UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 3rd April 2022
Topics for the day:
- FASTER (Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records)
- Nepal Becomes Fourth country to implement Rupay
- India-Australia deal seeks to double bilateral trade in 5 years
- Army inducts Russian MANPADS
- At Rs 1.42L crore, March GST haul is a record
- CJI fags ‘falling credibility’ of CBI
FASTER (Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records)

Context:
- The Chief justice of India launched digital platform ‘Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records’
- The platform would be used by the court officials to instantly to send e-copies of the orders through a secured electronic communication channel to intended parties thus ensuring that judicial orders can be communicated quickly.
- Through the use of this software, orders that were passed by the high courts (HC) and the Supreme Court (SC) will be transmitted safely without any third-party interference.
- Bail orders will be communicated via FASTER and for authentication purposes, it will have the digital signatures of the notified nodal officers of the SC as well as the Institutional digital signatures.
- In this manner, without much loss of time, bail orders would be received by all the concerned parties and quick necessary actions will be taken at their end.
Need for such a system :
- There have been cases in the past where the inmates were not released by the prison authorities despite bail orders passed by the court as the certified hard copies of their bail orders reached the prison late.
- Thus, for smooth transmission of court’s orders and effective implementation of Article 21, Right to Life, such a system was the need of the hour.
- Ensure that undertrials are not made to wait for days on end behind bars to be released because the certified hard copies of their bail orders took time to reach the prison.
- Prevent unnecessary arrests and custody of people even after the court had already granted them its protection.
Nepal Becomes Fourth country to implement Rupay

Context :
- Nepal became the fourth foreign country to operationalise the RuPay card with Prime Minister Modi and his Nepalese counterpart PM Sher Bahadur Deuba jointly launching the Indian electronic payment system in the Himalayan nation.
- The three other countries that have the RuPay card are Bhutan, Singapore and the United Arab Emirates.
More about Rupay system :
- RuPay is the first-of-its-kind domestic Card payment network of India, with wide acceptance at ATMs, POS devices and e-commerce websites across India.
- It is a highly secure network that protects against anti-phishing.
- RuPay is an initiative of the National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI), the umbrella organization that powers retail payments in the country.
Some of the benefits of RuPay cards are as follows:
- Data of consumers and all the transactions pertaining to the RuPay card are secured under this scheme.
- Safe transactions: With SMS alerts and notifications that are sent to the customer’s phone number after every transaction, RuPay cardholders can be ensured of a secure transaction.
- Greater reach: RuPay Card was associated with the Jan Dhan Account hence, consumers in rural areas can easily apply and get a RuPay card.
- Less transaction costs: When it comes to the RuPay cards transactions, all the processing happens within the country. This results in a lower cost of settlement and clearing for the transactions made using a RuPay debit card.
- Banks will profit immensely from this as costs for transaction processing become affordable.
- Payment solutions across platforms: RuPay debit card is designed to provide complete interoperability between payment channels including mobile technology, ATMs, cheques, etc.
- Suitable for Indian customers: RuPay cards have been customized keeping in mind the product and service requirements of Indian customers, merchants and banks.
- Accidental insurance for RuPay ATM cardholders: All RuPay ATM-cum-debit cardholders are presently eligible for accidental death and permanent disability insurance cover.
- RuPay Classic cardholders are eligible for a cover of Rs 1 lakh, whereas RuPay Premium cardholders are eligible for a cover of Rs 2 lakh.
India-Australia deal seeks to double bilateral trade in 5 years
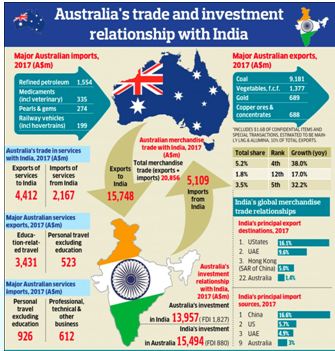
Context:
- India and Australia signed an Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA) on Saturday in the presence of Prime Minister Modi and his counterpart in Canberra Scott Morrison, with an eye on doubling bilateral trade to $50 billion in five years and easing movement of people, goods and services across borders.
Significance of the deal :
- The deal will increase the resilience of supply chains, and also contribute to the stability of the Indo-Pacific region
- The trade agreement is expected to double the bilateral trade to US$ 50 billion in five years and ease movement of people, goods and services across borders.
- The deal will facilitate work visas for two to four years for Indian students in Australia on a ‘reciprocal basis’ and allow Indian chefs and yoga professionals to work in the country.
- The trade and economic partnership deal with Australia, which is in the middle of a trade battle with China, is a significant milestone at a time when the developed world is looking to hedge its supply chain dependence.
What are the components of the deal ?
- The Agreement encompasses cooperation across the entire gamut of bilateral economic and commercial relations between the two countries.
- It covers areas like Trade in Goods, Trade in Services, Rules of Origin, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Customs Procedures, and Cooperation in other Areas.
-
Compulsory Review Mechanism:
- There will be a special review mechanism for compulsory review after 15 years for certain aspects of the agreement in a time-bound manner.
-
Zero Duty Access:
- Australia will provide zero-duty access to 96 per cent of India’s exports including shipments from key sectors such as engineering goods, gems and jewellery, textiles, apparel and leather.
- The agreement will also give about 85 per cent of Australia’s exports zero-duty access to the Indian market, including coal, sheep meat and wool, and lower duty access on Australian wines, almonds, lentils, and certain fruits.
-
Cheaper Raw Materials:
- Australian exports are more concentrated in raw materials and intermediates.
- Many industries in India will get cheaper raw materials and make them competitive, in particular for sectors like steel, aluminium, garments among others.
-
Service Sector Benefits: In the services sector, benefits for India include post study work visa of two-four years for Indian students on reciprocal basis.
- Easier movement of people: Work and holiday visa arrangement for young professionals will be eased.
- Eliminating Double Taxation: Australia has also agreed to amend its domestic tax law to stop the taxation of offshore income of Indian firms providing technical services in Australia.
Army inducts Russian MANPADS

Context and news :
- The Army which has long been looking for new man portable air defence systems (MANPADS), has inducted a small number of IglaS systems recently procured from Russia under emergency procurement
- However, a much larger contract for IglaS systems under the very short range air defence system (VSHORAD) deal is still pending and is under review by the Defence Ministry.
- The procurement was done through the ViceChief’s emergency financial powers given to the Services for the first time after the Balakot air strike and further extended after the standoff with China in Galwan.
- Under this, the Services can procure weapons systems up to ?300 crore on an urgent basis without any further clearances.
- The Request for Proposal for VSHORAD was issued in 2010 for over 5,000 missiles, 258 single launchers and 258 multilaunchers.
- Five contenders responded and eventually three made it to the trials – MBDA of France, Rosoboronexport of Russia and SAAB of Sweden. All three companies were declared technically compliant in 2017 and IglaS was declared the lowest bidder in 2018.
- VSHORADS are the soldier’s last line of defence against enemy combat aircraft and helicopters in the multilayered air defence network.
At Rs 1.42 L crore, March GST haul is a record

Context :
- GST revenue collected in March, 2022 stood at more than Rs 1.42 lakh crore – the highest recorded in a month since the introduction of GST.
- The GST revenues in March 2022 were 15% higher compared to March, 2021.
- Of the 1.42 lakh crore:
- Central GST (CGST) was about Rs 25,800 crore
- State GST (SGST) was about Rs 32,000 crore
- Inter-state GST (IGST) was about Rs 74,500 crore (incl Rs 39,000 crore collected on import of goods)
- Cess was Rs 9,400 crore (incl Rs 981 crore collected on import of goods)
- Reasons for high GST collections in March:
- Economic recovery and increased domestic consumption
- Anti-evasion activities by the government, especially action against fake billers
- Rate rationalization measures undertaken by the GST Council to correct ‘inverted duty structure’
- Inverted Tax Structure refers to a situation where the rate of tax, that is GST, on inputs is higher than the rate of tax on output supplies or finished goods.
More on GST :
- Goods and Services Tax is an indirect tax used in India on the supply of goods and services.
- It is a value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.
- It was launched in India on 1 July 2017 as a comprehensive indirect tax for the entire country.
- It is a comprehensive, multistage, destination based tax – comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except a few state taxes.
- It is paid by the consumers and is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.
- It is of three types i.e.
- CGST to be levied by the Centre
- SGST to be levied by the States
- IGST a tax levied on all Inter-State supplies of goods and/or services.
- All these taxes are levied at rates mutually agreed upon by the Centre and the States by the GST Council headed by the Union Finance Minister
- Import of goods or services would be treated as inter-state supplies and would be subject to Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST) in addition to the applicable customs duties.
- The products and taxes not subsumed under GST are(list not exhaustive) :
- Basic Customs Duty
- Social welfare surcharge
- National Calamity contingency duty
- Excise duty and state VAT on production/refining of Crude oil, Petrol (Motor Spirit), Diesel, Aviation Turbine Fuel and natural gas
- State Excise on production and sale of liquor for human consumption
- Electricity duty
- Road tax on vehicles
- Road and infrastructure cess
- Health cess
CJI fags ‘falling credibility’ of CBI
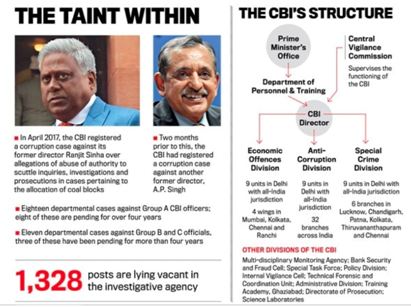
Context :
- Chief Justice of India (CJI) N.V. Ramana said that the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has come under deep public scrutiny.
- Its actions and inactions have raised questions regarding its credibility.
- In pursuit of reforming law enforcement agencies, the CJI has proposed an umbrella, independent and autonomous investigative agency.
What is the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)?
- The CBI was set up in 1963 by a resolution of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Now, the CBI comes under the administrative control of the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT) of the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- CBI derives power to investigate from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946.
- The establishment of the CBI was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption (1962–1964). T
- he CBI is the main investigating agency of the Central Government.
- It also provides assistance to the Central Vigilance Commission and Lokpal.
- It is also the nodal police agency in India which coordinates investigations on behalf of Interpol Member countries.
What are Associated Challenges With CBI?
- Political Interference: The Supreme Court of India has criticised the CBI by calling it a “caged parrot speaking in its master’s voice”, due to excessive political interference in its functioning.
- It has often been used by the government of the day to cover up wrongdoing, keep coalition allies in line and political opponents at bay.
- Overlapping Agencies: A single incident these days gets investigated by multiple agencies, often leading to dilution of evidence, contradiction in depositions, prolonged incarceration of innocents.
- Acute shortage of personnel: A major cause of the shortfall is the government’s sheer mismanagement of CBI’s workforce, through a system of inefficient, and inexplicably biased, recruitment policies – used to bring in favoured officers, possibly to the detriment of the organisation.
- Limited Powers: The powers and jurisdiction of members of the CBI for investigation are subject to the consent of the State Government, thus limiting the extent of investigation by CBI.
- Restricted Access: Prior approval of Central Government to conduct inquiry or investigation on the employees of the Central Government, of the level of Joint Secretary and above is a big obstacle in combating corruption at higher levels of bureaucracy.
How Law Enforcement Can be Improved?
- Creation of Independent Umbrella Institution: CJI proposed to bring various central agencies like the CBI, Enforcement Directorate and the Serious Fraud Investigation Office under one roof.
- This organisation should be headed by an independent and impartial authority, appointed by a committee akin to the one which appointed the CBI Director.
- The CJI said one additional in-built safeguard is to have separate and autonomous wings for prosecution and investigation, to ensure total independence.
- A reasonable check and balance would be a provision in the proposed law for annual audit of the institution’s performance by the appointing committee.
- With the police and public order under the State list, and the burden of investigation is primarily on the State police. The proposed Central law for the umbrella investigative body, can be suitably replicated by the States.
- Bringing Gender Parity: There was a need for adequate representation of women in the criminal justice system.
- Bringing Social Legitimacy: The need of the hour is to reclaim social legitimacy and public trust and the first step to gain the same is to break the nexus with the political executive.
- Criminal Justice System Reforms: There is need to implement long overdue Police Reforms and dealing with huge pendency of cases.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 3rd April 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

