changing pattern of the UPSC civil services exam. UPSC Prelims and Mains exams mix the current affairs with static core concepts. So, we give the background explanation for every current topic.
TOPICS OF THE DAY:
- Deep Ocean Mission
- Air pollution and its effects on Children
- Water sharing issue between India and China
- Global meet on criminal finances
- Learning Impacted
1) Deep Ocean Mission:
Relevant to: GS prelims
Context: India will soon launch an ambitious ‘Deep Ocean Mission’.
About the Mission:
- The mission proposes to explore the deep ocean similar to the space exploration started by ISRO about 35 years ago.
- The focus of the mission will be on deep-sea mining, ocean climate change advisory services, underwater vehicles and underwater robotics related technologies.
- Two key projects planned in the ‘Deep Ocean Mission’ report include a desalination plant powered by tidal energy and a submersible vehicle that can explore depths of at least 6,000 metres.
Significance:
- The mission will give a boost to efforts to explore India’s vast Exclusive Economic Zone and Continental Shelf.
- The plan will enable India to develop capabilities to exploit resources in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB).
Potential:
- India has been allotted 75,000 square kilometres in the Central Indian Ocean Basin (CIOB) by UN International Sea Bed Authority for exploration of poly-metallic nodules.
- CIOB reserves contain deposits of metals like iron, manganese, nickel and cobalt.
- It is envisaged that 10% of recovery of that large reserve can meet the energy requirement of India for the next 100 years.
What are PMN?
Polymetallic nodules (also known as manganese nodules) are potato-shaped, largely porous nodules found in abundance carpeting the sea floor of world oceans in deep sea.
Composition: Besides manganese and iron, they contain nickel, copper, cobalt, lead, molybdenum, cadmium, vanadium, titanium, of which nickel, cobalt and copper are considered to be of economic and strategic importance.
2) Air pollution and its effects on Children:
Relevant to: Prelims GS # Mains GS 2 and 3
Context: Recently, a two- year-long study, conducted in Delhi to find out the effect of air pollution on children, has been published collectively by researchers of AIIMS and CSIR -Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology.
Findings of Study:
- Spike in Air Pollution levels corresponded to an increase of 21-28% acute respiratory infections in children ranged from 5 months to 3 years.
Responsible Pollutants:
- The pollutants most strongly linked with more respiratory infections are Sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Paradoxically, the pollutants most strongly associated with air pollution PM 10 and PM 2.5 showed a weak links with an increase in infections.
- Nitrogen oxides and Sulphur dioxide emission associated with vehicular and industrial pollution are also associated with increase in infections, noted by a previous study.
Why Are Children More Susceptible?
- Immature growth of lungs, making them vulnerable to inflammatory and oxidative damage.
- Higher respiratory rates and outdoor physical activity, children retain more air pollutants per unit body weight than adults
Air Pollution in India:
- The WHO report (2019) said that 14 of world’s 15 most polluted cities were in India which includes Delhi, Kanpur and Varanasi.

Reasons of Air Pollution in India:
- High dependence on coal for power: share of coal in power generation in India continue to be around 80%.
Poor governance:
- The issue of environment and pollution is still to get the policy priority it deserves.
- Agencies like CPCB and SPCBs which ensure compliance to air pollution (control and mitigation) law continues to be under-resourced and under-staffed.
- Unplanned urbanization: haphazard growth of urban areas has led to proliferation of slums and poor public transport has increased the burden of personal vehicles on the road.
- Access to technology: India’s industrial landscape continues to be dominated by MSMEs which lack access to cleaner technologies.
- Continentality of Northern India: problem of pollution in the landlocked northern states gets exacerbated due to unfavorable winds and phenomenon of temperature inversion during winters.
Reasons for Air Pollution In Delhi And NCR Regions
Stubble Burning:
- Stubble burning in Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana is blamed for causing a thick blanket of smog in Delhi during winters.
- It emits large amounts of toxic pollutants in the atmosphere which contain harmful gases like Methane (CH4), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Volatile organic compounds (VOC) and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Vehicular Emissions:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and the National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) have declared vehicular emission as a major contributor to Delhi’s increasing air pollution.
- Vehicles contribute 40% of the total pollution load in the city.
Topography:
- Delhi lies in landlocked Indo-Gangetic region which does not have a geographical advantage that eastern, western or southern parts of the country enjoy.
- There is no sea breeze to disperse the concentrated pollutants.
- Fire Crackers: It may not be the top reason for air pollution, but it definitely contributed to its build up.
Government Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards and sector-specific emission and effluent standards for industries have been set up.
- Setting up of monitoring network for assessment of ambient air quality; Introduction of cleaner gaseous fuels like CNG, LPG etc and ethanol blending;
- Launching of National Air Quality Index (AQI) for air quality monitoring.
- Leapfrogging from BS-IV to BS-VI standards for vehicles by 1st April 2020;
- Promotion of public transport network;
- Issuance of directions under Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981;
- Regulating the bursting of pollution-emitting crackers;
- Notification of Graded Response Action Plan for Delhi identifying source wise actions for various levels of air pollution, etc.
Suggested Solutions
Curbing Stubble Burning by The most efficient technology to counter crop burning at the moment is Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) which is a machine mounted on a tractor that not only cuts and uproots the stubble, but can also drill wheat seeds in the soil that have just been cleared up. The straw is simultaneously thrown over the sown seeds to form a mulch cover.
- Establish Farm Machinery Banks for custom hiring of in-situ crop residue management machinery.
- Financial Assistance to the farmers for Procurement of Agriculture Machinery and Equipment.
- Public Transport: The push for public transport has long been highlighted as a potential solution.
- Robust Municipal Planning: Open burning of municipal solid waste and industrial waste is fouling up the air.
Air Quality Index (AQI)
- The AQI is an index for reporting daily air quality.
- It focuses on health effects one might experience within a few hours or days after breathing polluted air.
AQI is calculated for eight major air pollutants:
- Ground-level ozone, PM10, PM2.5, Carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide, Nitrogen dioxide, Ammonia, Lead, Ground-level ozone and airborne particles are the two pollutants that pose the greatest threat to human health in India
3) Water sharing issue between India and China:
Relevant to: Mains GS 2 and 3
Context: With India-China relations hitting its lowest point since the 1962 war, border infrastructure has come under intense scrutiny.
The construction of several dams along the Yarlung (Brahmaputra) river on the Chinese side has been a repeated cause for concern for Indian officials and the local people, whose livelihoods and security depend on the river.
Peculiar characteristics of Brahmaputra River that is cause of concern
- Two Floods: Inhabitants along the river have to deal with two floods annually, one caused by the melting of the Himalayan snow in summer and the other due to the monsoon flows
- Dangers of Climate Change: The frequency of these floods have increased and are devastating due to climate change and its impact on high and low flows.
- Dynamic in nature: The river is in itself dynamic as frequent landslides and geological activity force it to change course very often.
Water Issues of China
- Resource Constraints: China, which is home to close to 20 per cent of the world’s population, has only 7 per cent of its water resources.
- Consequence of Industrialization: Severe pollution of its surface and groundwater caused by rapid industrialisation is a source of concern for Chinese planners.
- Regional Imbalance within China: China’s southern regions are water-rich in comparison to the water-stressed northern part. The southern region is a major food producer and has significant industrial capacity as a consequence of more people living there.
- River interlinking Plans: China has an ambitious plan to link its south(water rich) and north(water stressed) through canals, aqueducts and linking of major rivers to ensure water security
- International Ramifications: In pursuit of above goals, China, being an upper riparian state in Asia, has been blocking rivers like the Mekong and its tributaries, affecting Southeast Asian countries like Thailand, Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia. It has caused immense damage to the environment and altered river flows in the region
- Geopolitical Tool: Such projects by China has the potential to significantly change the flow rate during times of standoffs and high tensions. In fact, during the 2018 Doklam border standoff between India and China, China stopped communication of water flow levels from its dams, effectively rendering India blind to floods during the standoff.
- Hegemonic Attitude: China sees such projects as a continuation of their historic tributary system as the smaller states have no means of effectively resisting or even significant leverage in negotiations. Chinese projects in the Himalayas have only recently begun to operate amid protests from India.
There are now multiple operational dams in the Yarlung Tsangpo basin with more dams commissioned and under construction. These constructions present a unique challenge for Indian planners because
- It will lead to degradation of the entire basin
• Massive amounts of silt carried by the river would get blocked by dams leading to a fall in the quality of soil and eventual reduction in agricultural productivity. - Impact on Ecological Diversity
• The Brahmaputra basin is one of the world’s most ecologically sensitive zones. It is identified as one of the world’s 34 biological hotspots.
• This region sees several species of flora and fauna that are endemic to only this part of the world — the Kaziranga National Park houses 35 mammalian species out of which 15 are listed as threatened in the IUCN conservation list.
• The river itself is home to the Gangetic river dolphin, which is listed as critically endangered
• Reduction in flow of waters downstream will have negative consequences of the flora and fauna of the surrounding ecosystem - Prone to Disasters
• The location of the dams in the Himalayas poses a risk. Seismologists consider the Himalayas as most vulnerable to earthquakes and seismic activity.
• Landslides resulting from earthquakes pose a significant threat — the 2015 Nepal earthquake and the resultant landslides wiped out several dams and other facilities.
• The sheer size of the infrastructure projects undertaken by China increases the vulnerability of the region to earthquakes and landslides - Lives & Livelihoods are in danger
• Close to a million people live in the Brahmaputra basin in India and tens of millions further downstream in Bangladesh.
• The projects in the Himalayas threaten the existence of hundreds of thousands of people.
Way Ahead: There are alternate solutions to solving the water crisis.
- Both sides must cease new constructions on the river and commit to potentially less destructive solutions.
- Building a decentralized network of check dams, rain-capturing lakes and using traditional means of water capture have shown effective results in restoring the ecological balance while supporting the populations of the regions in a sustainable manner.
- It is in the interest of all stakeholders to neutralize this ticking water bomb.
4) Global meet on criminal finances:
Relevant to: GS3: Internal Security, Topic: Organised
Context: Representatives from 132 countries attended the virtual 4th Global Conference on Criminal Finances and Cryptocurrencies organized y the Interpol, Europol, and the Basel Institute on Governance.
Objective of the conference:
- There has been an increase in the number and quality of investigations in the field of cryptocurrency-facilitated crime and subsequent money laundering.
- Therefore, the law enforcement and other public entities are continuing to enhance their level of knowledge and expertise in this crime area.
- In this regard, the conference served as an opportunity to underline the need for countries and jurisdictions to increase the exchange of tactical information and best practices, so that lessons learned by one entity can be useful to others.
What is Virtual Currency?
- As of now, there is no globally accepted definition of what exactly is virtual currency.
- Generally, it is known as a digitally tradable form of value, which can be used as a medium of exchange.
- Cryptocurrency is a specific type of virtual currency, which is decentralized and protected by cryptographic encryption techniques. (Ex: Bitcoins, Ethereum, Ripple, Petro, Alber etc…)
- In 2018, RBI prohibited banks and entities regulated by it from providing services related to virtual currencies.
Why did RBI ban Cryptocurrency?
- Excessive volatility in their value and their anonymous nature goes against global money laundering rules
- Chances of infringing data security and consumer protection
Supreme Court Judgement on Virtual Currencies:
- The Supreme Court clarified that RBI had the authority to regulate virtual currencies.
- It said that even though virtual currencies are generally not recognized as legal tender, they are capable of performing almost all the functions of money.
- It removed the ban by the RBIon banks and financial institutions from dealing with virtual currency holders and exchanges.
Why? The ban did not pass the five-point:
“proportionality” test.
What are those 5 points?
- Direct and immediate impact on fundamental rights
- The larger public interest sought to be ensured
- Necessity to restrict citizens’ freedom
- Inherent harmful nature of the act prohibited or its capacity to be harmful to the general public
- The possibility of achieving the same object by imposing a less drastic restraint.
So, Is it legal in India now? Yes
Why is it a matter of concern?
- Though virtual currency investors and businesses welcomed the Supreme Court’s order on cryptocurrency, this relief is only temporary because the Centre, in a draft law, has proposed to ban all private cryptocurrencies.
- But, the blanket ban of anything can push the entire system underground, which means no regulation that might result in illegal and criminal activities.
- Now, India plans to introduce a new law banning trade in cryptocurrencies.
So, what is the better solution?
- We need to develop a risk-based framework to regulate and monitor cryptocurrencies.
- A calibrated framework that deals with the reality of these technological advancements is very much needed
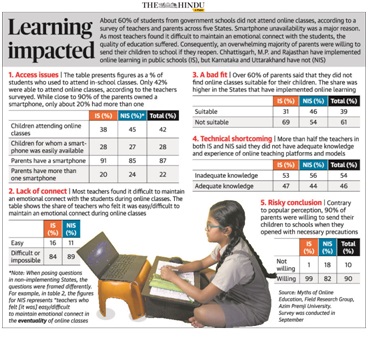
5) Learning Impacted:

Sarat Chandra IAS Academy provides civil services coaching not only for graduates but also for students pursuing their graduation. You can visit our website, telegram channel, facebook account, instagram for regular current affairs, daily questions on UPSC prelims and Mains for practice. Also we provide test series for prelims and mains, both Online classes and Offline classes (Vijayawada)