UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 6th March 2022
Topics for the day:
- No fly zone over ukraine
- FATF retains Pak. on its terror funding ‘grey list’
- IMF warns of ‘serious’ global economic impact
- Data protection bill
- National commission for protection of child rights
- Voter islands
No fly zone over ukraine
Context :
- Russia’s attack on Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant has renewed calls for NATO to impose a no-fly zone over Ukraine, despite the repeated rejection of the idea by western leaders concerned about triggering a wider war in Europe
- Ukrainian President asked the people of Western Europe to demand that their leaders change course because the shelling of a nuclear power plant in Ukraine threatens the security of the entire continent
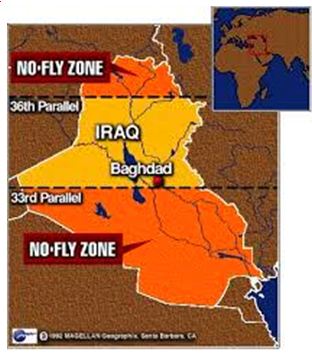
What is a no-fly zone ?
- A no-fly zone would bar all unauthorized aircraft from flying over Ukraine.
- Western nations imposed such restrictions over parts of Iraq for more than a decade following the 1991 Gulf War, during the civil war in Bosnia and Herzegovina from 1993-95, and during the Libyan civil war in 2011.
Consequences of a no-fly zone :
- US, Britain and their European allies are skeptical about imposing a no-fly zone because it could easily escalate the war in Ukraine into a nuclear confrontation between NATO and Russia
- Declaring a no-fly zone could force NATO pilots to shoot down Russian aircraft.
- In addition to fighter planes, NATO would have to deploy refueling tankers and electronic-surveillance aircraft to support the mission.
- To protect these relatively slow, high-flying planes, NATO would have to destroy surface-to-air missile batteries in Russia and Belarus, again risking a broader conflict.
What would a no-fly zone achieve?
- Ukrainian authorities and people cowering night after night in bomb shelters say a no-fly zone would protect civilians and now nuclear power stations from Russian air strikes.
FATF retains Pak. on its terror funding ‘grey list’
Context :
- The global money laundering and terrorist financing watchdog FATF has retained Pakistan on its terrorism financing “grey list” and asked Islamabad to address at the earliest the remaining deficiencies in its financial system
- Since then, the country continues to be on that list due to its failure to comply with the FATF mandates.
- The FATF decided against exiting Pakistan from the category despite the country meeting 32 out of 34 action points
Background :
- Pakistan has been on the grey list of the Paris-based Financial Action Task Force (FATF) since June 2018 for failing to check money laundering, leading to terror financing, and was given a plan of action to complete it by October 2019.
Commendable efforts :
- However, Pakistan’s robust progress on its global commitments to fight financial crimes was appreciated at the concluding session of its meeting, which noted that :
- Pakistan had completed 26 of the 27 action items in its 2018 action plan of the FATF
- For completing most of the seven action items of the 2021 action plan of the watchdog’s Asia Pacific Group on Money Laundering.
More about FATF :
- It is an Intergovernmental organisation created in 1989(Initiative of G7 to combat money laundering)
- In 2001,mandate expanded to include terrorist financing
- Its secretariat at headquarters of OECD itself in paris
- It monitors implementation through peer reviews
- India is a member.India became an observer in the grouping in 2006, and was inducted as a full member in 2010
- FATF depends on voluntary implementation of its reports by member countries
- Also, meetings of the group are carried out behind closed doors, and deliberations are not publicized
- Decisions are made by the grouping on a consensus basis, as they conduct reviews of countries on AML/CFT parameters(Anti-Money-Laundering & Countering Financing of Terrorism) (called “Mutual evaluations”), and then either clear them, or use a “colour coded” reference for them, placing countries in the “monitored jurisdictions” category or the “grey list”, or the “high risk jurisdictions” or “call for action” category, as the “blacklist” is formally known
- Pakistan is one of 18 countries on the greylist; Iran and North Korea are on the blacklist(Formally known as “high risk jurisdictions”)
IMF warns of ‘serious’ global economic impact
Context :
- The IMF warned that the already “serious” global economic impacts of the war in Ukraine would be “all the more devastating” should the conflict escalate.
- Even as forecasts remain subject to “extraordinary uncertainty, the economic consequences” of the invasion launched by Russia “are already very serious”, the IMF said.
- A surge in energy and commodity prices have piled on the inflationary hike that the world was already experiencing as economies recover from the pandemic.
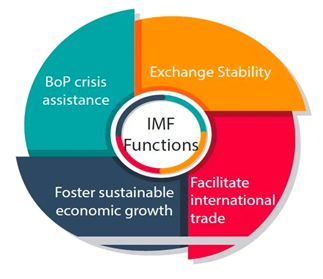
What is the IMF ?
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 189 member countries, each of which has representation on the IMF’s executive board in proportion to its financial importance
- Objective of the IMF :
- Foster global monetary cooperation
- Secure financial stability
- Facilitate international trade
- Promote high employment and sustainable economic growth
- Reduce poverty around the world
- The IMF was conceived at a UN conference in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, in July 1944.
- Countries are not eligible for membership in the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) unless they were members of the IMF.
What are IMF Quotas?
- The IMF is a quota-based institution.
- Quotas are the building blocks of the IMF’s financial and governance structure. An individual member country’s quota broadly reflects its relative position in the world economy.
- Nations with larger economic importance have larger quotas.
- Quotas are denominated in Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), the IMF’s unit of account.
- The quotas are increased periodically as a means of boosting the IMF resources in the form of Special Drawing Rights.
Multiple roles of quotas
- Resource Contributions – Quotas determine the maximum amount of financial resources a member is obliged to provide to the IMF.
- Voting Power – Quotas are a key determinant of the voting power in IMF decisions. Votes comprise one vote per SDR100,000 of quota plus basic votes (same for all members).
- Access to Financing – Quotas determine the maximum amount of financing a member can obtain from the IMF under normal access.
- SDR Allocations – Quotas determine a member’s share in a general allocation of SDRs.
Special Drawing Rights :
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) are supplementary foreign exchange reserve assets defined and maintained by the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- SDR is not a currency, instead represents a claim to currency held by IMF member countries for which they may be exchanged.
- The value of an SDR is defined by a weighted currency basket of major currencies – the US Dollar, the Euro, the British Pound, the Chinese Yuan and the Japanese Yen.
- Central banks of member countries hold SDRs with IMF which can be used by them to access funds from the IMF in case of financial crises in their domestic market.
India and the IMF :
- India’s quota in the IMF is SDR 13,114.4 million that gives India a shareholding of 2.76%.
- This makes India the eight largest quota holding country at the organization.
- In 2000, India completed the repayment of all the loans it had taken from the IMF.
Data protection bill
Context :
- The government has said that it is studying the inputs received on the draft data protection bill, and will carefully ensure that any legislation in the digital ecosystem will act as an enabler, fuelling the growth momentum.
- On December 16, 2021, the Joint Committee on Personal Data Protection Bill had tabled its report in both the Houses of Parliament, giving its views on various provisions.
Background :
- Nearly two years after it was constituted on 11 December 2019, the Joint Committee on the Personal Data Protection Bill, 2019, presented its final report on the upcoming bill in both Houses of Parliament on 16 December.
Key recommendations of the committee :
- Remove the word ‘personal’ from the existing title of ‘Personal Data Protection Bill’.
- This is intended to reflect that the bill, in order to better ensure privacy, will also be dealing with non-personal data, such as personal data that has been anonymised.
- Amend the section restricting the transfer of personal data outside India to say “sensitive personal data shall not be shared with any foreign government or agency unless such sharing is approved by the central government.
- No social media platform be allowed to operate in India unless its parent company, which controls the technology powering its services, sets up an office in the country.
- It proposes a separate regulatory body to be set up to regulate the media.
- Jail term of up to 3 years, fine of Rs 2 lakh or both if de-identified data is re-identified by any person.
- Central government may exempt any government agency from the legislation only under exceptional circumstances.
National commission for protection of child rights
Context :
- National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) celebrated its 17th Foundation Day, recently.
About the NCPCR:
- NCPCR was set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005, an Act of Parliament
- The Commission began operational on 5 March 2007.
- NCPCR is a statutory body under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development, Government of India.
Mandate of the commission :
- The Commission’s Mandate is to ensure that all Laws, Policies, Programmes, and Administrative Mechanisms are in consonance with the Child Rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Definition of a Child:
- Under the CPCR Act, The Child is defined as a person in the 0 to 18 years age group.
Functions of NCPCR:
- Under the RTE Act, 2009, the NCPCR can:
- Inquire into complaints about violation of the law.
- Summon an individual and demand evidence. Seek a magisterial enquiry.
- File a writ petition in the High Court or Supreme Court.
- Approach the government concerned for prosecution of the offender.
- Recommend interim relief to those affected.
Composition of NCPCR:
- This commission has a chairperson and six members.Of which at least two should be women.
- These are appointed by Central Government for three years.
- The maximum age to serve in commission is 65 years for Chairman and 60 years for members.
Voter islands
Context :
- Political leaders participating in the delimitation process in J&K as well as independent observers have raised fears of “islands” being formed.
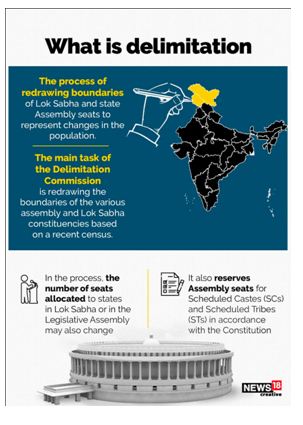
What’s the issue?
- The Delimitation Act, 2002 says that apart from population, the constituencies have to be geographically compact areas and contiguous.
- Observers say this principle is not being followed in the ongoing Delimitation exercise.
- For example, a village in one tehsil would be completely surrounded by villages in another Tehsil.
- Geographical connectedness is not being considered here.
- This gives rise to the voter islands.
- It is being said that the Commission “has carved out geographical islands and joined with the other Assembly segments without any proximity or connectivity”.
Delimitation exercise in J&K – Recent news :
- In 2020, the Delimitation Commission was constituted to carry out the exercise on the basis of 2011 Census, with a mandate to add seven more seats to the Union Territory and grant reservations to SC and ST communities.
- Now, the total number of seats in Jammu and Kashmir will be raised to 90 from the previous 83.
- This is apart from 24 seats which have been reserved for areas of PoK and have to be kept vacant in the Assembly.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 6th March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

