UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 28th February 2022
Topics for the day:
- Hunar Haat
- Voting at UNSC
- Lynching in India
- Chandrasekhar Azad
- Judiciary needs more judges
- Wait for the Cheetah is to get longer
- SPARSH: System for Pension Administration (Raksha):
- Council of Europe
Hunar Haat :
 ??
??
Context :
- Recently a Hunar Haat was held in hyderabad.
- Recently the Union Ministry of Minority Affairs has set a target to provide employment opportunities to 7 lakh 50 thousand artisans, craftsmen through 75 Hunar Haats
What are hunar haats?
- Hunar Haat is an exhibition of handicrafts and traditional products made by artisans from the minority communities.
- These are organised by the Ministry of Minority Affairs under USTTAD (Upgrading the Skills & Training in Traditional Arts/Crafts for Development) scheme.
- The USTTAD scheme aims to promote and preserve the rich heritage of the traditional arts & crafts of the minority communities.
Significance of these hunar haats :
- These Haat aims to provide market exposure and employment opportunities to artisans, craftsmen and traditional culinary experts.
- It envisages boosting the skills of craftsmen, weavers and artisans who are already engaged in the traditional ancestral work.
- Hunar Haat has proved to be an “Empowerment Exchange” for master artisans and craftsmen.
- It has proved to be immensely beneficial and encouraging for artisans and craftsmen as lakhs of people visit the “Hunar Haat” and purchase indigenous handmade products of artisans on a large scale.
- More than 5 lakh artisans, craftsmen and people associated with them have been provided employment and employment opportunities in the last about 5 years through “Hunar Haat”.
Voting at UNSC :
Context :
- India, along with China and the UAE, abstained from the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) resolution sponsored by the U.S. and Albania, and co-sponsored by nearly 80 countries
- It sought to condemn Russian aggression and called for the immediate withdrawal of Russian military from Ukraine
More on the news :
- The resolution, supported by 11 UNSC members, was vetoed by Russia.
- However the U.S. promised to take the issue to the General Assembly
- India’s stand :
- According to the indian representative at UN:
- “India is deeply disturbed by the recent turn of developments in Ukraine, We are also deeply concerned about the security of the Indian community”.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi spoke to Ukraine’s President Volodymyr Zelensky on phone on Saturday, hours after the UNSC vote and “The Prime Minister expressed his deep anguish on the loss of life and property in the conflict” according to the PMO.
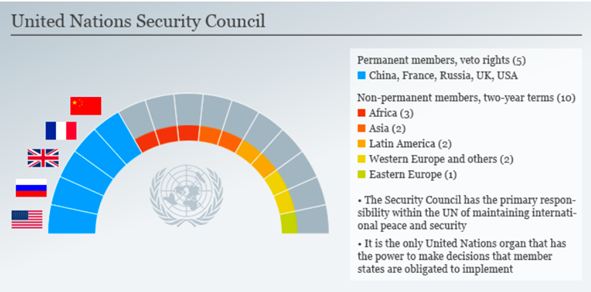
What is the UNSC ?
- The United Nation Security Council (UNSC) got five new non permanent members (Albania, Brazil, Gabon, Ghana and the United Arab Emirates).
- The Security Council was established by the UN Charter in 1945. It is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
- The other 5 organs of the United Nations are the General Assembly (UNGA), the Trusteeship Council, the Economic and Social Council, the International Court of Justice, and the Secretariat.
- Its primary responsibility is to work to maintain international peace and security. The council is headquartered at NewYork.
- Members :
- The council has 15 members: the five permanent members and ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- The five permanent members are the United States, the Russian Federation, France, China and the United Kingdom.
- India, for the eighth time, has entered the UNSC as a non-permanent member last year (2021) and will stay on the council for two years i.e 2021-22.
- Each year, the General Assembly elects five non-permanent members (out of ten in total) for a two-year term. The ten non-permanent seats are distributed on a regional basis.
- The council’s presidency is a capacity that rotates every month among its 15 members.
-
Voting Powers at the UNSC:
- Each member of the Security Council has one vote.
- Decisions of the Security Council on matters are made by an affirmative vote of nine members including the concurring votes of the permanent members.
- A “No” vote from one of the five permanent members blocks the passage of the resolution.
- Any member of the United Nations which is not a member of the Security Council may participate, without vote, in the discussion of any question brought before the Security Council whenever the latter considers that the interests of that member are specially affected.
Lynching in india :

Context :
- Recently a man was lynched in samastipur in Bihar
More about lynching :
- Mob lynching is a term used to describe the acts of targeted violence by a large group of people.
- The violence is tantamount to offences against human body or property
- The mob believes that they are punishing the victim for doing something wrong and they take the law in their own hands to punish the purported accused without following any rules of law.
Supreme Court observations on mob lynching
- In Tehseen Poonawalla vs Union of India, 2018, Supreme Court condemned recent incidents of lynching and mob violence against Dalits and minority community members as “horrendous acts of mobocracy“.
- It asked Parliament to pass law establishing lynching as a separate offence with punishment.
- Such a law should be effective enough to instill a sense of fear in the perpetrators
SC guidelines on lynchings :
- There shall be a “separate offence” for lynching and the trial courts must ordinarily award maximum sentence upon conviction of the accused person to set a stern example in cases of mob violence.
- The state governments will have to designate a senior police officer in each district for taking measures to prevent incidents of mob violence and lynching.
- The state governments need to identify districts, sub-divisions and villages where instances of lynching and mob violence have been reported in the recent past.
- Central and the state governments shall broadcast on radio, television and other media platforms about the serious consequences of mob lynching and mob violence.
- Despite the measures taken by the State Police, if it comes to the notice of the local police that an incident of lynching or mob violence has taken place, the police station shall immediately lodge an FIR.
- The State Governments shall prepare a lynching/mob violence victim compensation scheme in the light of the provisions of Section 357A of CrPC within one month from the date of this judgment.
- If a police officer or an officer of the district administration fails to fulfill his duty, it will be considered an act of deliberate negligence.
Chandrasekhar Azad

Context :
- Chandrasekhar Azad’s death anniversary was celebrated recently.
More about Azad :
- Azad was born on 23rd July 1906 in the Alirajpur district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Chandra Shekhar, then a 15-year-old student, joined a Non-Cooperation Movement in December 1921. As a result, he was arrested.
- On being presented before a magistrate, he gave his name as “Azad” (The Free), his father’s name as “Swatantrata” (Independence) and his residence as “Jail”. Therefore, he came to be known as Chandra Shekhar Azad.
- After the suspension of the non-cooperation movement in 1922 by Gandhi, Azad joined Hindustan Republican Association (HRA). HRA was a revolutionary organization of India established in 1924 in East Bengal by Sachindra Nath Sanyal, Narendra Mohan Sen and Pratul Ganguly as an offshoot of Anushilan Samiti.
- Members: Bhagat Singh, Chandra Shekhar Azad, Sukhdev, Ram Prasad Bismil, Roshan Singh, Ashfaqulla Khan, Rajendra Lahiri.
- Most of the fund collection for revolutionary activities was done through robberies of government property. In line with the same, Kakori Train Robbery near Kakori, Lucknow was done in 1925 by HRA. The plan was executed by Chandra Shekhar Azad, Ram Prasad Bismil, Ashfaqulla Khan, Rajendra Lahiri, and Manmathnath Gupta.
- HRA was later reorganised as the Hindustan Socialist Republican Army (HSRA). It was established in 1928 at Feroz Shah Kotla in New Delhi by Chandra Shekhar Azad, Ashfaqulla Khan, Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev Thapar and Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee.
- HSRA planned the shooting of J. P. Saunders, a British Policeman at Lahore in 1928 to avenge the killing of Lala Lajpat Rai.
- Azad died at Azad Park in Allahabad on 27th February 1931 after being surrounded by Police.
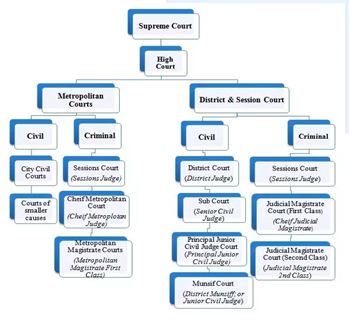
Judiciary needs more judges
Context :
- Chief Justice of India said there was a need to both increase the number of judges in High Courts and urgently fill existing vacancies.
- The vacancies in High Courts are at a staggering 455, as on 1st August, 2021.
Qualification of High court judges :
- He should be a citizen of India.
- He should have held a judicial office in the territory of India for ten years;
- He should have been an advocate of a high court (or high courts in succession) for ten years.
Salaries and Allowances :
- The salaries, allowances, privileges, leave and pension of the judges of a high court are determined from time to time by the Parliament.
- They cannot be varied to their disadvantage after their appointment except during a financial emergency.
- In 2018, the salary of the chief justice was increased from ?90,000 to 2.50 lakh per month and that of a judge from ?80,000 to 2.25 lakh per month
- The retired chief justice and judges are entitled to 50% of their last drawn salary as monthly pension
Removal of HC judges :
- A judge of a high court can be removed from his office by an order of the President.
- The President can issue the removal order only after an address by the Parliament has been presented to him in the same session for such removal.
- The address must be supported by a special majority of each House of Parliament (i.e., a majority of the total membership of that House and majority of not less than two-thirds of the members of that House present and voting).
- The grounds of removal are two–proved misbehaviour or incapacity.
- Thus, a judge of a high court can be removed in the same manner and on the same grounds as a judge of the Supreme Court.
- The Judges Enquiry Act (1968) regulates the procedure relating to the removal of a judge of a high court by the process of impeachment:
- A removal motion signed by 100 members (in the case of Lok Sabha) or 50 members (in the case of Rajya Sabha) is to be given to the Speaker/Chairman.
- The Speaker/Chairman may admit the motion or refuse to admit it.
- If it is admitted, then the Speaker/ Chairman is to constitute a three-member committee to investigate into the charges.
- The committee should consist of (a) the chief justice or a judge of the Supreme Court, (b) a chief justice of a high court, and (c) a distinguished jurist.
- If the committee finds the judge to be guilty of misbehaviour or suffering from an incapacity, the House can take up the consideration of the motion.
- After the motion is passed by each House of Parliament by special majority, an address is presented to the president for removal of the judge.
- Finally, the president passes an order removing the judge.
- No HC judge has been removed till now.
- The President can transfer a judge from one high court to another after consulting the Chief Justice of India
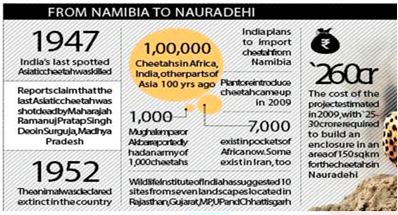
Wait for the Cheetah is to get longer
Context :
- It could be many months before cheetahs from Namibia make it to India.
- An expert team of wildlife officials from Madhya Pradesh, the Indian Forest Department and the Wildlife Institute of India that visited Namibia for a site visit last week is reportedly “satisfied”, but a formal Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) regarding the transfer is yet to be signed.
More on the news :
- An “action plan” was launched at the 19th meeting of the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- The action plan states that a cohort of 10-12 young cheetahs that are ideal for reintroduction would be imported from Namibia or South Africa as a founder stock during the first year.
- The animals lineage and genetic history will be examined to ensure that they are not from an excessively inbred stock and are in the ideal age group, so that they make up a suitable founding population.
- The proposed site for re-introduction is the Kuno Palpur National Park (KNP) in Madhya Pradesh, though at least three other reserves in Central India are being considered.
- ‘Reintroduction’ of a species means releasing it in an area where it is capable of surviving.
- Reintroductions of large carnivores have increasingly been recognised as a strategy to conserve threatened species and restore ecosystem functions.
Background :
- Recently, the Supreme Court had lifted its seven-year-long stay on a proposal to introduce African Cheetahs from Namibia into the Indian habitat.
- Court has now allowed the re-introduction of foreign Cheetahs into the Palpur Kuno sanctuary in Madhya Pradesh on an experimental basis.
- In 1952, the Asiatic Cheetah was officially declared extinct from India.
Characteristics of the Cheetah :
- African Cheetah :
- IUCN status is Vulnerable
- CITES status is Appendix-I of the List. This List comprises of migratory species that have been assessed as being in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of their range.
- Around 6,500-7,000 African cheetahs present in the wild.
- Bigger in size as compared to Asiatic Cheetah.
- Asiatic Cheetah :
- IUCN status is Critically Endangered.
- CITES status is Appendix-I of the List.
- Only 40-50 cheetahs are found only in Iran.
- Smaller and paler than the African cheetah. Has more fur, a smaller head and a longer neck. Usually have red eyes and they have a more cat-like appearance.
SPARSH: System for Pension Administration (Raksha):
Context :
- The Ministry of Defense has signed an agreement with CSC e-Governance Services India Limited (under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology)
- Agreement was to expand the coverage of pension services under SPARSH or System for Pension Administration (Raksha) across four lakh Common Service Centers.
More about the news :
- This will provide last mile connectivity to pensioners, especially those who live in remote areas of the country and those who do not have access or technical knowledge and skill to use SPARSH.
- SPARSH is an initiative of the Ministry of Defense.
- It aims to provide comprehensive services to defense pensioners.
- It promotes the Government’s vision of ‘Digital India’, ‘Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT)’ and ‘Minimum Government, Maximum Governance’.
Council of Europe
Context:
- Russia’s membership in the Council of Europe has been suspended after its invasion of Ukraine.
What’s the issue?
- Russia has launched a full-blown attack on Ukraine, with Russian forces entering the Obolon district, which is less than 10 km away from Central Kyiv the capital of Ukraine
More about council of europe :
- The Council of Europe is an international organization founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe.
- Founded in 1949 (Treaty of London (1949)), it has 46 member states (including all 27 EU members), with a population of approximately 820 million, and operates with an annual budget of approximately 500 million euros.
- Headquarters: Palace of Europe, Strasbourg, France.
- The Council of Europe cannot make binding laws, but it does have the power to enforce select international agreements reached by European states on various topics.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 28th February 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

