CURRENT AFFAIRS
Topics for the day:
- Exports cross $400-bn annual target as goods shipments jump
- The controversy over the proposed Mekedatu water project
- The Artemis programme, NASA’s new moon mission
- Article 355 needed in Bengal
- China: Russia can’t be ousted from G20
- Criminal Justice Reforms
Exports cross $400-bn annual target as goods shipments jump
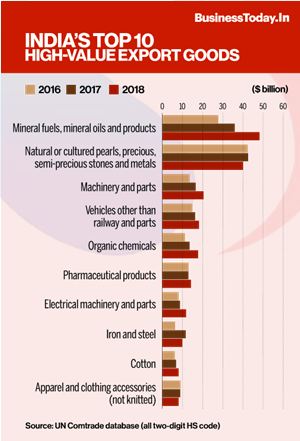
Context :
- India’s annual goods exports crossed the $400billion mark for the first time ever, the government announced, buoyed by an increase in shipments of merchandise, including engineering products, apparel and garments, gems and jewellery and petroleum products.
- Commerce and Industry Minister asserted that neither the COVID19 pandemic nor the global uncertainties following the Ukraine crisis had affected India’s ability to reach its export goals.
- Exports had reached $331.02 billion in the pre pandemic fiscal year of 2018-19.
- The boost in the exports was likely to bolster India’s position in the ongoing negotiations for Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with several trade partners.
- Noting that the agriculture sector too had recorded its highest ever export during 2021-22 with the help of export of “rice, marine products, wheat, spices and sugar”
Initiatives to improve exports :
Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP) :
- The scheme was formed to replace the existing MEIS (Merchandise Exports from India Scheme)
- It is a fully automated route for Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the GST (Goods and Service Tax) to help increase exports in India.
- ITC is provided to set off tax paid on the purchase of raw materials, consumables, goods or services that were used in the manufacturing of goods or services.
- This helps in avoiding double taxation and the cascading effect of taxes.
- It was started in January 2021 as a replacement for the MEIS, which was not compliant with the rules of the World Trade Organisation.
- The tax refund rates range from 0.5% to 4.3% for various sectors.
- The rebate will have to be claimed as a percentage of the Freight On Board value of exports.
- It is implemented by Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Special economic zone :
- An SEZ is a territory within a country that is typically duty-free (Fiscal Concession) and has different business and commercial laws chiefly to encourage investment and create employment.
- SEZs are created also to better administer these areas, thereby increasing the ease of doing business.
- Benefits available to SEZ’s :
- Duty free import/domestic procurement of goods for development, operation and maintenance of SEZ units.
- Exemption from various taxes like Income Tax, minimum alternate tax, etc.
- External commercial borrowing by SEZ units upto US $ 500 million in a year without any maturity restriction through recognized banking channels.
- Single window clearance for Central and State level approvals
Niryat Bandhu Scheme
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) is implementing the Niryat Bandhu Scheme for mentoring budding exporters on the intricacies of foreign trade through counseling, training, and outreach programs.
- Given the rise of small and medium scale enterprises and their role in employing people, MSME clusters have been identified for focused interventions to increase exports.
- To achieve the objectives of the scheme, outreach activities are being organized in a structured manner with the assistance of Export Promotion Councils and other willing knowledge partners in academia and the research community.
The controversy over the proposed Mekedatu water project
Context :
- Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are heading for a political confrontation over the Mekedatu drinking water project across river Cauvery, proposed by the former.
- Within days of Tamil Nadu Assembly’s resolution against the project, Karnataka’s legislative assembly is set to counter it with a resolution seeking the project’s early implementation and clearances from the Centre.
- As Karnataka heads into an election year in 2023, the Mekedatu issue has been resonating within Karnataka and in Tamil Nadu as well.
- With Cauvery being an emotive issue that binds people in the Cauvery basin districts in Old Mysore region, Mekedatu is likely to impact election results.
Background :
- The Rs. 9,000 crore Mekedatu project aims to store and supply water for drinking purposes for the Bengaluru city.
- Around 400 megawatts (MW) of power is also proposed to be generated through the project.
- It was first approved by the Karnataka state government in 2017 and it received approval from the erstwhile Ministry of Water Resources for the detailed project report and is awaiting approval from the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- The approval from MoEFCC is crucial because 63% of the forest area of the Cauvery Wildlife Sanctuary will be submerged.
- However In 2018, Tamil Nadu approached the Supreme Court (SC) against the project
Tamil Nadu’s stand :
- The project is against the final order of the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal (CWDT) in which the SC held that no state can claim exclusive ownership or assert rights to deprive other states of the waters of inter-state rivers(as given under Helsinki rules on uses of water)
- It has also held that the reservoir is not just for drinking water alone, but to increase the extent of irrigation, which is in clear violation of the Cauvery Water Disputes Award.
- Acc to TN, Karnataka has no right to construct any reservoir on an inter-state river without the consent of the lower riparian state
Cauvery Dispute so far :
- From 1974, Karnataka started diverting water into its four newly made reservoirs, without the consent of Tamil Nadu resulting in a dispute.
- To resolve the matter, the CWDT was established in 1990 which took 17 years to arrive at the final order (2007) on how Cauvery water should be shared between the 4 riparian states in normal rainfall conditions.
- In distress years, a pro-rata basis shall be used, it instructed. The government again took 6 year and notified the order in 2013.
- The verdict of the CDWT was challenged through a special leave petition in the SC.
- The final verdict of the SC came in 2018 where it declared the Cauvery a national asset and largely upheld the water-sharing arrangements finalised by the CWDT and also reduced the allocation of water from Karnataka to Tamil Nadu.
- As per the SC,
- Karnataka would get 284.75 thousand million cubic feet (tmcft)
- Tamil Nadu 404.25 tmcft
- Kerala 30 tmcft
- Puducherry 7 tmcft.
- It also directed the Centre to notify the Cauvery Management Scheme. The centre did so in June 2018, constituting the ‘Cauvery Water Management Authority’ and the ‘Cauvery Water Regulation Committee’.
The Artemis programme, NASA’s new moon mission
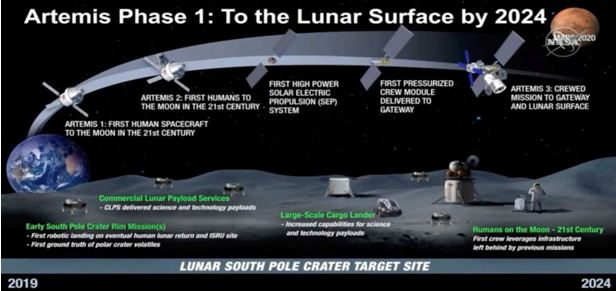
Context :
- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) rolled out its Artemis I moon mission to the launchpad for testing at the Kennedy Space Centre in Florida, United States.
- The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion capsule of the mission were hurled out to the launchpad by NASA’s Crawler Transporter 2 vehicle
What is the Artemis program :
- NASA’s Artemis mission is touted as the next generation of lunar exploration
- The program is divided into three parts:
- Artemis I involves an uncrewed flight to test the Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft.
- Artemis II will be the first crewed flight test and is targeted for 2023.
- Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon’s South Pole in 2024.
- Artemis I is the first of NASA’s deep space exploration systems.
- It is an uncrewed space mission where the spacecraft will launch on SLS, the most powerful rocket in the world and travel 2,80,000 miles from the earth for over four to six weeks during the course of the mission.
- The Orion spacecraft is going to remain in space without docking to a space station, longer than any ship for astronauts has ever done before.
- The SLS rocket has been designed for space missions beyond low earth orbit and can carry crew or cargo to the moon and beyond.
- With the Artemis programme, NASA aims to land humans on the moon by 2024, and it also plans to land the first woman and first person of colour on the moon.
- With this mission, NASA aims to contribute to scientific discovery and economic benefits and inspire a new generation of explorers.
- NASA will establish an Artemis Base Camp on the surface and a gateway in lunar orbit to aid exploration by robots and astronauts.
- The gateway is a critical component of NASA’s sustainable lunar operations and will serve as a multi-purpose outpost orbiting the moon.
- Other space agencies are also involved in the Artemis programme.
- The Canadian Space Agency has committed to providing advanced robotics for the gateway
- The European Space Agency will provide the International Habitat and the ESPRIT module, which will deliver additional communications capabilities among other things.
- The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency plans to contribute habitation components and logistics resupply.
Article 355 needed in Bengal

Context:
- Parties in West Bengal have demanded that the law and order situation in West Bengal is completely broken and Article 355 should be invoked to ensure the State is governed as per the provisions of the Constitution.
What’s the issue?
- On 21st March 2022, there was a violent fight between two groups of the ruling party in Bogtui village in Birbhum district.
- The Deputy Pradhan, was killed and in retaliation houses in the area were attacked and set on fire resulting in 12 deaths including that of women and children. All the members belong to the minority community.
What is Article 355?
- Article 355 refers to the provision in the Constitution that states that “It shall be the duty of the Union to protect every State against external aggression and internal disturbance and to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution”.
Use of article 355
- The article is extremely important when there are communal violence incidents.
- Subjects “public order” and “police” are state subjects and states have exclusive power to legislate on these matters.
- These subjects were entrusted to states because states would be in better position to handle any law and order problem.
- However, there might be some circumstances where states are unable to maintain public order and protect people.
- In such situation, centre can invoke article 355 and take measures such as taking law and order of state under its own hand, deployment of military etc.
China: Russia can’t be ousted from G20

Context :
- The U.S. and its Western allies are assessing whether Russia should remain within the Group of Twenty major economies following its invasion of Ukraine
- But any move to exclude Russia would probably be vetoed by others in the group
- China, which has not condemned Russia’s invasion, defended Moscow, calling Russia an “important member” of the G20.
What is the G20 ?
- It is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- It does not have a permanent secretariat or Headquarters.
- The membership comprises a mix of the world’s largest advanced and emerging economies, representing about two-thirds of the world’s population, 85% of global gross domestic product, 80% of global investment and over 75% of global trade.
- Presidency of the G20 :
- The group has no permanent staff of its own, so every year , a G20 country from a rotating region takes on the presidency.
- That country is then responsible for organising the next summit, as well as smaller meetings for the coming year.
- They can also choose to invite non-member countries along as guests.
How has the G20 Evolved?
- After the Asian Financial Crisis in 1997-1998, it was acknowledged that the participation of major emerging market countries is needed on discussions on the international financial system, and G7 finance ministers agreed to establish the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors meeting in 1999.
- Later the Global Financial Crisis (2007-08) fixed G20’s reputation as the premier crisis management and coordination body.
- The US,held the G20 Presidency in 2008, elevated the meeting of the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to Heads of State, resulting in the first G20 Summit.
Members of the grouping :
- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
Criminal justice reforms :
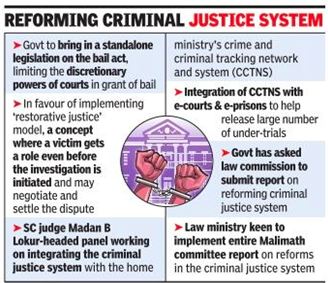
Context :
- Aiming to make comprehensive changes in criminal laws, the government has initiated the process of amendment to laws such as Indian Penal Code, the Code of Criminal Procedure and the Indian Evidence Act in consultation with all stakeholders.
Current concerns/challenges:
- The delay in disposal of cases was leading to human rights violations of the under-trials and convicts.
- Despite the Supreme Court’s directions on police reforms, there had been hardly any changes on the ground.
- Court orders convicting a person are also taking years to implement.
Committee For Reform In Criminal Law:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has constituted a national level committee for reform in criminal law.
- The committee has been constituted under Ranbir Singh and several other members.
- Other committees for the same criminal justice reforms are Malimath commission,Madhav menon commission etc.
Suggested Reforms:
- Special laws and fast-track courts could replace certain offences under the Indian Penal Code in order to reduce the piling up of cases at every police station.
- Digitisation of documents would help in speeding up investigations and trials.
- The construction of new offences and reworking of the existing classification of offences must be guided by the principles of criminal jurisprudence which have substantially altered in the past four decades.
- The classification of offences must be done in a manner conducive to management of crimes in the future.
- The discretion of judges in deciding the quantum and nature of sentence differently for crimes of the same nature should be based on principles of judicial precedent.
Malimath committee recommendations :
- does not favor the death penalty for rapists and infact says wherever possible death penalty be converted to life term
- gave restorative justice – a concept where a victim gets a role before investigation is initiated and may negotiate the dispute
- Borrow from the inquisitorial system – courts will conduct investigation and prosecution unlike now where representatives conduct prosecution. Courts would be bestowed powers to summon any person whether listed or not for examination
- Courts to move from “proof beyond reasonable doubt” to “convinced that it is true” approach
- set up a police establishment board for dealing with postings,transfers etc
Criminal law in India:
- The Criminal law in India is contained in a number of sources – The Indian Penal Code of 1860, the Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955, Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961 and the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989. etc.
- Criminal Justice System can impose penalties on those who violate the established laws.
- The criminal law and criminal procedure are in the concurrent list of the seventh schedule of the constitution.
- Lord Thomas Babington Macaulay is said to be the chief architect of codifications of criminal laws in India.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 24th March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

