UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 10th April 2022
Topics for the day:
- FY22 tax kitty up 34% at record ?1L crore
- Positive indigenisation list
- Indian tent turtle
- nod to supply fortified rice via PDS
- Sangeet Natak Awards for 2018, while the Lalit Kala Akademi’s Fellowship and National Awards for 2021
- Alternate Dispute redressal mechanism
FY22 tax kitty up 34% at record Rs.27.1L crore
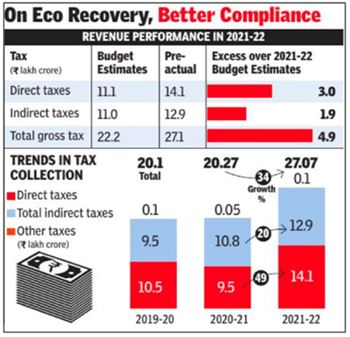
Context :
- The country’s gross tax receipts surged to a record high of Rs 27. 1 lakh crore for 2021-22.
- It is expected that the trend of recovery in the economy and tax revenues of the Government will continue to grow.
Key Highlights :
- Surge in gross tax receipts Against the Union Budget estimates of Rs 22.2 lakh crore, the revenue receipts according to the pre-actual figures totalled Rs 27.1 lakh crore.
- This is about Rs 5 lakh crore above the Budget estimate.
- This shows a growth of 34% over last year’s revenue collection of Rs 20.3 lakh crore. This growth was led by 49% surge in direct taxes and supported by 20% growth in indirect taxes.
- Highest tax-to-GDP ratio in 23 years
- 2021-22 marks the highest tax-GDP ratio of 11.7%, with direct tax-to-GDP ratio at 6.1% and indirect taxto-GDP ratio at 5.6%.
- Tax buoyancy
- The tax buoyancy is at a very healthy figure of 1.9, with 2.8 for direct taxes and 1.1 for indirect taxes.
- Tax buoyancy is a measure of growth in tax revenues as compared to GDP growth.
- The ratio of direct to indirect taxes recovered from 0.9 in 2020-21 back to 1.1 in 2021-22.
- Corporate taxes
- The gross corporate taxes during 2021-22 was ?6 lakh crore against ?6.5 lakh crore last year.
- This shows that the new simplified tax regime with low rates and no exemptions has lived upto its promise.
- GST has seen an exemplary growth
- On the indirect taxes, GST has seen an exemplary growth during 2021-22 despite two waves of COVID-19 pandemic.
- CGST revenues increased from ?6 lakh crore last year to ?5.9 lakh crore in 2021-22.
- Customs duty has witnessed a growth rate
- During 2021-22, Customs duty has witnessed a growth rate of 48%.
- During last two years, Government has undertaken comprehensive review and rationalization of the Customs tariff structure.
- It has rationalized various exemptions and simplified the tariff structure.
Factors behind this robust revenue performance :
- This growth was due to robust revenues from income, corporate taxes, customs and GST on the back of a strong economic recovery and rising compliance.
- This revenue growth has also been propelled by rapid economic recovery after successive waves of Covid.
- Use of technology is ensuring better compliance and better revenues. A lot of technology is being used where GST figures are now being matched with income tax figures and compliances are being ensured.
Positive Indigenisation list

Context :
- Recently, the Ministry of Defence has released the third positive indigenisation list of 101 items, comprising major equipment/platforms.
- The ‘First Negative Indigenisation’ List comprising 101 items was notified in August 2020.
- The Second Indigenisation list was notified in June 2021 import list for 108 items.
- The Third List includes Highly complex Systems, Sensors, Weapons and Ammunitions like Light Weight Tanks, Mounted Arty Gun Systems, Next Generation Offshore Patrol Vessels (NGOPV) etc.
What is the positive indigenisation list?
- Introduced in August 2020, the negative list essentially means that the Armed Forces – Army, Navy and Air Force will only procure such items from domestic manufacturers.
- The manufacturers could be private sector players or Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs).
Why was this policy needed?
- As per Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, India has been the second largest importer of weapons between 2014 and 2019 with US$ 16.75 billion worth of imports during this period.
- The government wants to reduce the dependence on imported items in defence and give a shot in the arm to the domestic defence manufacturing industry.
- By denying the possibility of importing the items on the negative list, the domestic industry is given the opportunity to step up and manufacture them for the needs of the forces.
Significance and implications of this move:
- Recognises the potential of the local defence industry.
- Invigorate impetus to domestic Research and Development by attracting fresh investment into technology and manufacturing capabilities.
- Provides an excellent opportunity for ‘start-ups’ as also Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
Indian tent turtle

Context :
- The Union Minister of Environment said in Parliament that there are no reports to indicate that the Indian tent turtle is on the verge of extinction due to illegal mining in the Narmada River.
More about the turtle :
- The Indian tent turtle is listed in Schedule I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 and is thereby provided the highest degree of protection.
- The males are smaller than the females in size and have longer and thicker tails.
- It is a species of turtle that is native to India, Nepal and Bangladesh and it is quite similar to the Indian roofed turtle.
- IUCN status : Lower Risk/ least concern.
Basic trivia of Narmada River
- Narmada is the largest west flowing river of the peninsular region flowing through a rift valley between the Vindhya Range on the north and the Satpura Range on the south.
- It rises from Maikala range near Amarkantak in Madhya Pradesh.
- It drains a large area in Madhya Pradesh besides some areas in the states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- The river near Jabalpur (Madhya Pradesh) forms the DhuanDhar Falls.
- There are several islands in the estuary of the Narmada of which Aliabet is the largest.
- Major Tributaries: Hiran, Orsang, the Barna and the Kolar.
- The major Hydro Power Projects in the basin are Indira Sagar, Sardar Sarovar etc.
Govt. nod to supply fortified rice via PDS

Context and the news :
- The government on Friday approved the distribution of fortified rice across government schemes such as the public distribution system, and nutrition services for school children and anganwadi beneficiaries.
- The entire cost of the scheme of ?2,700 crore will be borne by the Centre
- The Food Corporation of India and State agencies are engaged in procuring fortified rice and so far nearly 88.65 LMT [lakh metric tonnes] of fortified rice has been procured
The initiative will be implemented in three phases :
- In the first phase, anganwadi centres under Integrated Child Development Services and PM POSHAN (or erstwhile mid-day meals) will be covered.
- The second phase will cover targeted public distribution system and other welfare schemes in all 291 aspirational districts as well as districts with high burden of stunting by March 2023.
- In the final phase the remaining districts of the country will be covered by March 2024.
What is fortification of Rice ?
- Fortification is the addition of key vitamins and minerals such as iron, iodine, zinc, Vitamin A & D to staple foods such as rice, milk and salt to improve their nutritional content.
- These nutrients may or may not have been originally present in the food before processing.
- According to the Food Ministry, fortification of rice is a cost-effective and complementary strategy to increase vitamin and mineral content in diets.
What are the Initiatives related to Fortification?
- FSSAI Regulations: In 2016, FSSAI operationalized the Food Safety and Standards (Fortification of Foods) Regulations, 2016 for fortifying staples namely Wheat Flour and Rice (with Iron, Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid), Milk and Edible Oil (with Vitamins A and D) and Double Fortified Salt (with Iodine and Iron) to reduce the high burden of micronutrient malnutrition in India.
- Nutritional Strategy: India’s National Nutritional strategy, 2017, had listed food fortification as one of the interventions to address anemia, vitamin A and iodine deficiencies apart from supplementation and dietary diversification.
- Milk Fortification Project – The Milk Fortification Project was launched by the National Dairy Development Board (NDDB) in collaboration with the World Bank and Tata Trusts, as a pilot project in 2017.
Sangeet Natak Awards for 2018, and the Lalit Kala Akademi’s Fellowship and National Awards for 2021

Context :
- Forty-three artists were presented the Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship and Sangeet Natak Awards for 2018, while the Lalit Kala Akademi’s Fellowship and National Awards for 2021 were given to 23 by Vice-President at a joint ceremony.
More on the news :
- Sangeet natak awards :
- The Sangeet Natak Akademi Awards are national honours bestowed by the government on performing artists and teachers and scholars in the field of performing arts.
- The awards were given in the categories of music, dance, and theatre.
- In addition, one category was reserved for traditional, folk, and tribal dance, music, theatre and puppetry.
- In addition, tabla maestro Zakir Hussain, Sattriya dancer Jatin Goswami, Odissi exponent Sonal Mansingh and Thiruvidaimarudur Kuppiah Kalyanasundaram were given fellowships for their contribution to the field of dance.
- Among the 13 honoured for music are Hindustani vocalists Mani Prasad and Madhup Mudgal, santoor player Tarun Bhattacharya, Tejendra Narayan Majumdar for sarod, and Carnatic vocalists Alamelu Mani and Malladi Suribabu.
- Bharatanatyam dancer Radha Sridhar, Mohiniyattam dancer Gopika Varma, Kuchipudi dancer Ramalinga Sastry are among the 10 dancers who got the award.
- Among the eight theatre artistes who have been given the award are Suhas Joshi and Teekam Joshi for acting, Rajiv Naik and Laltluangliana Khiangte for playwriting, and Sanjay Upadhyay for direction.
-
Lalitkala akademi awards :
- Lalit Kala Akademi organises art exhibitions and award ceremonies every year to promote art as well as to honour talents.
- Their important exhibitions include the National Exhibition of Art, International Triennale India etc.
- Sculptor Himmat Shah, and painters Jyoti Bhatt and Shyam Sharma were awarded the prestigious Lalit Kala Akademi fellowship.
- More on the sangeet natak akademi :
- The Sangeet Natak Akademi is India’s national academy for music, dance and drama.
- It was created by a resolution of the (then) Ministry of Education, Government of India
- It is presently an Autonomous Body of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India and is fully funded by the Government for implementation of its schemes and programmes.
- They also collaborate with international organizations like UNESCO to save the cultural heritage of India.
- They are not only supposed to be the central agency to monitor the preservation of our cultural heritage but they need to collaborate with the State and Union territory governments to preserve and promote their culture on a national platform
- The Akademi establishes and looks after institutions and projects of national importance in the field of the performing arts.
- Few important ones are:
- National School of Drama
- Jawaharlal Nehru Manipur Dance Academy in Imphal
- Kathak Kendra (National Institute of Kathak Dance) in New Delhi
- National Projects of Support to Kutiyattam (Sanskrit theatre of Kerala), Chhau dances of eastern India, Sattriya traditions of Assam, etc.
- More on the lalit kala akademi :
- The Government of India established the National Academy of Art, also known as the Lalit Kala Akademi, in 1954 with the primary purpose of promoting fine arts in India.
- The academy is a self-governing organization supported by the Ministry of Culture which promotes the appreciation and knowledge of beautiful arts
- It is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Culture.
- The Lalit Kala Akademi, is the newest of the three Akademies formed by the Indian government and was founded to fulfill the desire of Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, India’s first Prime Minister, for a cultural and national identity.
- Although they deal with national and international art, their focus is on the promotion and preservation of Indian art.
- Their main centre is in Delhi and they have Regional Centres in Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Shimla, Shillong and Bhubaneswar.
- Other functions of the akademi :
- They also have the task to preserve the long tradition of visual arts in India.
- They have established centres to preserve and document a permanent collection, which focuses on the modern and contemporary art in India.
- They also publish and promote art-related literature, such as monographs, journals, and other publications.
High time for ADR mechanisms : CJI

Context :
- Chief Justice of India N.V. Ramana stressed the need for increasing the use of alternative dispute resolution (ADR) mechanisms that can change the judicial landscape, bringing justice to millions and settling grievances without protracted legal proceedings.
- Speaking on the signifcance of mediation as an ADR mechanism, Chief Justice urged that an “active effort must be taken by courts to make negotiations and mediation mandatory as part of case management.”
- The concept of ADR, through Lok Adalats, Gram Nyayalayas, mediation and arbitration centres, has the potential to transform the legal landscape of India by providing millions of people a platform to settle their grievances according to the CJI.
- Justice Ramana also spoke on ‘FASTER’, a digital platform recently launched by the Supreme Court for fast and secured delivery of urgent court orders in encrypted electronic format to the stakeholders, as well as live streaming of court proceedings.
Various ADR mechanisms available :
- Arbitration and Conciliation are modes of the Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism, in which disputes are settled without litigation.
- ADR mechanism facilitate parties to deal with the underlying issues in dispute in a more cost-effective manner and with increased efficacy.
- Arbitration:
- The dispute is submitted to an arbitral tribunal which makes a decision (an “award”) on the dispute that is mostly binding on the parties.
- It is less formal than a trial, and the rules of evidence are often relaxed.
- There’s no right to appeal on arbitral award usually
- Conciliation:
- A non-binding procedure in which an impartial third party, the conciliator, assists the parties to a dispute in reaching a mutually satisfactory agreed settlement of the dispute.
- Conciliation is a less formal form of arbitration.
- The parties are free to accept or reject the recommendations of the conciliator.
- Mediation:
- In mediation, an impartial person called a “mediator” helps the parties try to reach a mutually acceptable resolution of the dispute.
- The mediator does not decide the dispute but helps the parties communicate so they can try to settle the dispute themselves
More on Gram Nyayalayas Act :
- The Gram Nyayalayas Act, 2008 has been enacted to provide for the establishment of the Gram Nyayalayas at the grass roots level for the purposes of providing access to justice to the citizens at their doorsteps
- Features under the Act :
- The Gram Nyayalaya shall be court of Judicial Magistrate of the first class and its presiding officer (Nyayadhikari) shall be appointed by the State Government in consultation with the High Court
- The Gram Nyayalaya shall be established for every Panchayat at intermediate level or a group of contiguous Panchayats at intermediate level
- The Nyayadhikaris who will preside over these Gram Nyayalayas are strictly judicial officers
- The Gram Nyayalaya shall be a mobile court and shall exercise the powers of both Criminal and Civil Courts.
- The Central as well as the State Governments have been given power to amend the First Schedule and the Second Schedule of the Act, as per their respective legislative competence
- The Gram Nyayalaya shall try to settle the disputes as far as possible by bringing about conciliation between the parties and for this purpose
- Gram Nyayalaya shall not be bound by the rules of evidence provided in the Indian Evidence Act, 1872 but shall be guided by the principles of natural justice
- Appeal in criminal cases shall lie to the Court of Session, which shall be heard and disposed of within a period of six months from the date of filing of such appeal. Appeal in civil cases shall lie to the District Court, which shall be heard and disposed of within a period of six months from the date of filing of the appeal.
- A person accused of an offence may file an application for plea bargaining.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 10th April 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

