UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 8th April 2022
Topics for the day:
- UNGA suspends Russia from UNHRC. India abstains from voting again
- India offers help to end Russia-Ukraine conflict
- Bill to ban funding of weapons of mass destruction passed in Lok Sabha
- Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
- Centre constitutes Dam Safety Authority with temporary officials
- Nipah Virus research
- ‘Prakriti’ green initiatives for effective plastic waste management
UNGA suspends Russia from UNHRC. India abstains from voting again

Context :
- Russia was suspended from the UN Human Rights Council after the 193-member General Assembly voted to adopt a resolution moved by the US that received 93 votes in favour and 58 abstentions, including by India.
- The resolution titled ‘Suspension of the rights of membership of the Russian Federation in the Human Rights Council’ was adopted
- Those abstaining included Bangladesh, Bhutan, Brazil, Egypt, Indonesia, Iraq, Malaysia, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, Sri Lanka and UAE.
-
Decision of India :
- Since January this year, India has abstained on at least eight occasions on procedural votes and draft resolutions in the UN Security Council, the General Assembly and the Human Rights Council that deplored Russian aggression against Ukraine.
- According to the Ambassador to the UN TS Tirumurti – “India has abstained on the resolution with regard to suspension of the Russian Federation from the Human Rights Council adopted in the General Assembly today. We do so for reasons of both substance and process”
More about the UNHRC :
- The Human Rights Council is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system responsible for strengthening the promotion and protection of human rights around the world
- The Council was created by the United Nations General Assembly in 2006. It replaced the former United Nations Commission on Human Rights.
- The Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) serves as the Secretariat of the Human Rights Council.
- OHCHR is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Membership :
- It is made up of 47 United Nations Member States which are elected by the UN General Assembly (UNGA).
- The UNGA takes into account the candidate States’ contribution to the promotion and protection of human rights, as well as their voluntary pledges and commitments in this regard.
- Members of the Council serve for a period of three years and are not eligible for immediate re-election after serving two consecutive terms.
- Important mechanisms :
- Universal Periodic Review: UPR serves to assess the human rights situations in all United Nations Member States.
- UN Special Procedures: These are made up of special rapporteurs, special representatives, independent experts and working groups that monitor, examine, advise and publicly report on thematic issues or human rights situations in specific countries.
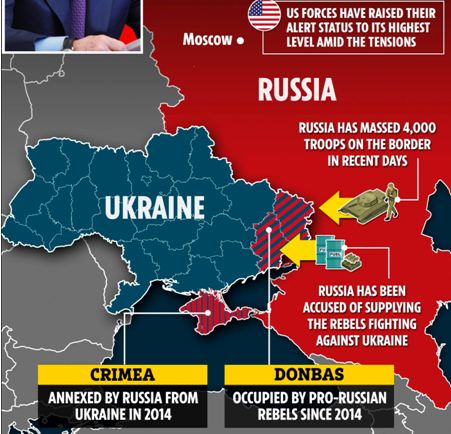
India offers help to end Russia-Ukraine conflict
Context :
- India will be “glad” to help in bringing about a resolution for the crisis in Ukraine, External Afairs Minister S. Jaishankar said.
- Speaking in the Lok Sabha during a discussion under Rule 193 regarding the crisis in Ukraine and its implications, Dr. Jaishankar said that Russia is “a very important partner” but also held that India is against the conflict.
- He acknowledged the support from Russia, Ukraine and even Indian nationals based in Eastern Europe during Operation Ganga to evacuate Indian students from Ukraine.
His speech :
- In terms of diplomacy, India continues to press forcefully for an immediate cessation of hostilities and an end to violence.
- We encourage talks between Ukraine and Russia, including at the level of their Presidents. The Prime Minister has spoken to them both. This was the message that was conveyed to Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov when he was in Delhi.
- If India can be of any assistance in this matter, we will be glad to contribute,he said.
- Our efort today is to stabilise economic transactions between India and Russia because this is very important for us. Russia is a very important partner in a variety of areas, indirectly referring to the crucial role Russia plays in India’s defence sector.
- Russia continues to remain the largest arms supplier to India despite strong competition from France, Israel, the United States and other western countries.
Operation Ganga :
- Operation Ganga is an ongoing operation by the Government of India to provide humanitarian assistance amidst the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine to Indian citizens who have crossed over to neighboring countries.
- This then involves transport assistance from the neighboring countries of Romania, Hungary, Poland, Moldova, Slovakia to reach India.
- Four union ministers were sent to the neighboring countries to assist in prioritising coordination with local authorities.
- The Indian Air Force and multiple private airlines (Air India, IndiGo, Air India Express and SpiceJet) provided logistical support
Other such missions :
-
Vande bharat mission –
- When the Covid-19 pandemic hit the world, the Centre launched the Vande Bharat Mission to bring back Indian citizens stranded in foreign countries.
- In the multiple phases of the operation, about 60 lakh Indians were brought back as on 30th April, 2021
-
Operation samudra setu –
- It was a naval operation as part of the national effort to bring home Indian citizens from overseas during the Covid-19 pandemic.
- It successfully brought back 3,992 Indian citizens to their homeland by sea.
- Indian Naval ships Jalashwa (Landing Platform Dock), and Airavat, Shardul and Magar (Landing Ship Tanks) participated in this operation which lasted over 55 days and involved traversing more than 23,000 km by sea.
-
Operation rahat –
- In 2015, a conflict raged between the Yemeni government and Houthi rebels.
- Thousands of Indians were stranded and Yemen was not accessible by air due to a no-fly zone announced by Saudi Arabia.
- Under Operation Raahat, India evacuated nearly 5,600 people from Yemen.
-
Operation sankat mochan
- Operation Sankat Mochan was an operation of the Indian Air Force to evacuate Indian citizens and other foreign nationals from South Sudan during the South Sudanese Civil War.
- The operation was carried out in view of 2016 Juba clashes.
Bill to ban funding of weapons of mass destruction passed in Lok Sabha

Context :
- The Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Amendment Bill, 2022 has been unanimously passed in Lok Sabha.
- The Bill seeks to amend The Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act, 2005, to provide against the financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems in line with India’s international obligations.
- The 2005 Act prohibits unlawful activities (such as manufacturing, transport, or transfer) related to weapons of mass destruction, and their means of delivery.
More on the new bill :
- Prohibition on financing certain activities: The Bill bars persons from financing any prohibited activity related to weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems.
- To prevent persons from financing such activities, the central government may freeze, seize or attach their funds, financial assets, or economic resources (whether owned, held, or controlled directly or indirectly).
- It may also prohibit persons from making finances or related services available for the benefit of other persons in relation to any activity which is prohibited.
Need for the bill :
- The need to amend the Act has arisen from the fact that in recent times, regulations relating to proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems by international organisations have expanded.
- The United Nations Security Council’s targeted financial sanctions and the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force have mandated against financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction and their delivery systems.
What are weapons of mass destruction ?
- While there is no single, authoritative definition of a WMD in international law, the expression is usually understood to cover nuclear, biological, and chemical (NBC) weapons.
- According to the United States Department of Homeland Security, “A weapon of mass destruction is a nuclear, radiological, chemical, biological, or other device that is intended to harm a large number of people.”
- India’s 2005 WMD Act defines:
- “Biological weapons” as “microbial or other biological agents, or toxins…of types and in quantities that have no justification for prophylactic, protective or other peaceful purposes; and weapons, equipment or delivery systems specially designed to use such agents or toxins for hostile purposes or in armed conflict”
- “Chemical weapons” as “toxic chemicals and their precursors” except where used for peaceful, protective, and certain specified military and law enforcement purposes; “munitions and devices specifically designed to cause death or other harm through the toxic properties of those toxic chemicals”; and any equipment specifically designed for use in connection with the employment of these munitions and devices.
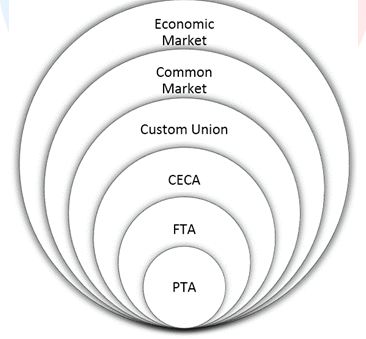
Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Context :
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry informed Lok Sabha about the Free Trade Agreements (FTAs).
More about the news:
- So far, India has signed 13 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners.
- This includes the 3 agreements, namely India-Mauritius Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA), India-UAE Comprehensive Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (IndAus ECTA) signed during the last five years.
The list of FTAs signed by India is as under:
- India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
- Agreement on South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA)
- India-Nepal Treaty of Trade
- India-Bhutan Agreement on Trade, Commerce and Transit
- India-Thailand FTA – Early Harvest Scheme (EHS)
- India-Singapore Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA)
- India-ASEAN CECA – Trade in Goods, Services and Investment Agreement
- India-South Korea Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
- India-Japan CEPA India-Malaysia CECA
- India-Mauritius Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA)
- India-UAE CEPA
- India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA)
In addition, India has signed the following 6 limited coverage Preferential Trade Agreements (PTAs):
- Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA)
- Global System of Trade Preferences (GSTP)
- SAARC Preferential Trading Agreement (SAPTA)
- India-Afghanistan PTA
- India-MERCOSUR PTA
- India-Chile PTA
Centre constitutes Dam Safety Authority with temporary officials

Context :
- The Union Ministry of Jal Shakti has established the National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) with a temporary composition of officials.
More on the news :
- Conceived under the Dam Safety Act, which came into force on December 30, the NDSA is the regulatory body.
- It will implement policies and address unresolved issues between two States.
- The Act provides that the NDSA will perform the role of the State Dam Safety Organisation for a dam located in one State and used by another, as in the case of the Mullaperiyar dam.
- For now :
- The Member (Designs & Research) in the Central Water Commission (CWC) has been entrusted additionally with the charge of being the chairperson of the Authority.
- Four chief engineers in the CWC have been made members in charge of Policy & Research, Technical, Regulation, and Disaster & Resilience.
- The Joint Secretary & Financial Advisor in the Ministry is the Member for Administration and Finance.
- The chief engineers and the Joint Secretary will all hold the posts in the Authority as additional charge.
- The four regional offices of the CWC would assist the members.
Features of the dam safety bill :
- National Committee on Dam Safety: The National Committee on Dam Safety will be constituted and will be chaired by the Chairperson, Central Water Commission.
- Functions of the Committee will include formulating policies and regulations regarding dam safety standards and prevention of dam failures, and analysing the causes of major dam failures and suggesting changes in dam safety practices.
- National Dam Safety Authority: The Bill also envisages setting up of a National Dam Safety Authority to be headed by an officer not below the rank of an Additional Secretary, to be appointed by the central government.
- The main task of the National Dam Safety Authority includes implementing the policies formulated by the National Committee on Dam Safety, resolving issues between State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSOs), or between an SDSO and any dam owner in that state, specifying regulations for inspection and investigation of dams.
- The NDSA will also provide accreditation to agencies working on construction, design and alteration of dams.
- State Dam Safety Organisation: The proposed legislation also envisages constituting a State Dam Safety Organisation whose functions will be to keep perpetual surveillance, inspection, monitoring the operation and maintenance of dams.
- Obligations of Dam Owners: The owners of the specified dams are required to provide a dam safety unit in each dam. This unit will inspect the dams before and after the monsoon session, and during and after every earthquake, flood, or any other calamity or sign of distress
- Punishment: The Bill provides for two types of offences – obstructing a person in the discharge of his functions, and refusing to comply with directions issued under the proposed law.
- Offences will be cognisable only when the complaint is made by the government, or any authority constituted under the Bill.
Nipah Virus research
Context :
- Scientists at Pune’s Indian Council of Medical Research – National Institute of Virology were able to detect the presence of IgG antibodies against Nipah virus infection (NiV) in 51 bats that were captured from Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
What is Nipah virus ?
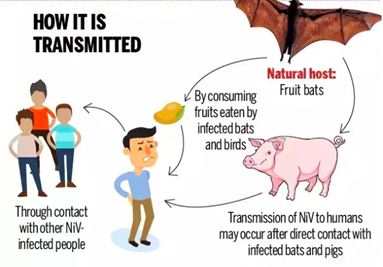
- It is a zoonotic virus (it is transmitted from animals to humans).
- It first broke out in Malaysia and Singapore in 1998 and 1999.
- It first appeared in domestic pigs and has been found among several species of domestic animals including dogs, cats, goats, horses and sheep.
Spread:
- The virus is transmitted to people from animals and can also be passed on through contaminated food or directly from person-to-person.
- Fruit bats are considered to be a natural reservoir of the virus.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms include acute encephalitis and respiratory illnesses.
Prevention: Currently, there are no vaccines for both humans and animals. Intensive supportive care is given to humans infected by Nipah virus.
What are Antibodies ?
- Antibody (Ab) is also known as an immunoglobulin(Ig).
- These are large, Y-shaped blood proteins produced by plasma cells. They bind to foreign particles and invade them
Types of antibodies :
- IgM
- IgM is the first antibody produced in response to a microbial attack by B cells.
- It is the largest antibody
- It circulates in the blood and lymph and constitutes 6% of the total antibody content in the serum.
- IgG
- Most abundant isotype in the plasma, and comprises 80% of the total antibody content in the serum.
- It detoxifies substances that are harmful and recognizes the antibody-antigen complex.
- It is transferred to the placenta through the foetus and protects the infant until its birth.
- IgA
- Usually found in liquids such as breast milk, serum, saliva, fluids of the intestine.
- IgA in breast milk protects an infant’s gastrointestinal tract from microbial activity.
- It constitutes 13% of the total antibody content in the serum and is divided into 2 sub-classes- IgA1 and IgA2.
- IgD
- It comprises less than 1% of the total antibody content in serum.
- It acts as a receptor on the B cell surface and participates in B cell activation and differentiation.
- IgE
- IgE is present in the least amounts, around 0.02% of the antibody content in the serum.
- These are present in the linings of the respiratory and intestinal tracts and respond to allergic reactions.
‘Prakriti’ green initiatives for effective plastic waste management

Context :
- In a step toward eliminating single-use plastic(SUP), the Union Environment Ministry has launched “Prakriti”, a mascot to spread greater awareness about small changes that can be sustainably adopted in the lifestyle for a better environment
Other green initiatives launched at the same time :
- National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management (MoEFCC): This aims to connect all stakeholders including Central Ministries/ Departments, State/UT Governments, etc. through one platform and track status and progress made for elimination of single use plastic & effective management of plastic waste.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Portal for Plastic Packaging (CPCB): This portal will look after tasks that will help in overall operational functions like improving accountability, traceability, transparency and facilitating ease of reporting compliance to EPR Obligations by Producers, Importers and Brand-owners.
- Mobile App for Single Use Plastics Grievance Redressal (CPCB): This app will allow citizens to check sale/usage/manufacturing of single use plastic in their region and tackle the plastic menace.
- Monitoring module for single use plastic (CPCB): This will be for local bodies, State pollution control board/PCCs and CPCB, etc. to invent details of single use plastic production, its sale & usage, etc. in commercial establishments at district level, and on-ground enforcement of ban on single use plastics.
- Industrial production of Graphene from Waste Plastic (G B Pant NIHE & NRDC) will promote more industries to come forward to upcycle plastic waste.
Government’s strategy to ban SUP’s:
- A government committee has identified the single use plastic (SUP) items to be banned based on their utility and environmental impact.
- It has proposed a three-stage ban:
- The first category of SUP items proposed to be phased out are plastic sticks used in balloons, flags, candy, ice-cream and ear buds, and thermocol that is used in decorations.
- The second category, proposed to be banned from July 1, 2022, includes items such as
- plates, cups, glasses and cutlery such as forks, spoons, knives, straws, trays;
- wrapping and packing films used in sweet boxes;
- invitation cards;
- cigarette packets; stirrers and plastic banners that are less than 100 microns in thickness.
- A third category of prohibition is for non-woven bags below 240 microns in thickness. This is proposed to start from September next year.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 8th April 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

