Sarat Chandra IAS Academy brings to you the daily current affairs keeping in mind the changing pattern of the UPSC civil services exam. UPSC Prelims and Mains exams mix the current affairs with static core concepts. So, we give the background explanation for every current topic.
TOPICS OF THE DAY:
- POSHAN ABHIYAN
- NEGATIVE BOND YIELD (NBY)
- LARGE CORPORATES IN BANKING
- DESALINATION PLANTS AND THEIR FEASIBILITY
- SAHAKAR PRAGYA
1) POSHAN ABHIYAN:
Relevant to: Prelims GS # Mains GS 2
Context: NITI Aayog has released a review report on Poshan Abhiyaan.
Suggestions made:
The programme must be stepped up to meet the targets set by the Centre to reduce stunting, wasting and anemia by 2022.
Graduate to a POSHAN-plus strategy which apart from continued strengthening the four pillars of the Abhiyaan also requires renewed focus on other social determinants in addition to addressing the governance challenges of NHM/ICDS delivery mechanisms.
Lay as much emphasis on complementary feeding as it does on breastfeeding. This can help avert 60% of the total stunting cases in India.
About Poshan Abhiyaan:
The programme seeks to improve nutritional outcomes for children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
Launched in 2018 with specific targets to be achieved by 2022
It aims to reduce:
- Stunting and wasting by 2% a year (total 6% until 2022) among children.
- Anemia by 3% a year (total 9%) among children, adolescent girls and pregnant women and lactating mothers.
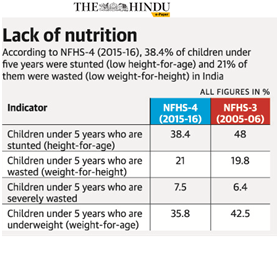
- The target of the mission is to bring down stunting among children in the age group 0-6 years from 38.4% to 25% by 2022.
Background:
More than a third of the children under five face stunting and wasting and 40% aged between one and four are anaemic. Over 50% of pregnant and other women were found to be anaemic, said the National Family Health Survey 4 released in 2016.
2) Negative bond yield (NBY):
Relevant to: Prelims GS # Mains: GS2
Context: Last week, China sold negative-yield debt for the first time.5-year bond was priced with a yield of –0.152%, and the 10-year and 15-year securities with positive yields of 0.318% and 0.664%.
What are NBY?
These are debt instruments that offer to pay the investor a maturity amount lower than the purchase price of the bond. Can be issued by central banks or governments Here, investors pay interest to the borrower to keep their money with them.
Then, why do Investors buy such bonds?
Such instruments are usually in demand during times of stress and uncertainty. This is to protect their capital from significant erosion.
From currency fluctuations to deflation, there are scenarios in which purchasers of negative-yield bonds can come out ahead.
Relationship between Bond Price and Yield:
A bond’s price moves inversely with its yield or interest rate; the higher the price of a bond, the lower the yield. The reason for the inverse relationship between price and yield is due, in part, to bonds being fixed-rate investments.
Investors might sell their bonds if it’s expected that interest rates will rise in the coming months and opt for the higher-rate bonds later on.
Conversely, bond investors might buy bonds, driving the prices higher, if they believe interest rates will fall in the future because existing fixed-rate bonds will have a higher rate or yield.
What is the key factor driving this demand today?
It is the massive amount of liquidity injected by the global central banks after the pandemic began that has driven up prices of various assets including equities, debt and commodities.
Many investors could also be temporarily parking money in negative-yielding government debt for the purpose of hedging their risk portfolio in equities.
In case the fresh wave of the Covid-19 pandemic leads to further lockdowns of economies, then there could be further negative pressure on interest rates, pushing yields down further, and leading to profits even for investors who put in money at the current juncture
3) LARGE CORPORATES IN BANKING:
Relevant to: Mains: GS 3
CONTEXT: A recent report by an Internal Working Group of the Reserve Bank of India has attracted a lot of attention as well as criticism. The IWG was constituted to “review extant ownership guidelines and corporate structure for Indian private sector banks”.
ABOUT THE RECOMMENDATION
The IWG submitted several recommendations, but one, in particular, has raised a lot of concern.
This had to do with allowing large corporate/industrial houses to be promoters of private banks.
WHY SHOULD LARGE CORPORATES BE ALLOWED IN BANKING?
- RBI’s working group feels that allowing corporates to promote banks can be an important source of capital. In a capital-starved economy like India, this makes sense.
- Further, these corporates can bring “management expertise, experience, and strategic direction to banking”.
- The group also noted that internationally, “there are very few jurisdictions which explicitly disallow large corporate houses”
- All these reasons make sense, but there are major drivers behind RBI not allowing corporate intrusion in the banking sector over the last five decades.
- At the heart of this is the conflict of interest it would create or more technically, “connected lending”.
WHAT IS CONNECTED LENDING?
Connected lending refers to a situation where the promoter of a bank is also a borrower and, as such, it is possible for a promoter to channel the depositors’ money into their own ventures.
WHAT ARE VIEWS OF ECONOMISTS?
Economists Raghuram Rajan and Viral Acharya have strongly criticised a recent proposal by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) panel to allow large corporate groups into the banking sector, calling it a “bombshell” move that could further exacerbate the concentration of economic
and political power in “certain business houses”.
WHY RECOMMEND IT?
- The Indian economy, especially the private sector, needs money (credit) to grow.
- Far from being able to extend credit, the government-owned banks are struggling to contain their non-performing assets.
- Government finances were already strained before the Covid crisis. With growth faltering, revenues have plummeted and the government has limited ability to push for growth through the public sector banks.
- Large corporates, with deep pockets, are the ones with the financial resources to fund India’s future growth.
- Of course, choosing this option is not without serious risks.
4) DESALINATION PLANTS AND THEIR FEASIBILITY:
Relevant to : Prelims GS # Mains: GS 3
Context: Worldwide, desalination is seen as one possible answer to stave off water crisis. Recently Maharashtra government announced the setting up of a desalination plant in Mumbai, becoming the fourth state in the country to experiment with the idea.
What is desalination?
A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink. The most commonly used technology used for the process is reverse osmosis where an external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a membrane.
The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side. These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.

How widely is this technology used in India?
- Desalination has largely been limited to affluent countries in the Middle East and has recently started making inroads in parts of the United States and Australia.
- In India, Tamil Nadu has been the pioneer in using this technology, setting up two desalination plants near Chennai in 2010 and then 2013.
- The two plants supply 100 million litres a day (MLD) each to Chennai. Two more plants are expected to be set up in Chennai.
- The other states that have proposed these plants are Gujarat, which has announced to set up a 100 MLD RO plant at the Jodiya coast in Jamnagar district.
What is the need to set up a desalination plant in Mumbai?
According to the BMC’s projection, the population of Mumbai is anticipated to touch 1.72 crore by 2041 and accordingly, the projected water demand would be 6424 MLD by then. • Currently, BMC supplies 3850 MLD as against the requirement of 4200 MLD each day.
Is it ecologically safe?
The high cost of setting up and running a desalination plant is one reason why the Maharashtra government has over the last decade been hesitant in building such a plant. • Desalination is an expensive way of generating drinking water as it requires a high amount of energy. The other problem is the disposal of the byproduct — highly concentrated brine — of the desalination process
5) Sahakar Pragya:
Relevant to: Prelims GS #Mains: GS 2 and 3
Context : Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Rural Development, Panchayat Raj and Food Processing Industries unveiled Sahakar Pragya.
Key points:
- It is the latest in the series of farmer focused steps by National Cooperative Development Corporation(NCDC).
- These 45 training modules of Sahakar Pragya is to be delivered at Lakshmanrao Inamdar National Cooperative Research and Development Academy (Linac).
- Training is done along with countrywide network of Regional Training Centres.
- It will address the need for training of Primary cooperatives, FPO-Cooperatives and Self Help Groups federating.
The training programmes will be supported under following NCDC schemes
- 10000 FPO formation scheme of Government of India
- Agri Infra Fund scheme of Government of India
- PM-FME scheme of Min of Food Processing Industry
- Dairy Infra Dev Fund scheme of Government of Indi
- Fisheries Infra Dev Fund scheme of Government of India
- PM MatsyaSampada Yojana of Government of India
- Min of Rural Dev schemes State/UT schemes Other organizations’ schemes.
Cooperative Sector in India
- Cooperative sector play a role in making the village-poor-farmers Atma Nirbhar.
- India boasts a huge network of over 8.50 lakh cooperative societies with about 290 million members.
- Around 94% of the farmers in India are member of at least one cooperative society.
- Cooperatives lends strength to farmers to minimise risks in agriculture and allied sectors.
- They also act as shield against exploitation by unscrupulous traders.
National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC)
Purpose Of NCDC –
- It has been created for the following purposes.
- Planning and promoting programmes for the production processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce foodstuffs industrial goods, livestock, certain other commodities and services like hospital, healthcare, education etc. on cooperative principles.
- It extends financial assistance to cooperatives at all the three tiers, Primary, District and Apex / Multi-State.
- It is Known for hand-holding cooperatives across the country with funding and project ideas.
- NCDC has been proactive in delivering innovative solutions for the cooperative sector.
- NCDC has emerged as a financial powerhouse giving the client cooperatives a wide range of products and services.
- So far it has advanced loans to the tunes of Rs 1.58 lakh crores to cooperative societies of various categories across the country
Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel
- In the series of initiatives by NCDC, it had earlier launched the Sahakar Cooptube NCDC Channel.
- It aims to involve youth in the cooperative movement.
- NCDC’s guidance videos is in different languages covering local requirements of 18 States.
- In this channel, NCDC strengthens the major initiative of Government of India to promote and form 10,000 FPOs.
Earlier launches By NCDC- Following are the earlier launched various initiatives and programmes by NCDC.
- SAHAKAR-22 – It is to develop cooperatives in Focus 222 districts. It includes aspirational districts, Nurturing Primary Level Cooperatives.
- SAHAKAR MITRA – It is a Scheme on Internship Programme.
- YUVA SAHAKAR. – It is a Start Up Scheme in Cooperatives
- AYUSHMAN SAHAKAR- It is for creation of healthcare infrastructure and services.
Sarat Chandra IAS Academy provides civil services coaching not only for graduates but also for students pursuing their graduation. You can visit our website, telegram channel, facebook account, instagram for regular current affairs, daily questions on UPSC prelims and Mains for practice. Also we provide test series for prelims and mains, both Online classes and Offline classes (Vijayawada)