UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 3rd March 2022
Topics for the day:
- GST revenue crosses 1.3lakh cr in February
- AAP govt and L-G at loggerheads
- CBI books arihant coal
- Non Alignment of india
- S-400 missile system
- National testing Agency to conduct JEE-mains first phase
GST revenue crosses 1.3 lakh cr in February
Context :
- The Gross Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenue in February was 26% higher than the pre-pandemic levels at 1,33,026 crore.
- The collections are 18% higher than those of February 2021 and mark the fifth time that GST revenues have crossed 1.3 lakh crore since its launch in July 2017.
- Revenues from import of goods were 38% higher year on-year, while revenues from domestic transaction, including import of services, were 12% higher than the revenues from these sources during February 2021.
- GST Compensation Cess collections crossed 10,000 crore in a month for the first time in February
More on GST :
- Goods and Services Tax is an indirect tax used in India on the supply of goods and services.
- It is a value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.
- It was launched in India on 1 July 2017 as a comprehensive indirect tax for the entire country.
- It is a comprehensive, multistage, destination based tax – comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except a few state taxes.
- It is paid by the consumers and is remitted to the government by the businesses selling the goods and services.
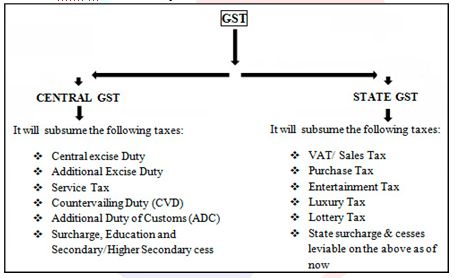
- It is of three types i.e.
- CGST to be levied by the Centre
- SGST to be levied by the States
- IGST a tax levied on all Inter-State supplies of goods and/or services.
- All these taxes are levied at rates mutually agreed upon by the Centre and the States by the GST Council headed by the Union Finance Minister
- Import of goods or services would be treated as inter-state supplies and would be subject to Integrated Goods & Services Tax (IGST) in addition to the applicable customs duties.
- The products and taxes not subsumed under GST are(list not exhaustive) :
- Basic Customs Duty
- Social welfare surcharge
- National Calamity contingency duty
- Excise duty and state VAT on production/refining of Crude oil, Petrol (Motor Spirit), Diesel, Aviation Turbine Fuel and natural gas
- State Excise on production and sale of liquor for human consumption
- Electricity duty
- Road tax on vehicles
- Road and infrastructure cess
- Health cess
GST compensation cess :
- States are guaranteed compensation for any revenue shortfall below 14% growth (base year 2015-16) for the first five years ending 2022.
- GST compensation is paid out of Compensation Cess every two months by the Centre to states.
- The compensation cess was specified by the GST (Compensation to States) Act, 2017.
- Under it, GST council recommended Union Govt to impose “GST Compensation Cess” on specified luxury & demerit goods, like :
- pan masala (60%)
- tobacco products (cess varies as per product)
- aerated water & Caffeinated Beverages (12%)
- coal / lignite (?400 per tonne)
- motor vehicles-aircraft-yacht (3-22% depending on type of vehicle)
- Automobiles
LG and Delhi govt at odds

Context :
- The Delhi government and Raj Niwas found themselves at loggerheads over the withdrawal of police cases related to the anti-farm laws agitation registered in the Capital
- The governors office was wondering as to why the Delhi govt was sitting on the file to withdraw cases registered against the protestors
- While the Delhi govt spokesperson held there was no delay in disposal of cases
Delhi Govt v/s LG
- The tussle between the LG and the Delhi govt has been a long drawn one due to the co-existence of Article 239 and 239AA, there is a jurisdictional conflict between the government of NCT and the Union Government and its representative, the Lieutenant Governor
- According to the Union government, New Delhi being a Union Territory Article 239 empowers the Lieutenant Governor to act independently of his Council of Ministers.
- However, the state government of Delhi held that the Article 239AA of the Constitution bestows special status to Delhi of having its own legislatively elected government.
The GNCT of Delhi(Amendment) Act 2021 :
- The Government of National Capital Territory (GNCT) of Delhi (Amendment) Act, 2021, which gives primacy to the Lieutenant Governor (L-G) over the elected government in the city, has recently come into force.
- It amended the Sections 21, 24, 33 and 44 of the 1991 NCT Act.
- States that the “government” in the National Capital Territory of Delhi meant the Lieutenant-Governor of Delhi.
- It gives discretionary powers to the L-G even in matters where the Legislative Assembly of Delhi is empowered to make laws.
- It seeks to ensure that the L-G is “necessarily granted an opportunity” to give her or his opinion before any decision taken by the Council of Ministers (or the Delhi Cabinet) is implemented.
- It bars the Assembly or its committees from making rules to take up matters concerning day-to-day administration, or to conduct inquiries in relation to administrative decisions.
CBI books arihant coal
Context :
- The Central Bureau of Investigation has booked Arihant Coal Sales (I) Private Limited and its senior functionarie for cheating bank of baroda
- Recently CBI booked a case against ABG shipyard in the biggest banking fraud in india’s history
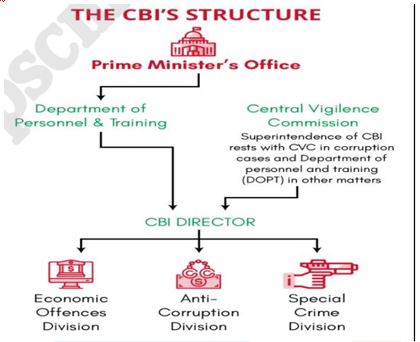
More about the CBI :
- The establishment of the CBI was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption
- The CBI is not a statutory body. It derives its powers from the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946.
- The CBI is the main investigating agency of the Central Government. It plays an important role in the prevention of corruption and maintaining integrity in administration.
- It also provides assistance to the Central Vigilance Commission and Lokpal.
- CBI investigates crime of corruption, economic offences and serious and organized crime other than terrorism.
- The Director of CBI has been provided security of two-year tenure in office by the CVC Act, 2003
- CBI is exempted from the provisions of the Right to Information Act, thus, lacking public accountability
- Composition of the CBI as given under lokpal act,2013:
- The Central Government shall appoint the Director of CBI on the recommendation of a three-member committee consisting of the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and the Chief Justice of India or Judge of the Supreme Court nominated by him.
- There shall be a Directorate of prosecution headed by a Director for conducting the prosecution of cases under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act, 2013. The director shall be appointed by the Central Government on the recommendation of the Central Vigilance Commission. He shall hold office for a period of two years.
- The Central Government shall appoint officers of the rank of SP and above in the CBI on the recommendation of a committee consisting of the Central Vigilance Commissioner as Chairperson, the Vigilance Commissioners, the Secretary of the Home Ministry and the Secretary of the Department of Personnel
Non Alignment of India
Context :
- India recently ??abstained on a UN General Assembly resolution that strongly deplored Russia’s aggression against Ukraine, the third abstention in less than a week by the country in the world body
What is non alignment ?
- Non alignment is not neutrality but rather NAM had sought to “create an independent path in world politics that would not result in member States becoming pawns in the struggles between the major powers.”
More about non alignment :
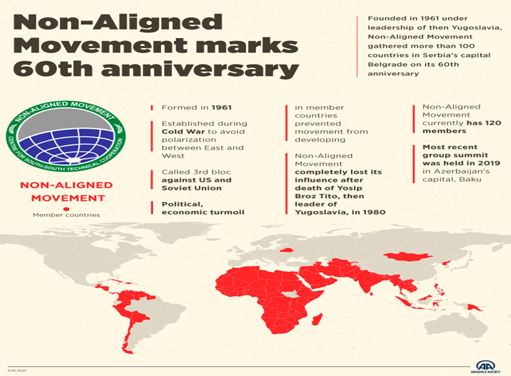
- The Non-Aligned Movement was formed during the Cold War as an organization of States that did not seek to formally align themselves with either the United States or the Soviet Union, but sought to remain independent or neutral.
- The basic concept for the group originated in 1955 during discussions that took place at the Asia-Africa Bandung Conference held in Indonesia.
- The first NAM Summit Conference took place in Belgrade, Yugoslavia, in September 1961.
- The Non-Aligned Movement was founded and held its first conference (the Belgrade Conference) in 1961 under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito of Yugoslavia, Gamal Abdel Nasser of Egypt, Jawaharlal Nehru of India, Kwame Nkrumah of Ghana, and Sukarno of Indonesia.
- The purpose of the organization was enumerated in Havana Declaration of 1979 to ensure “the national independence, sovereignty, territorial integrity and security of non-aligned countries” in their struggle against imperialism, colonialism, neo-colonialism, racism, and all forms of foreign subjugation.
- It has 120 members as on April 2018 comprising 53 countries from Africa, 39 from Asia, 26 from Latin America and the Caribbean and 2 from Europe (Belarus, Azerbaijan).
- The indian PM has skipped the last two NAM summits in venezuela (2016) and Baku(2019)
S-400 missile system
Context :
- With tensions escalating between Russia and the West over the Ukraine crisis, India, which has major defence cooperation with Moscow and Kyiv, faces uncertainty over timely deliveries in the near future in addition to the lingering threat of the U.S. sanctions under CAATSA (Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act) over the S-400 deal.
- In the past, tensions between Russia and Ukraine had considerably delayed the modernisation of the An-32 transport fleet of the Indian Air Force (IAF)
More about the S-400 system :
- India signed a 43 billion USD deal with Russia for the S-400 Triumf missile system despite objections from the US and the threat of sanctions under Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA)
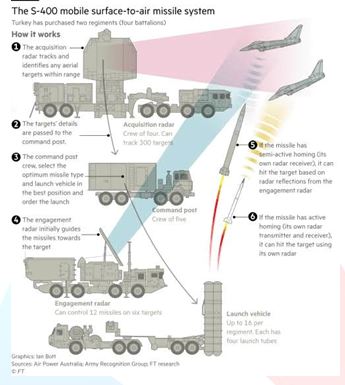
- The S-400 Triumf is a mobile, surface-to-air missile system (SAM) designed by Russia.
- It is the most dangerous operationally deployed modern long-range SAM (MLR SAM) in the world, considered much ahead of the US-developed Terminal High Altitude Area Defense system (THAAD).
- It has radars that can pick up an incoming object up to a distance of 1,000 kilometres, track several dozen incoming objects simultaneously, distribute the targets to missile systems and ensure a high success rate.
- The system can engage all types of aerial targets including aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) and ballistic and cruise missiles within the range of 400km, at an altitude of up to 30km.
- The system can track 100 airborne targets and engage six of them simultaneously.
Significance for India :
- India’s acquisition is crucial to counter attacks in a two-front war, including even high-end F-35 US fighter aircraft.
- From India’s point of view, China is also buying the system. In 2015, China signed an agreement with Russia to purchase six battalions of the system
National testing Agency to conduct JEE-mains first phase
Context :
- The JEE-Main’s first phase will be conducted in April while the second phase is scheduled in May, officials of the National Testing Agency (NTA) said.
National testing agency :
- National Testing Agency is responsible for conducting competitive entrance exams like NEET, JEE, CTET, GATE, GPAT, GMAT, CAT, UGC NET, etc.
- National Testing Agency (NTA) was established as a Society registered under the Indian Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It is an autonomous and self-sustained testing organization to conduct entrance examinations for admission/fellowship in higher educational institutions.
Governance of the NTA :
- NTA is chaired by an eminent educationist appointed by the Ministry of Human Resource Development.
- The Chief Executive Officer (CEO) will be the Director-General to be appointed by the Government.
- There will be a Board of Governors comprising members from user institutions.
Significance of NTA
- Establishment of a specialized testing body like NTA has relieved the agencies such as CBSE, AICTE of their responsibilities of conducting Entrance examinations.
- Examinations are conducted by NTA in the online mode at least twice a year, in order to give enough opportunities to candidates and to bring out the best in them.
- In order to increase the accessibility and meet the requirements of the rural students, it will locate centers at sub-district and district level.
Functions of NTA :
- To identify partner institutions with adequate infrastructure from the existing schools and higher education institutions which would facilitate the conduct of online examinations without adversely impacting their academic routine.
- To create a question bank for all subjects using modern techniques.
- To establish a strong R&D culture as well as a pool of experts in different aspects of testing.
- To provide training and advisory services to the institutions in India.
- To collaborate with international organizations like ETS (Educational Testing Services).
- To undertake any other examination that is entrusted to it by the Ministries/Departments of Government of India/State Governments.
- To undertake the reforms and training of school boards as well as other bodies where the testing standards should be comparable with the entrance examinations.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 3rd March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

