UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 12th & 13th March 2022
Topics for the day:
- One nation one election
- Textile ministry receives PLI applications from 67 firms
- Most favoured nation (MFN) status
- Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility
- International Arbitration and Mediation Centre
- Employees Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) interest rate
- 5th India-Canada Ministerial Dialogue on Trade & Investment
- Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry scheme
- Rashtriya Raksha University
One Nation one election

Context :
- Chief Election Commissioner Sushil Chandra has said that the Election Commission is ready to hold simultaneous elections or ‘One Nation, One Election’.
- Earlier on National Voters’ Day, Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his address had raised the topics of ‘One Nation, One Election’ and ‘One Nation, One Voters’ list’, and had said that the continuous cycle of election results is affecting development works.
Problems due to frequent elections :
- Massive expenditure due to conduct of multiple elections.
- Policy paralysis that results from the imposition of the Model Code of Conduct during election time.
- Impact on delivery of essential services.
- Burden on crucial manpower such as teachers,paramilitary forces etc. that is deployed during election time.
- Puts pressure on political parties, especially smaller ones, as elections are becoming increasingly expensive.
What are simultaneous elections ?
- The idea is about structuring the Indian election cycle in a manner so that elections to the Lok Sabha and the State Assemblies are synchronised together so that the election to both can be held within a given span of time.
Benefits of Simultaneous Elections:
- Governance and consistency: The ruling parties will be able to focus on legislation and governance rather than having to be in campaign mode forever.
- Reduced Expenditure of Money and Administration.
- Continuity in policies and programmes.
- Efficiency of Governance: Populist measures by governments will reduce.
- The impact of black money on the voters will be reduced as all elections are held at a time.
Challenges with simultaneous elections :
- It is almost impossible to achieve in practice as Assemblies might get dissolved at an untimely manner due to political realities. Earlier dissolution, which breaches the principle of simultaneous elections, is brought about by several methods like
- The PM or CM advises the president or the governor, as the case may be, to prematurely dissolve the Lok Sabha or state assembly and force snap elections to gain electoral advantage.
- By passing the no-confidence motion against a government or defeating the government’s confidence motion.
- Central government has misused its powers under Article 356 by imposing the president’s rule in states ruled by opposition parties and dissolving assemblies resulting in premature elections.
- According to Article 85 and Article 174, elections to Lok Sabha and Legislative assemblies have to be held within six months (respectively) of dissolving either of them. This is not feasible if elections are held only at fixed durations.
- If elections are not held within six months, it would be a travesty of democracy.
- Frequent elections bring the politicians back to the voters and enhance the answerability and accountability of politicians to the public.
- Will keep the politicians in touch with ‘pulse of the public’ and the result of elections at various levels can ensure the government the necessary ‘course correction’.
- May mix up issues of local and national issues in the minds of the voters, This may give a boost to regional and local issues, while national issues can take a set-back.
- The issue of logistics and requirement of security personnel, election and administrative officials as there is a dearth of enough officials to conduct simultaneous elections throughout the country in one go.
Textile ministry receives PLI applications from 67 firms
Context :
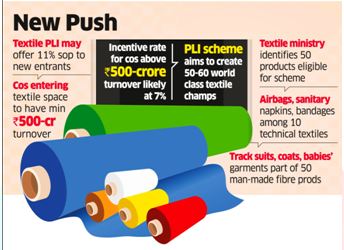
- The textile ministry has received applications from as many as 67 companies to avail benefits of the production linked incentive (PLI) scheme for man-made fibres and technical textile sectors
What is the PLI scheme ?
- The PLI scheme for textiles covers 40 man-made Fibre (MMF) garment items, 14 MMF fabric goods, and 10 technical textile products.
- The government had approved the PLI scheme, worth ?10,683 crore, for the sector with an aim to boost domestic manufacturing, create jobs and promote exports.
- The scheme aims to give companies incentives on incremental sales from products manufactured in domestic units
- Incentives will be given to eligible producers in two phases:
- First: Any person or company willing to invest a minimum of Rs 300 crore in plant, machinery, equipment and civil works (excluding land and administrative building cost) to produce products of MMF fabrics, garments and products of technical textiles will be eligible to participate.
- Second: Investors willing to spend a minimum of Rs 100 crore under the same conditions (as in the case of the first phase) shall be eligible to apply.
- The scheme aims to attract fresh investment of Rs 19,000 crore in the sector for production of in-demand textiles, and additional turnover of Rs 3 lakh crore over five years.
Most Favoured Nation :

Context :
- The United States, the European Union, Britain, Canada and Japan are planning to jointly revoke Russia’s “most favoured nation” (MFN) status over its invasion of Ukraine.
What is MFN status ?
- The World Trade Organization’s 164 members commit to treating other members equally so they can all benefit from each other’s lowest tariffs, highest import quotas and fewest trade barriers for goods and services.
- This principle of non-discrimination is known as most favoured nation (MFN) treatment.
- There are some exceptions, such as when members strike bilateral trade agreements or when members offer developing countries special access to their markets.
Removal of MFN status :
- There is no formal procedure for suspending MFN treatment and it is not clear whether members are obliged to inform the WTO if they do so.
- India suspended Pakistan’s MFN status in 2019 after a suicide attack by a Pakistan-based Islamist group killed 40 CRPF personnel.
- Pakistan never applied MFN status to India.
What does losing MFN status mean?
- Revoking Russia’s MFN status sends a strong signal that the United States and its Western allies do not consider Russia a economic partner in any way, but it does not in itself change conditions for trade.
- It does formally allow the Western allies to increase import tariffs or impose quotas on Russian goods, or even ban them, and to restrict services out of the country.
- They could also overlook Russian intellectual property rights.
Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility

Context :
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has issued the draft notification pertaining to Motor Vehicles (Registration and Functions of Vehicle Scrapping Facility Amendment) Rules, 2022.
- These amendments have been done to simplify and digitalize the process of vehicle scrapping for all stakeholders in the ecosystem ,such as vehicle owners, RVSF operators, dealers, regional transport authorities etc.
- These amendments also lay down the procedure for establishment of Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facility (RVSF)
What are the amendments ?
- Provision for vehicle owners to apply digitally for vehicle scrapping. All applications for vehicle scrapping shall be submitted digitally. RVSFs will act as facilitation centres to help vehicle owners apply digitally to scrap their vehicles.
- Necessary checks to be done from “Vahan” database before submission of application by vehicle owner have been specified. These checks include
- surrender of hire-purchase, lease or hypothecation agreement of the vehicle
- no criminal record against the vehicle in records of the National Crime Records Bureau
- no pending dues on the vehicle, and no record of blacklisting of the vehicle by regional transport authorities.
- Application for vehicles failing any of these checks shall not be submitted.
- Introduction of undertakings by vehicle owner and RVSF operators at the time of vehicle submission to ensure that there is transparency in the responsibility of the vehicle before and after submission for scrapping
- Inclusion of more details in the Certificate of Deposit pertaining to the vehicle submitted for scrapping to enable transparency in trading of the said certificate.
- The said certificate will be available to the vehicle owners digitally and shall be valid for a period of 2 years
- Introduction of Transfer Certificate of Deposit to ensure that consumers obtaining the certificate of deposit through electronic trading have a digital proof of the transaction
Provisions of the vehicle scrappage policy :
- Fitness Test: Old vehicles will have to pass a fitness test before re-registration and as per the policy government commercial vehicles more than 15 years old and private vehicles which are over 20 years old will be scrapped.
- Old vehicles will be tested at the Automated Fitness Center and the fitness test of the vehicles will be conducted according to international standards.
- Emission test, braking system, safety components will be tested and the vehicles which fail in the fitness test will be scrapped.
- The Ministry has also issued rules for registration procedure for scrapping facilities, their powers, and scrapping procedure to be followed.
- As a disincentive, increased re-registration fees would be applicable for vehicles 15 years or older from the initial date registration.
International Arbitration and Mediation Centre

Context :
- Chief Justice of India, N.V. Ramana laid the foundation stone for the International Arbitration centre in Hyderabad.
- The Centre could be on the lines of the Singapore International Arbitration Centre, or the London Commercial Arbitration Centre.
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism :
- Arbitration and Conciliation are modes of the Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanism, in which disputes are settled without litigation.
- ADR mechanism facilitate parties to deal with the underlying issues in dispute in a more cost-effective manner and with increased efficacy.
-
Arbitration:
- The dispute is submitted to an arbitral tribunal which makes a decision (an “award”) on the dispute that is mostly binding on the parties.
- It is less formal than a trial, and the rules of evidence are often relaxed.
- There’s no right to appeal on arbitral award usually
-
Conciliation:
- A non-binding procedure in which an impartial third party, the conciliator, assists the parties to a dispute in reaching a mutually satisfactory agreed settlement of the dispute.
- Conciliation is a less formal form of arbitration.
- The parties are free to accept or reject the recommendations of the conciliator.
-
Mediation:
- In mediation, an impartial person called a “mediator” helps the parties try to reach a mutually acceptable resolution of the dispute.
- The mediator does not decide the dispute but helps the parties communicate so they can try to settle the dispute themselves.
Employees Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) interest rate
Context :
- Union Minister for Labour & Employment announced the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) interest rate for the year 2021-2022
- The return on workers’ retirement savings parked with the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has been slashed to 8.1% for 2021-22 from the 8.5% rate credited to members’ accounts in the previous years.
- The last time the EPF savings were paid an annual return this low was in 1977-78
What is the EPFO ?
- It is a government organization that manages provident fund and pension accounts of member employees and implements the Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952
- The Act is administered by the Central Board of Trustees, EPF is a Statutory Board constituted by the Central Government under Section 5A of the Act.
- The Central Board of Trustees is made up of a tripartite group of trustees :
- Government (Union + state) – 15 nominees
- Employers (industrialists) – 10 nominees
- Employees (workers) – 10 nominees
- They make policy decisions about where to invest money (usually G-sec>C-Bonds>Shares; with minimum and maximum slabs) and they decide how much interest should be paid to subscribers.
- Principal and the interest are returned upon retirement age/ death
- Partial withdrawal upto “X%” allowed for education, marriage, illness and house construction.
- In 2020,under the PM ATMANIRBHAR Garib Kalyan Package the labour ministry allowed EPFO subscribers to withdraw upto “X%” of EPF fund to help the workers during lockdown.
- The Employees’ Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 provides for the institution of provident funds for employees in factories and other establishments.
- It is administered by the Ministry of Labour & Employment, Government of India.
- It is one of the World’s largest Social Security Organisations in terms of clientele and the volume of financial transactions undertaken.
5th India-Canada Ministerial Dialogue on Trade & Investment

Context :
- It was attended to by the minister of commerce and industry from india while the trade minister attended from canada
- The Ministers agreed to formally re-launch the negotiations for India-Canada Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and also consider an Interim Agreement or Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA) that could bring early commercial gains to both the countries.
- The Interim Agreement would include high level commitments in goods, services, rules of origin, sanitary and phytosanitary measures, technical barriers to trade, and dispute settlement, and may also cover any other areas mutually agreed upon.
- Canada also agreed to examine expeditiously the request for Conformity Verification Body (CVB) status to APEDA (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority) for facilitating Indian organic export products.
- India-Canada Bilateral Center will be set up for dedicated science and technology activities between the two countries. India has already established such bilateral centres in countries like US, Germany and France.
India canada relations :
- People to People Connect
- Canada hosts one of the largest Indian diasporas in the world, numbering 1.6 million (PIOs and NRIs) which account for more than 3% of its total population.
- The diaspora has done commendably well in every sector in Canada.
- In the field of politics, in particular, the present House of Common (total strength of 338) has 22 Members of Parliament of Indian-origin.
-
Economic Cooperation
- Bilateral trade amounted to USD 6.3 billion in 2018-19.
- Canadian Pension Funds have invested around US$22 billion in India till now.
- More than 400 Canadian companies have a presence in India, and more than 1,000 companies are actively pursuing business in the Indian market.
- Indian companies in Canada are active in the field such as Information Technology, software, steel, natural resources and banking sectors.
- India and Canada are discussing the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and the Bilateral Investment Promotion and Partnership Agreement (BIPPA/FIPA).
-
Energy Cooperation
- Energy has been a primary area of our focus in the relations.
- The scope of the Energy Dialogue was expanded to additionally include electricity, energy efficiency and renewable.
- India Oil Corporation has a 10% participating interest in a Liquid Natural Gas project in British Columbia.
- A Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (NCA) with Canada was signed in June 2010 that allows for uranium export to india.
-
Science and Technology
- Department of Biotechnology under IC-IMPACTS program implements joint research projects in health care, agri-biotech and waste management.
- Department of Earth Science and Polar Canada has started a programme for the exchange of knowledge and scientific research on Cold Climate (Arctic) Studies.
- ISRO and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) have signed MOUs in the field of exploration and utilisation of outer space
- ANTRIX, the Commercial arm of ISRO, has launched several nano-satellites from Canada. ISRO in its 100th Satellite PSLV launched on 12 January 2018, also flew Canadian first LEO satellite
-
Concerns in relations:
- Canada remains an insignificant trading partner for India.
- In 2017, compared to other North American countries, Indian exports to Canada stood at just over US$2 billion, behind the US and Mexico.
- However, imports from Canada were valued at more than US$4.5 billion in 2017, ahead of Mexico.
- For India Canada is an attractive destination for skilled immigrants and a source of agricultural commodities and energy resources; it is hardly a strategic partner.
- India’s Canada policy, on the other hand, has partly been affected by the presence of Khalistan sympathizers who espouse anti-India sentiments.
- Canada’s criticism of New Delhi regarding the CAA protests,Farmer movements etc. has dented India’s interest in engaging Canada as a strategic partner.
Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry scheme
Context :
- The Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers has recently released the guidelines for the “Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry (SPI)” scheme
- The scheme will extend support required to existing pharma clusters and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises across the country.
- The objective of the scheme is to improve productivity, quality and sustainability of the pharma industries with a total financial outlay of five hundred crore rupees for the period from financial year 2021-22 to 2025-26.
Components of the scheme :
- The Assistance to Pharmaceutical Industry for Common Facilities (APICF) programme aims to strengthen existing pharmaceutical clusters’ capacity for sustained growth by creating common facilities.
- Support for clusters for the establishment of common facilities with a focus on Research and development labs, Testing Laboratories, Effluent Treatment Plants, Logistic Centers, and Training Centers is proposed
- The Pharmaceutical Technology Upgradation Assistance Scheme (PTUAS) assists Micro, Small, and Medium Pharma Enterprises (MSMEs) with a proven track record in meeting national and international regulatory standards.
- Support for SME Industries is proposed under the PTUAS sub-scheme, either through interest subvention of up to 5% per annum (6% in the case of units owned and managed by SC/STs) or through credit linked capital subsidy of 10%.
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Promotion and Development Scheme (PMPDS) to promote the growth and development of the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Sectors through study/survey reports, awareness programs, database creation, and industry promotion.
- Knowledge and awareness regarding the pharmaceutical and MedTech industries will be promoted through the PMPDS sub-scheme.
Rashtriya Raksha University
Context :
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi dedicated to the nation the building of Rashtriya Raksha University near Gandhinagar in Gujarat
About the university :
- Rashtriya Raksha University is an institution of National Importance as established by the Indian Parliament Act(Rashtriya Raksha University Act,2020)
- The University aims to become an academic-research-training ecosystem for national security and police.
- Its endeavors focus on highly professional national security, police education, research, and training through its qualified civilian and security faculty
The functions of the University include:
- providing instructions and research in police sciences, including coastal policing and cyber security
- establishing and maintaining colleges
- prescribing courses, holding exams, and granting degrees and other distinctions.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 12th & 13th March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

