UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 15th March 2022
Topics for the day:
- Retail inflation climbs to 6.07%
- Microfinance firms can fix interest rates
- Supplementary demand for grants
- Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Subordinate Debt (CGSSD)
- Maternal mortality ratio (MMR) of India
- Gallium Nitride
- 32 new roads along China border
Retail inflation climbs to 6.07%
Context :
- India’s retail inflation inched up to an eight-month high of 6.07% in February from 6.01% in January, with rural India experiencing a sharper price rise at 6.38%.
- For urban consumers, the inflation rate, in fact, fell from 5.91% in January to 5.75% in February.
More on the news :
- Food prices saw an upward trajectory, with inflation measured by the Consumer Food Price Index rising to 5.85% in February from 5.43% in January.
- This trend was divergent for rural and urban India, with the latter seeing a slight moderation in food inflation, while rural food inflation shot up by 0.7 percentage points to 5.87%.
- Food and beverages inflation hit a 15-month high, and the rising prices of edible oils are likely to pose a challenge in coming months
- Inflation in wholesale prices resurged to 13.11% in February after two months of mild cooling off, staying above the 10% mark for the eleventh month in a row
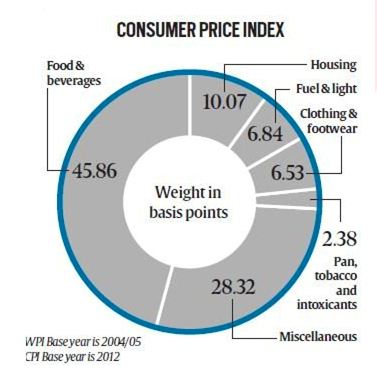
Consumer Price index :
- Monthly CPI Components in (All India index) – Food & Beverages makes 45%,Services make 21% and housing makes 10% etc
- It measures price changes from the perspective of a retail buyer.
- It is released by the National Statistical Office (NSO).
- The CPI calculates the difference in the price of commodities and services such as food, medical care, education, electronics etc, which Indian consumers buy for use.
- The CPI has several sub-groups including food and beverages, fuel and light, housing and clothing, bedding and footwear.
- At present, India has five consumer price indexes (CPIs), three of which are working-class specific :
- CPI for Industrial Workers (IW).
- CPI for Agricultural Labourer (AL).
- CPI for Rural Labourer (RL).
- These three indexes are compiled by the Labour Bureau in the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- CPIs AL and RL are used to fix minimum wages of agricultural labourers and rural unskilled employees.
Headline inflation :
- Headline CPI is the inflation figure arrived based on all of the above components of CPI
Core inflation :
- Core CPI is Headline CPI without inflation in food & energy.
- This is Because Food and fuel price shocks are transitory,mainly supply driven and therefore can’t be controlled by RBI’s monetary policy tools.
Fighting inflation :
- RBI – Tight / dear / Hawkish Monetary Policy to make loans more expensive. This would reduce liquidity in the market
- Central Govt –
- Tax deduction / exemption / subsidy benefits towards producers to decrease the cost of production.
- Curtailing Fiscal Deficit
- Curtailing schemes/subsidies that increase money in the hands of beneficiaries without increasing production.
- Ordering RBI to issue inflation Indexed Bonds, Sovereign Gold Bonds
- Essential commodities act, Stock limits, Minimum Export Price, FCI’s Open Market Sale Scheme, Operation Greens for TOP, Price stabilization fund,Offering higher MSP to farmers to increase cultivation of a particular crops
Microfinance firms can fix interest rates
Context :
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Monday allowed microfinance institutions to fix interest rates on loans, with a caveat that the rates should not be usurious.
More on the news :
- In revised guidelines that will take effect on April 1, the RBI tweaked the definition of a microfinance loan to indicate a collateral-free loan given to a household with annual income of up to ?3 lakh.
- Earlier, the upper limits were ?2 lakh for rural borrowers and ?2 lakh for urban borrowers.
- As per the revised norms, regulated entities (REs) should put in place a Board Approved policy regarding pricing of microfinance loans, a ceiling on interest rate and all other charges applicable to microfinance loans.
- Each RE shall disclose pricing-related information to a prospective borrower in a standardized, simplified factsheet
- Any fees to be charged to the microfinance borrower by the RE and/ or its partner/ agent shall be explicitly disclosed in the factsheet.
- The borrower shall not be charged any amount which is not explicitly mentioned in the factsheet
- Each RE would have to put in place a mechanism for identification of the borrowers facing repayment-related difficulties, engagement with such borrowers and providing them necessary guidance about the recourses available
- Also RE will provide the details of recovery agents to the borrower while initiating the process of recovery to ensure due notice and appropriate authorisation
- There shall be no pre-payment penalty on micro finance loans.
- Penalty, if any, for delayed payment shall be applied on the overdue amount and not on the entire loan amount
- Any change in interest rate or any other charge shall be informed to the borrower well in advance and these changes shall be effective only prospectively
- Interest rates and other charges/ fees on micro finance loans should not be usurious. These shall be subjected to supervisory scrutiny by the Reserve Bank
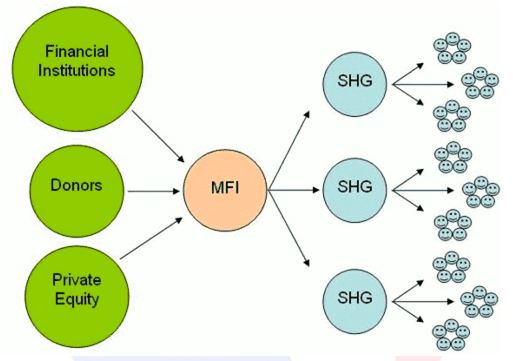
Background of microfinance institutions :
- Based on the Malegam Committee recommendations, RBI came out with detailed guidelines for microfinance institutions
- These guidelines introduced a new category of NBFCs, ie. NBFC-MFIs (microfinance institutions).
- It also set norms for income criteria for clients of MFIs, repayment period, borrower loan limits, interest rate norms and caps, limits on a number of lenders to a borrower and a host of other norms and criteria
Supplementary demand for grants
Context :
- The government has sought approval from Parliament to spend an extra ?07 lakh crore in the current fiscal year.
- The additional spending of 58 trillion is required for expenditure commitments towards settling loans taken from National Small Savings Funds for PM Awas Yojana and higher fertilizer subsidy outgo.
What are Supplementary Demands for Grants?
- The supplementary demand for grants is needed for government expenditure over and above the amount for which Parliamentary approval was already obtained during the Budget session.
Constitutional provisions:
- Supplementary, additional or excess grants and Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants are mentioned in the Constitution of India.
- Article 115: Supplementary, additional or excess grants
- Article 116: Votes on account, votes of credit and exceptional grants
What are these grants ?
Supplementary Grant
- It is granted when the amount authorised by the Parliament through the appropriation act for a particular service for the current financial year is found to be insufficient for that year.
Additional Grant
- It is granted when a need has arisen during the current financial year for additional expenditure upon some new service not contemplated in the budget for that year.
Excess Grant
- It is granted when money has been spent on any service during a financial year in excess of the amount granted for that service in the budget for that year.
- It is voted by the Lok Sabha after the financial year.
- Before the demands for excess grants are submitted to the Lok Sabha for voting, they must be approved by the Public Accounts Committee of Parliament.
Vote of Credit
- It is granted for meeting an unexpected demand upon the resources of India, when on account of the magnitude or the indefinite character of the service, the demand cannot be stated with the details ordinarily given in a budget.
- Hence, it is like a blank cheque given to the Executive by the Lok Sabha.
Exceptional Grant
- It is granted for a special purpose and forms no part of the current service of any financial year.
Token Grant
- It is granted when funds to meet the proposed expenditure on a new service can be made available by reappropriation.
- A demand for the grant of a token sum (of Re 1) is submitted to the vote of the Lok Sabha and if assented, funds are made available.
- Reappropriation involves transfer of funds from one head to another. It does not involve any additional expenditure.
Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board
Context :
- The Kerala State Road Transport Corporation argued in the Supreme court that the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act of 2006 mandated the constitution of an independent authority to fix fuel prices
What is the Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board
- PNGRB was established in 2006 under Petroleum and Natural Gas Regulatory Board Act, 2006.
- Its mandate is to regulate the refining, processing, storage, transportation, distribution, marketing and sale of petroleum, petroleum products and natural gas excluding production of crude oil and natural gas so as to ensure an uninterrupted and adequate supply of petroleum, petroleum products and natural gas in all parts of the country.
- It also ensures enough supply across country, foster fair trade, protect consumer interest and authorise companies that will build and operate fuel pipelines.
- The PNGRB consists of Chairperson, a Member (Legal) and three other members.
- It also has power of civil court and bench comprising member (legal) and one or more members nominated by chairperson which decides on disputes arising among downstream companies or with outsiders.
- The Appellate Tribunal under the Electricity Act will serve as the Appellate Tribunal for the PNGRB.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Subordinate Debt (CGSSD)

Context :
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Subordinate Debt (CGSSD) extended upto 31.03.2023.
About:
- Government announced creation of ‘Distressed Assets Fund – Subordinate Debt for Stressed MSMEs’, under the Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Package.
- Later a scheme called ‘Credit Guarantee Scheme for Subordinate Debt’ was launched in 2020 to provide credit facility through lending institutions to the promoters of stressed MSMEs ie. SMA-2 and NPA accounts who are eligible for restructuring as per RBI guidelines.
- As per the Scheme, guarantee cover worth Rs. 20,000 crores will be provided to the promoters who can take debt from the banks to further invest in their stressed MSMEs as equity.
- The scheme will be operationalised through Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for MSEs (CGTMSE).
Implementation:
- Promoters of the MSMEs will be given credit equal to 15% of their stake (equity plus debt) or Rs. 75 lakh whichever is lower.
- Promoters in turn will infuse this amount in the MSME unit as equity and thereby enhance the liquidity and maintain the debt-equity ratio.
- 90% guarantee coverage for this sub-debt will be given under the Scheme and 10% would come from the concerned promoters.
- There will be a moratorium of 7 years on payment of principal whereas the maximum tenor for repayment will be 10 years.
Maternal mortality ratio (MMR) of India
Context :
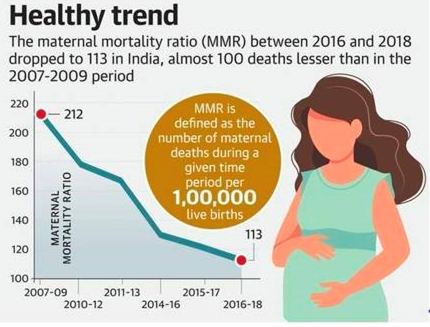
- The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) of India has declined by 10 points, says a special bulletin released by the Registrar-General of India.
What is MMR ?
- It is the number of maternal deaths during a given time period per 1,00,000 live births
More about the news :
- It has declined from 113 in 2016-18 to 103 in 2017-19, an 8.8% decline.
- The country has been witnessing a progressive reduction in the MMR from 130 in 2014-16, 122 in 2015-17 and 113 in 2016-18 to 103 in 2017-19, said the release.
- With this persistent decline, India is on the verge of achieving the National Health Policy (NHP) target of 100 per lakh live births by 2020 and certainly on the track to achieve the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of 70 per lakh live births by 2030.
- The number of States that have achieved the Sustainable Development Goal target has now risen from five to seven – Kerala (30), Maharashtra (38), Telangana (56), Tamil Nadu (58), Andhra Pradesh (58), Jharkhand (61), and Gujarat (70).
- There are now nine States that have achieved the MMR target set by the National Health Policy, which includes the above seven States and Karnataka (83) and Haryana (96).
- Chhattisgarh (160), Madhya Pradesh (163), Uttar Pradesh (167) and Assam (205) have the ratio above 150.
Gallium Nitride(GaN)
Context :
- Gallium Nitride Ecosystem Enabling Centre and Incubator (GEECI) has been set up in Bengaluru.
- The facility has been jointly set up by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and IISc Bengaluru.
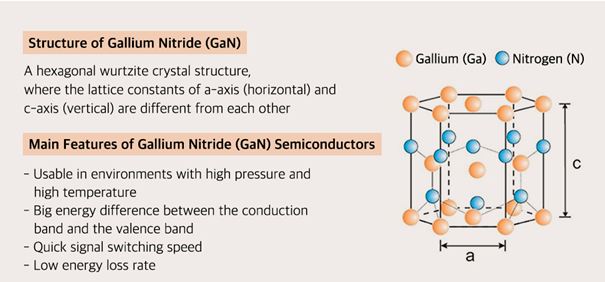
About Gallium Nitride:
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) is believed to be the second most important material after silicon for electronics chips.
Properties of Gallium Nitride:
- High heat capacity
- Sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low
- faster-switching speed
- higher thermal conductivity and lower on-resistance.
Applications:
- GaN is a semiconductor commonly used in blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
- Gallium Nitride Technology is of strategic importance with its application in the field of 5G, space and defense.
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) plays a key role in enabling e-vehicles and wireless communication.
32 new roads along china border
Context :
- Post-Galwan incident, the Government of India sanctioned 32 roads along the China border, of which work has started on eight roads, a report tabled in the Rajya Sabha said.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) informed a parliamentary panel that 32 helipads were being constructed and upgraded along the China border.
More on the news :
- The report on Demands for Grants (2022-23) of the MHA by the parliamentary standing committee said the Ministry had demanded 3,637.92 crore (in Budget) for border infrastructure in the coming fiscal though it was able to spend only 50% of the allocated budget till December 2021.
- The Ministry informed the panel that to improve the existing infrastructure and to enhance the operational capabilities of security forces, the government had undertaken various projects and schemes in the past few years along the China border.
- It stated that under the Indo-China Border Roads Phase-I (ICBR-I), the construction of 25 roads, measuring 751.58 km, at an estimated cost of Rs.3482.52 crore was taken up. Out of this, 18 roads measuring 475.29 km were in operational use while the work on the remaining seven roads was on.
- The first phase was initiated in 2005 when it was decided that the MHA would construct 27 priority roads totaling 608 km along China border.
- The second phase (ICBRII) was approved on September 21, 2020, months after 20 Indian soldiers were killed in clashes with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army in eastern Ladakh.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 15th March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

