Topics
- 5G Technology
- RBI AND CRYPTOCURRENCY
- H10N3 Bird Flu Strain
- Positive Indigenisation List
- Research Design & Standards Organization (RDSO)
1.5G Technology
Context: Environmental activist and Bollywood actor, Juhi Chawla has moved the Delhi High Court against 5G rollout in India.
About:
- Actor has moved the Delhi High Court seeking a scientific study on any adverse effects of 5G technology and low intensity radiofrequency (RF) electronic magnetic field (EMF) radiation on ‘health, life, organ or limb of adult or child, or to flora and fauna’ before its official rollout in the country.
- Trial runs for the same have started in India now.
- The fifth-generation of wireless networks for mobile broadband, promises ultra-fast connectivity and low-latency among its benefits. However, 5G and its rollout in many countries has been hampered due to fears over health concerns even some conspiracy theories as well, which have tried to link it with the coronavirus among other things.
What is 5G technology:
- 5G is the 5th generation mobile network. It is a new global wireless standard after 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G networks.
- 5G enables a new kind of network that is designed to connect virtually everyone and everything together including machines, objects, and devices.
Features and benefits of the 5G technology:
- Operate in the millimeter wave spectrum (30-300 GHz) which have the advantage of sending large amounts of data at very high speeds.
- Operate in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high frequency spectrum.
- Reduced latency will support new applications that leverage the power of 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence.
- Increased capacity on 5G networks can minimize the impact of load spikes, like those that take place during sporting events and news events.
- 5G promises to revolutionise mobile broadband and is a big generational leap over the existing 4G technology.
- Help power IoT (Internet of Things) networks to run connected cars and homes smarter.
- It will also support streaming of rich media.
When will it roll out in India?
- Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea have been given trial spectrum to test 5G technology in the country.
- Once this is over, it is expected that networks will go live with the 5G bands by the end of this year. The 5G rollout is expected to gather pace in the country by 2022.
What are the fears around the impact of 5G radiation on human health?
- The claim is that the more powerful 5G waves will emit more radiation and cause harm to humans as well as other living beings. Also, 5G will require more towers in order to ensure better connectivity, and since it will power more than just our smartphones, it will increase human exposure to such radiation in general.
- But radiation from cellphone towers, mobile phones, WiFi routers is typically called non-ionising radiation like radio waves, microwaves, and optical radiation.
- RF fields have been classified by WHO’s International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B).
- But the agency also adds that more research is needed on the subject, especially whether exposure to RF radiation increases risk for certain kinds of brain cancers.
- Radiation at very high levels, also referred to as ionising radiation, heats up our tissue and can eventually lead to cancer.
- But there are increasing concerns that our smartphones, other WiFi-ready devices such as laptops, and mobile phone towers which also emit low level RF radiation are damaging our bodies given the constant exposure.
- Given the growing concerns, the WHO is conducting “a health risk assessment from exposure to radio frequencies, covering the entire radiofrequency range, including 5G.” This study will be published by 2022.
How will 5G affect the global economy?
- 5G is driving global growth.
- $13.1 Trillion dollars of global economic output
- $22.8 Million new jobs created.
- Through a landmark 5G Economy study, we found that 5G’s full economic effect will likely be realized across the globe by 2035—supporting a wide range of industries and potentially enabling up to $13.1 trillion worth of goods and services.
- Enhanced mobile broadband: In addition to making our smartphones better, 5G mobile technology can usher in new immersive experiences such as VR and AR with faster, more uniform data rates, lower latency, and lower cost-per-bit.
- Massive IoT: 5G is meant to seamlessly connect a massive number of embedded sensors in virtually everything through the ability to scale down in data rates, power, and mobility—providing extremely lean and low-cost connectivity solutions.
- Mission-critical communications: 5G can enable new services that can transform industries with ultra-reliable, available, low-latency links like remote control of critical infrastructure, vehicles, and medical procedures.
Difference between Telecom Generations:

- RBI AND CRYPTOCURRENCY
Context: Days after some leading banks cautioned people against dealing in crypto currencies, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) said banks cannot cite its April 2018 order on virtual currencies – that had banned them – as it has been set aside by the Supreme Court of India in 2020.
Key Details:
- The RBI clarification came after State Bank of India and HDFC Bank cautioned their customers against dealing in virtual currencies such as Bitcoin citing the April 2018 order of the RBI.
- Banks also warned customers that failure to adhere to the advisory may lead to cancellation or suspension of their cards.
- The clarification from the RBI is expected to give some relief to customers who have invested around 10,000 crore in cryptocurrencies as per few estimations.
- RBI circular banning virtual currencies dating April 8, 2018 was set aside by the Supreme Court on March 4, 2020 in the matter of writ petition ‘Internet and Mobile Association of India vs Reserve Bank of India’ case
What are banks expected to do now?
- Banks may continue to carry out customer due diligence processes in line with regulations governing standards for Know Your Customer (KYC), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Combating of Financing of Terrorism (CFT) and obligations of regulated entities under Prevention of Money Laundering Act, (PMLA), 2002.
- Banks can ensure compliance with relevant provisions under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) for overseas remittances.
- But banks can’t take action against investors in virtual currencies following the court and RBI directives.
What’s the RBI’s position?
- The RBI’s 2018 position was more restrictive. RBI had asked all entities regulated by it not to deal in VCs or provide services for facilitating any person or entity in dealing with or settling VCs.
- However, RBI has indicated it’s “very much in the game”, and getting ready to launch its own digital currency.
What are Cryptocurrencies and how does they work?
- A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange wherein individual coin ownership records are stored in a ledger existing in a form of a computerized database.
- It uses strong cryptography to secure transaction records, to control the creation of additional coins, and to verify the transfer of coin ownership.
- Cryptography makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend.
- It typically does not exist in physical form (like paper money) and is not issued by a central authority.
- Crypto currencies typically use decentralized control as opposed to centralized digital currency and central banking systems.
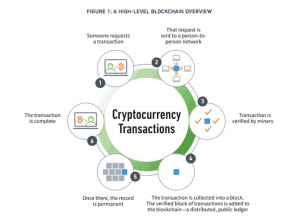
- Crypto currencies work using a technology called blockchain. Blockchain is a decentralized technology spread across many computers that manages and records transactions.
- Crypto currency mining is the process in which transactions between users are verified and added to the block chain public ledger.
- The process of mining is also responsible for introducing new coins into the existing circulating supply and is one of the key elements that allow crypto currencies to work as a peer-to-peer decentralized network, without the need for a third party central authority.
Concerns with Crypto currencies:
- Crypto currencies face criticism for a number of reasons, including their use for illegal activities, exchange rate volatility, and vulnerabilities of the infrastructure underlying them.
- Power consumption: Since validating transactions is energy-intensive, it may have adverse consequences for the country’s energy security (the total electricity use of bitcoin mining, in 2018, was equivalent to that of mid-sized economies such as Switzerland).
- Regulatory bypass: A central bank cannot regulate the supply of crypto currencies in the economy. This could pose a risk to the financial stability of the country if their use becomes widespread.
However, they also have been praised for their portability, divisibility, inflation resistance, and transparency.
Block chain and Crypto transactions:
- H10N3 Bird Flu Strain
Context: China has reported the world’s first human infection of the H10N3 bird flu strain.
Key Details:
- The National Health Commission of China said on Tuesday that they have found one case of human infection with the H10N3 strain of bird flu in Jiangsu province.
- There has not been any case of human infection of H10N3 reported in the world before.
- To date, there is no evidence of sustained human-to-human transmission of the avian influenza virus.
About H10N3:
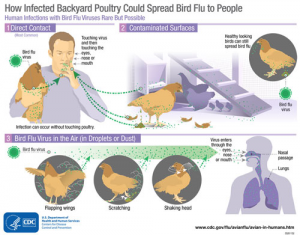
- H10N3 is a type of bird flu or avian flu and is a less severe strain of virus in poultry. The risk of it transmitting on a large scale is also very low.
- In about 40 years, only 160 isolates of this virus were reported, in wild birds or waterfowl across Asia and North America. It has not been detected in chickens.
- Little is known about the virus, which appears to be rare in birds, according to the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), and does not cause severe disease.
Spread and transmission:
- Infected birds shed avian flu in their saliva, mucus, and poop, and humans can get infected when enough of the virus gets in the eyes, nose, or mouth, or is inhaled from infected droplets or dust.
What are the risks?
- The risk of further infection with H10N3 is currently believed to be very low, with experts describing the case as “sporadic”.
- Such cases occur occasionally in China which has huge populations of both farmed and wild birds of many species.
- And with growing surveillance of avian influenza in the human population, more infections with bird flu viruses are being picked up.
- In February, Russia reported the first human infection with the H5N8 virus that caused huge damage on poultry farms across Europe, Russia and East Asia last winter. The virus, however, isn’t yet spreading among people.
- Flu viruses can mutate rapidly and mix with other strains circulating on farms or among migratory birds, known as “reassortment,” meaning they could make genetic changes that pose a transmission threat to humans.
Avian influenza or avian flu or Bird flu:
- It is a highly contagious viral disease caused by Influenza Type A viruses which generally affects poultry birds such as chickens and turkeys. There are many strains of the virus – some of them are mild and may merely cause a low egg production or other mild symptoms among chickens, while others are severe and lethal.
- There are 16 hem agglutinin (H1 to H16) and 9 neuraminidase types (N1 to N9) identified till date.
- There are various modes of transmission of human influenza including inhalation, direct or indirect contact etc. can have manifestations ranging from mild to severe or fatal disease.
- Avian influenza A (H5N1) results in a high death rate amongst infants and young children.
- The first outbreak of human infection by avian influenza viruses (H5N1) was observed in 1997 in Hong Kong. Since then a large number of outbreaks have been reported in different parts of the world.
- Hundreds more have died worldwide in subsequent outbreaks, especially of highly virulent strains like H7N9.

How to prevent the spread of H10N3 among people?
- People should avoid contact with sick or dead poultry and avoid direct contact with live birds as much as possible.
- People must pay attention to food hygiene at the moment.
- People should wear masks and improve self-protection awareness, while constantly monitoring fever and respiratory symptoms.
- Positive Indigenisation List
Context: Ministry of Defence notifies ‘Second Positive Indigenisation List’ of 108 items to promote self-reliance & defence exports.
- Negative Import list is now renamed as ‘Positive Indigenisation List’
Key Details:
- These items can now only be purchased from indigenous sources as per Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020.
- The first positive indigenisation list of 101 Defence Items was announced in August 2020. The second list takes the total number on the list to 209.
- The list of 108 items comprises complex systems, sensors, simulator, weapons and ammunitions like Helicopters, Next Generation Corvettes, Air Borne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) systems, Tank Engines, Medium Power Radar for Mountains, MRSAM Weapon Systems and many more such items to fulfil the requirements of Indian Armed Forces.
- This second list is planned to be implemented progressively with effect from December 2021 to December 2025.
What does Positive Indigenisation List mean?
- Introduced in August 2020, Positive indigenisation list essentially means that the Armed Forces—Army, Navy, and Air Force—will only procure all of these 209 items from domestic manufacturers.
- The manufacturers could be private sector players or defense Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs).
Significance and implications of this move:
- This is in pursuance of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s endeavour of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ and to boost indigenisation in the Defence sector.
- This will give further boost to indigenisation with active participation of public and private sector for fulfilling the twin objectives of achieving self-reliance and promoting defence exports.
- Recognises the potential of local defence industry.
- Invigorate impetus to domestic Research and Development by attracting fresh investment into technology and manufacturing capabilities.
- Provides an excellent opportunity for ‘start-ups’ as also Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- Out of Rs 1.35 lakh crore allocated for capital acquisition for defence in this year’s budget, the government has reserved more than 60 per cent — Rs 70,221 crore — for domestic procurement.
Why was this policy needed? What will be the impacts?
- As per Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, India has been the second largest importer between 2014 and 2019 with US$ 16.75 billion worth of imports during this period.
- The government wants to reduce the dependence on imported items in defence and give a shot in the arm to the domestic defence manufacturing industry
- By denying the possibility of importing the items on the negative list, the domestic industry is given the opportunity to step up and manufacture them for the needs of the forces.
Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020:
- It enables the notification of a List of Weapons or Platforms that will be banned for import.
- It focuses on Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in defence manufacturing and indigenization of the manufacturing prices.
- It also introduces several new ideas such as the need to incorporate artificial intelligence in platforms and systems, use of indigenous software in defence equipment and ‘innovation’ by Start-ups and MSMEs as a new category of defence acquisition.
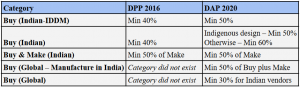
- It includes following procurement categories: Buy (Indian – Indigenously Designed Developed and Manufactured), Buy (Indian), Buy and Make (Indian), Buy (Global – Manufacture in India) and Buy (Global).
- It increases the Indigenous Content (IC) requirement for all projects from 40% to 50% earlier, depending on the category, to 50% to 60%.
- Only under procurement through Buy (Global), foreign vendors can have 30% IC from Indian companies.

- Research Design & Standards Organization (RDSO)
Context: Indian Railways’ Research Design & Standards Organization (RDSO) has recently become the nation’s first institution to be declared as Standard Developing Organization (SDO) under the mission called “One Nation One Standard” on Bureau of Indian Standards.
Key Details:
- RDSO took the initiative to seek recognition as a Standard Developing Organization (SDO) under the BIS SDO Recognition Scheme.
- The recognition is valid for 3 years and will require renewal after completion of the validity period.
- Now with this recognition, the RDSO’s standard formulation procedures will be more focused on consensus-based decision making and will entail the extensive engagement of all stakeholders including Academia, Industry, Users, Test Houses, Recognized Labs, etc, in the standard making process from the very initial stages.
Major benefits out of this recognition by the Bureau of Indian Standards:
- Larger participation of industry/vendors/technology developers/MSME’s in Indian Railways supply chain
- The competitiveness amongst the industry will increase
- There will be a reduction in cost and quantum improvement in the quality of product and services
- There will be smooth induction of latest evolving & emerging technologies on Indian Railways
- Dependence on imports will reduce and “Make-in-India” will get a boost
- Improved ease-of-doing-business
- RDSO will be recognized on international standards-making bodies and there will be integration with global supply chain/global trade
What is One Nation One Standard mission?
- The idea of One Nation One Standard Mission was first conceived in 2019, it was envisioned on the line of one nation, one ration card scheme in order to ensure quality products in the country.
- To attain the One Nation One Standard vision of the Government of India, BIS launched a scheme which provides for Recognition of SDO.
- The purpose of setting standards and enforcing them is not to bring back “inspection raj” but to ensure that quality products are made available to consumers.
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), the only national body that frames standards, has come out with more than 20,000 standards for various products and services so far.
- Besides this, there are about 50-odd agencies that have framed about 400 standards in the country.
- There are multiple standards in the country for a single product/service. The new mission is to converge such standards with the BIS.
Objectives:
- BIS, through this scheme, aims at aggregating as well as integrating the existing capabilities and dedicated domain specific expertise that are available with the country’s various organizations engaged in standards development in their specific sectors, and allow the convergence of India’s all standard development activities resulting in “One National Standard for One Subject”.
- Having uniform national standards will help in making it mandatory for more products.
- The government proposes to set Indian standards in line with the global benchmarks, just like other countries enforce their standards on imported products.
- The Centre, through this move, wants foreign goods coming into India to comply with Indian standards.
- This will help in establishing in the long run Brand India. This will also ensure market relevance for the Indian standards.
Other Initiatives of BIS:
- BIS-Care App: With this app, consumers can check the authenticity of the ISI-marked and hallmarked products and lodge complaints.
- Covid-19 Standards: BIS developed Covid-19 standards for Cover-all and Ventilators and issued norms for grant of licence for N95 Masks, surgical masks and eye protectors which has resulted in an increased production of ISI-marked Personal Protection Equipment (PPE) items.
- Quality Control Orders: BIS has been playing an important role in the formulation of Quality Control Orders (QCO) to make the standards mandatory.
- Portal for Consumer Engagement: BIS is developing a portal on Consumer Engagement, which will facilitate the online registration of Consumer Groups, submission of proposals and approval thereof and complaint management.
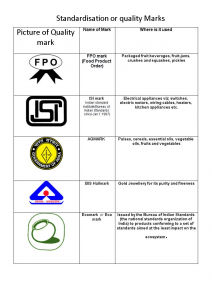
Bureau of Indian Standards:
- It has been established for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- BIS is the only national body that frames standards.
- It works under the aegis of Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Government of India.
- It was established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986 which came into effect in December 1986.
- The Bureau of Indian standards (BIS) Act 2016 establishes the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) as the National Standards Body of India.
- The Act enables the Central Government to appoint any authority/agency, in addition to the BIS, to verify the conformity of products and services with the established standard and issue certificate of conformity.
- There is a provision for repair or recall, of the products (bearing Standard Mark) that do not conform to the relevant Indian Standard.
Research Designs & Standards Organization:
- It is the sole R&D Wing of the Ministry of Railways, is one of India’s leading Standard formulating bodies undertaking standardization work for the railway sector situated in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
Some standards applied in India