CURRENT AFFAIRS
TOPICS :
-
ISRO rescheduled upcoming Space Missions
-
Law on Abortion
-
Asian Development Bank
-
Fisheries Subsidies in India
-
First Tribal Woman President of India
-
Hattis of Himachal
ISRO rescheduled upcoming Space Missions
Context:
Indian Space research Organisation (ISRO) has rescheduled its upcoming space missions.
About the new deadlines:
- The India’s first Solar mission, third lunar mission, and XpoSat are the 3 upcoming space missions which are given new deadlines.
- These are scheduled to be launched in next year, these have been repeatedly postponed from 2020.
- There were only 2 launches in 2020 and 2021 together. Where as 2022 already witnessed two satellite launches that includes a Singaporean satellite as well.
- However, the first abort demonstration for Gaganyaan mission is scheduled to be in the last quarter of this year. This is meant to be the first abort demonstration mission.
Abort missions:
- Aim: aim of abort missions is to help crew escape mid-flight in case of a failure.
- Earlier there was a pad abort system demonstration had been conducted, where the crew members can escape from the spacecraft in case of an emergency at launch pad
The major upcoming missions:
Aditya L1 mission:
- It is ISRO’s first solar mission.
- It was conceived as 400kg class satellite carrying one payload, the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC). It is planned to be placed in an 800km low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Aditya L1 mission will see an Indian spacecraft going 1.5kms away to L1 (Lagrange point1) between Sun and Earth. Lagrange point is position in space where the gravity pull of both bodies on satellite is equal to force required to keep it in orbit without spending extra fuel.
XpoSat:
- It is the second astronomical observatory in space after the AstroSat.
- XpoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite) is to study polarisation of cosmic X-rays.
- It is expecting to be launched in second quarter of the next year 2023.
Chandrayaan 3:
- Chandrayaan 3 is the third lunar exploration mission by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is a follow up of Chandrayaan2. It will be a lander rover mission aiming for soft landing on the Moon that was planned for Chandrayaan 2.
- Its launch has been pushed to Q1 of next year.
About the Gagayaan Mission:

The Gaganyaan Programme envisages undertaking the demonstration of human spaceflight to Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
- Aim: to demonstrate indigenous capability to undertake human space flight mission to LEO.
- Under the Gaganyaan, a total of three spaceflights that includes two unmanned and one manned spaceflight to be launched.
- The human spaceflight intends to send 3 astronauts to space for a period of 5-7 days.
Components involved:
- crew module: it is a spacecraft which carries the human beings
- service module: that is powered by two liquid propellants. It is mated to the crew module.
- it also consists of crew escape system.
Launch vehicle: it is to be launched by GSLV Mk III (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) a three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle. It is also known as Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM-3).
Vyomamitra: a humanoid robot is to be send in an unmanned spacecraft ahead of the human spaceflight. It will stimulate exact human functions in space and it will check whether the systems are right.
Law on Abortion
Context:
Supreme Court has allowed an unmarried woman whose relationship status has changed during pregnancy to terminate her 24 weeks foetus. SC has underlined that in abortion, women’s choice matters.
About the plea:
- An unmarried pregnant woman (from Manipur) has reached out the Court as there is no provision in law regarding the unmarried pregnant women to undergo abortion.
- Delhi High Court earlier had rejected her plea by stating that we cannot allow what law prohibits.
- Later, Supreme Court has allowed her plea to terminate pregnancy highlighting that she should not be denied the merely on the ground that she is unmarried.

Law on abortion in India:
- The Indian Penal Code, 1860 under section 312 criminalised the act of voluntarily “causing miscarriage” even when the miscarriage is with the pregnant woman’s consent, with an exception on the ground that if the miscarriage is caused to save the woman’s life.
- This strict restriction has encouraged women to indulge in using unsafe methods to terminate the pregnancy which are dangerous as well.
- Later, in order to liberalise the access to the abortion, The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act (MTP Act), 1971 was introduced.
- The act provided for two stages in clearing pregnancy. In case of termination of pregnancy under 12 weeks then one doctor opinion was required.
- In case of pregnancy termination between 12-20 weeks old, opinion of 2 doctors was required.
- Before agreeing to termination, these doctors will have to determine whether the continuance of pregnancy poses a risk of the life to her or there is any substantial risk to the child to be born like physical or mental abnormalities.
- Recent Amendment: The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act (MTP Act), 1971 was amended in 2021, this increased the termination up to 20 weeks with one doctor’s opinion and two doctors’ opinion for 20-24 weeks old pregnancy.
- Eligible categories of women: Also, the amendment specified for seven categories of women for eligible for termination of pregnancy between 20 and 24 weeks. They are,
- survivors of sexual assault or rape or incest;
- minors;
- change of marital status during the ongoing pregnancy (widowhood and divorce);
- women with physical disabilities;
- mentally ill women including mental retardation;
- the foetal malformation that has substantial risk of being incompatible with life or if the child is born it may suffer from such physical or mental abnormalities to be seriously handicapped; and
- women with pregnancy in humanitarian settings or emergency situations as may be declared by the Government.
- In all these conditions there has been no provision for an unmarried woman. This led that unmarried woman with 24 weeks pregnancy to reach out to court.
Way forward
- In comparison with many other countries such as US which has very strict abortion law, India’s abortion law is considered progressive.
- As India’s abortion law is progressive in nature, it needs to focus more on the women and their reproductive rights.
Asian Development Bank
Context:
Asian Development Bank (ADB) has cut its economic growth forecast for India to 7.2% from its earlier estimate of 7.5% (in April) in its supplement to Asian Development outlook report.
ADB’s outlook Supplement findings:
- ADB has lowered economic growth forecast from7.5% to 7.2%.
- Reason for lowering: It cited the inflation which is rising higher than anticipated inflation since April and the tightening monetary policy as reason.
- It also lowered the GDP growth estimate for 2023-24 from 8% to 7.8%.
- The inflation forecast has raised from 5.8% to 6.7% on account of higher-than-expected oil prices.
- ADB also highlighted that, there will be shrinkage of net exports because of the subdued global demand and rising real effective exchange rate eroding the export competitiveness despite a depreciating rupee.
- Suggestion by ADB: ADB suggested that by a cut in excise duties, the provision of fertilizer and gas subsidies, and the extension of free food distribution programme some of the effect of high prices can be reduced.
- It also predicted that private investment will soften because of the higher cost of borrowing for firms as the continuous rising of policy rate by RBI to contain inflation.

Asian Development Bank:
- Asian Development Bank is a regional developmental bank established on 19th December 1966.
- ADB assists its members and partners by providing loans, technical assistance, grants and equity investments to promote social and economic development.
Members: at the time of founding there were 31 members, now it’s member strength to 68members which include 49 from Asia and Pacific remaining 19 are from outside. India is one of the founding members.
Headquarters: headquarters is located Mandaluyong, Philippines.
Fisheries Subsidies in India
Context:
Minister of fisheries, animal Husbandry and Dairying has clarified that the fisheries subsidies will not bring down in the country.
Fisheries in India:
- According to Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) as per 2016 census marine fisherfolk population in country stands at 3.77million. (0.90 million families)
- Nearly 63% of these families belong to the Below Poverty Line (BPL)
- In 2019, marine capture production was 3.8 million tonnes against the estimated fishing potential of more than 4.4 million tonnes.
- In 2018 India provided subsidies worth $277 million to small fishers.
The Geneva package and India:
- A concern regarding curbing down fisheries subsidies following Geneva Package agreements was cleared by the Ministry of fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- The Geneva Package Deal was concluded on June 17th during the 12th session of Ministerial Conference of 164 members of WTO held at Geneva.
- The Geneva package: The Deal contains agreements on curbing harmful fishing subsidies and a temporary patent waiver for production of covid19 vaccines. It also includes subsidies on overfishing, deep sea fishing and unregulated fishing.
- India had sought a 25-year transition period by asserting that fisheries sector in India needs the Government support as most of the coastal areas fisher folks still rely on small scale fishing for livelihood.
- Government also said that Subsidies provided to them are to acquire and modernize their relatively small fishing vessels, and as insurance charges.
First Tribal Woman President of India
Context:
Droupadi Murmu has been elected as the president of India in recently conducted elections.
New president of India:
- Droupadi Murmu has been elected as the 15th president of India.
- She created history by becoming the first ever tribal woman to be president of India.
- She is also the youngest and first president who has born after Independence.
- She will take oath as a president on 25th
- Every president or every person discharging presidential duties before entering the office of president has to take an oath in the presence of Chief Justice of India (CJI) to preserve, protect and to defend the constitution and the law (Article 60).
- Droupadi Murmu will hold the office for next 5 years followed by the oath (2022-2027).

About Droupadi Murmu:
- She belongs to mayurbanj district in odisha.
- She hails from the santhal tribe.
- She has worked as an MLA, and served as Minister in odisha.
- She has also worked as the Governor of Jharkhand state (only governor of Jharkhand to serve full term till present).
Hattis of Himachal
Context:
There is a demand for tribal status for Himachal Pradesh’s Trans- Giri and scheduled tribe status for Hatti community.
Hattis:
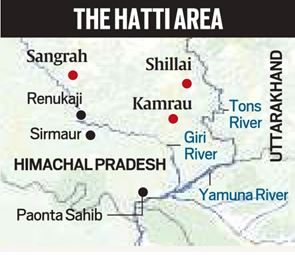
- Hattis are a close knit community.
- Their name was derived from their traditional occupation, which is selling of home-grown crops, vegetables, meat, and wool at small town markets known as “Haats”.
- Hatti men traditionally wears different white headgear during ceremonial occasions.
- Their homeland spread between Haryana -UP border in the basin of the Giri and tons rivers (tributaries of the Yamuna).
- Present estimated population of Hattis is estimated to be around 3lakhs, they live in 154 panchayts areas in Himachal Pradesh.
- Hattis are governed by khumbil which is a traditional council like Khaps of Haryana.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 22nd June 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube


