UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 4th April 2022
Topics for the day:
- In Turkmenistan, President pushes for TAPI gas pipeline project
- The human genome project
- India’s exports top 400bn$ for the first time
- Another wildfire breaks out in forest area in the Sariska Tiger Reserve
- P. seeks more time to develop Amaravati
- NFC technology for instant payments
In Turkmenistan, President pushes for TAPI gas pipeline project
Context :
- President Kovind is on a State visit to Turkmenistan. This is the first-ever visit of the President of India to independent Turkmenistan.
More on the visit :
- List of MoUs signed/exchanged :
- MoU between Financial Monitoring Service at both the countries
- MoU on Cooperation in the field of Disaster Management
- Programme of Cooperation in the fields of Culture and Arts for the period 2022-2025
- MoU on Cooperation in Youth Matters
- Commemorative Postal stamp released
- India-Turkmenistan commemorative Postal stamp, celebrating the 30th anniversary of establishment of Diplomatic Relations was released.
- Need to increase bilateral trade and economic cooperation
- The leaders noted that the bilateral trade between two countries which currently stands at less than US $100 million is not living up to its potential.
- They noted the role of the India-Turkmenistan Intergovernmental Joint Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific and Technical Cooperation as a coordinating body for enhancing cooperation in this regard.
- Cooperation in the energy sector
- Cooperation in the energy sector was one of the key areas of discussion.
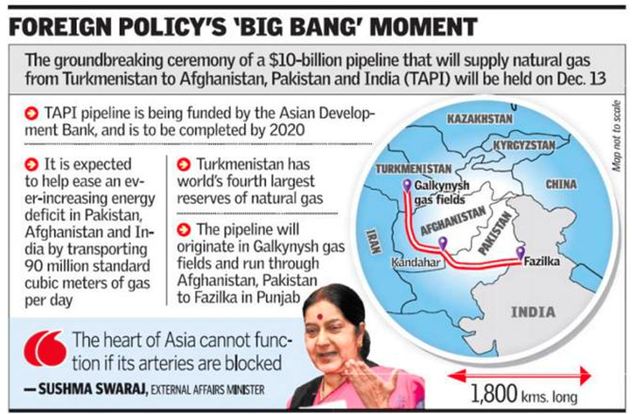
- The Turkmenistan side highlighted the benefits of the TAPI gas pipeline project for the economic development of the region.
- It agreed to examine India’s proposals of ensuring integrity, safety and security of the project.
- Cooperation in the energy sector was one of the key areas of discussion.
More on India-Tukmenistan ties :
- Turkmenistan shares borders with Kazakhstan in the north, Uzbekistan in the north and North-east, Iran in the South and Afghanistan in the Southeast.
- India’s ‘Connect Central Asia’ policy 2012 envisages deeper mutual relations with the region and energy linkage is an important component of the policy.
- India has joined the Ashgabat agreement, which envisages setting up of an international transport and transit corridor linking central Asia with the Persian Gulf to significantly ramp up trade and investment.
- India considers the TAPI pipeline (Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India) a ‘key pillar’ in its economic relations with Turkmenistan.
- India provides training for Turkmen nationals under ITEC (Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation) programme.
- Turkmenistan supports India’s permanent position in the UN Security Council.
- Recently, the 3rd meeting of the India-Central Asia Dialogue was held in New Delhi.
- It is a ministerial-level dialogue between India and the Central Asian countries namely Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan.
- Turkmenistan possesses very large reserves of natural gas.
- Turkmenistan is also strategically placed in Central Asia and connectivity through Turkmenistan will pay dividends.
Issues in the relations :
- Turkmenistan is a USD 40 billion plus economy, but the bilateral trade with India is below its potential.
- India can increase its economic presence in Turkmenistan, particularly in the Information and communication technologies (ICT) sector.
- This would help maintain the future balance of trade.
- There exists no direct connectivity with the Central Asian countries which causes hurdles in terms of trade,exchanges etc.
The human genome project
Context :
- Two decades after most of the human genome was mapped, scientists have now filled in the gaps that remained.
- Earlier about 8% of the human DNA was left unsequenced.
What is Genome?
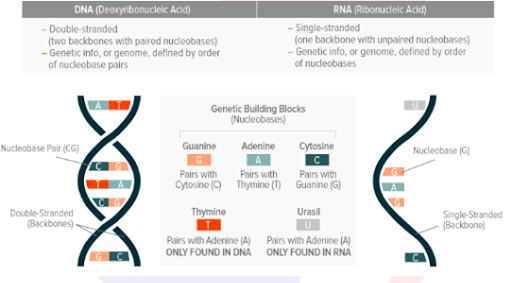
- A genome refers to all of the genetic material in an organism, and the human genome is mostly the same in all people, but a very small part of the DNA does vary between one individual and another.
- Every organism’s genetic code is contained in its Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid (DNA), the building blocks of life.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism. In humans, a copy of the entire genome contains more than 3 billion DNA base pairs.
Background of the news :
- The genetic sequence was made available in 2003 from the Human Genome Project.
- Human Genome Project is an international collaboration containing information from a region of the human genome known as the euchromatin.
- The 8% that was left out was in the area called heterochromatin, which is a smaller portion of the genome, and does not produce protein.
- The fully sequenced genome is the result of the efforts of a global collaboration called the Telomere-2-Telomere (T2T) project.
- The invention of new methods of DNA sequencing and computational analysis helped complete the reading of the remaining 8% of the genome.
What is the Significance of this Breakthrough?
- Make Easier the Study of Genetic Variations:
- A complete human genome makes it easier to study genetic variations between individuals or between populations.
- Can be used for reference while Studying the Genome:
- By constructing a complete human genome, scientists can use it for reference while studying the genome of various individuals. It would help them understand which variations, if any, might be responsible for disease.
- Study Provides a More Accurate Information:
- The T2T consortium used the now-complete genome sequence as a reference to discover more than 2 million additional variants in the human genome.
- Complement the Standard Human Reference Genome:
- The new T2T reference genome will complement the standard human reference genome, known as Genome Reference Consortium build 38 (GRCh38), which originated from the Human Genome Project and has been updated since.
India’s exports top 400bn$ for the first time

Context:
- India’s goods exports grew 43.2% in 2021-22 to nearly $418 billion, rising over $125 billion over the COVID-hit 2020-21
- Earlier it was revealed that the total merchandise imports had crossed $550 billion by February 2022, leading to a trade defcit of $175.75 billion in the frst 11 months of the year.
- A bulk of the merchandise exports growth was attributed to engineering goods and agriculture products exports, both of which hit an all-time high in 2021-22.
- Engineering goods exports grew 46% over the year at $111 billion, of which about $16 billion worth goods were shipped to the United States alone.
- Agricultural exports are reckoned to have crossed $50 billion with a sharp growth in rice, wheat, marine products, cofee and dairy products.
- It is to be noted that wheat exports have grown from 2 lakh tonnes in 2019-20 to 21.55 lakh tonnes last year and over 70 lakh tonnes in 2021-22.About half of this wheat was exported to Bangladesh.
- Exports had reached $331.02 billion in the pre pandemic fiscal year of 2018-19.
Initiatives to improve exports :
- Remission of Duties or Taxes on Export Product (RoDTEP) :
- The scheme was formed to replace the existing MEIS (Merchandise Exports from India Scheme)
- It is a fully automated route for Input Tax Credit (ITC) in the GST (Goods and Service Tax) to help increase exports in India.
- ITC is provided to set off tax paid on the purchase of raw materials, consumables, goods or services that were used in the manufacturing of goods or services.
-
Special economic zone :
- An SEZ is a territory within a country that is typically duty-free (Fiscal Concession) and has different business and commercial laws chiefly to encourage investment and create employment.
-
Niryat Bandhu Scheme
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) is implementing the Niryat Bandhu Scheme for mentoring budding exporters on the intricacies of foreign trade through counseling, training, and outreach programs.
Another wildfire breaks out in forest area in the Sariska Tiger Reserve
Context :
- A fire broke out at Sariska Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan’s Alwar on Sunday and spread to around a three-square km area
More about Sariska :
- Vegetation: arid forests, dry deciduous forests, scrub-thorn and grasslands.
- It is a part of the Aravalli Range and the Kathiawar-Gir dry deciduous forests’ ecoregion.
- It is rich in mineral resources, such as copper.
- Major Fauna: Bengal tiger, Indian leopard, golden jackal, chital, sambar deer, nilgai, rhesus macaque, etc.
- Threats: marble mining, habitat fragmentation,forest fires and poaching.
- In January 2005, it was reported that there were no tigers left in Sariska.In July 2008, two tigers from Ranthambhore National Park were relocated to Sariska Tiger Reserve.
Some of the biggest threats to wildlife are:
- Illegal wildlife trade
- Habitat destruction
- Deforestation
- Invasive species
- Pollution
- Climate change
Nearby National parks and tiger reserves :
-
Keolodeo Ghana :
- The park is a freshwater swamp and is flooded during the monsoon.
- It was previously known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary.
- It is a famous avifauna sanctuary that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season.
- It is a Ramsar Site and UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Vegetation: tropical dry deciduous forests mixed with dry grasslands and wetlands.
- It is the only regular wintering area in India for the Siberian crane (CR).
- Avian Major Fauna: Migratory waterfowl, painted storks, sarus crane (VU) (large non-migratory crane found in parts of India), etc.
- Major Fauna: rhesus macaque, nilgai, blackbuck, hog deer, chital deer, sambar, etc.
-
Ranthambore national park :
- It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River.
- The confluence of the Banas River and the Chambal River is just a few miles to the east of the park.
- According to experts, there is overcrowding at the Ranthambore reserve.
- The Rajasthan government has announced its plan to develop the Bundi sanctuary as a tiger reserve to provide a second habitat for tigers in the Ranthambore Reserve.
- Vegetation: dry deciduous forests and grasslands.
- Major Fauna: Bengal Tiger, Indian leopard, nilgai, sambar, sloth bear, mugger crocodile, etc.
- Threats: poaching, poisoning of tigers by villagers, habitat fragmentation, etc.
A.P. seeks more time to develop Amaravati
Context :
- The Andhra Pradesh government has requested the High Court to remove the timelines, or extend the time granted by it, for developing infrastructure in the capital city of Amaravati by five years without prejudice to the option to seek legal remedies, keeping in view the impossibility of complying with the court directions in the given time frame.
-
Problems involved :
- Acc to the govt the process of development entails the revival or restarting of contracts for various works connected with the Land Pooling Scheme (LPS) which are incomplete and consequently revival agreements have to be signed with the existing contractors.
- Most of the development works were executed primarily in anticipation of loans from Multilateral Financial Institutions (MFIs) but most of them did not fructify.
- Revival of these contracts required the resumption of negotiations with the MFIs and the works were also partly contingent upon the release of grants by the Central government.
- Besides the government had limited resources and constraints and there were priorities of welfare and development activities.
Background :
- Earlier the Andhra Pradesh High Court directed the State government to construct and develop Amaravati, the capital city of the State, and the capital region within six months
- The court directed the government and the Capital Region Development Authority (CRDA) to discharge their duties enshrined under theP. CRDA Act and Land Pooling Rules.
- It directed the State to develop the reconstitutional plots belonging to landowners and hand them over to landowners within three months and to complete the infrastructure works in the region within one month from the date of its order
NFC technology for instant payments
Context :
- Google Pay has recently launched a new feature in India, ‘Tap to pay for UPI’
- The feature makes use of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. The functionality will allow users with NFC-enabled Android smartphones and UPI accounts linked to Google Pay to carry out transactions just by tapping their phones on any Android point-of-sale (POS) terminal across the country, Google said in a release.
- Till now, Tap to Pay was only available for cards.
What is NFC and how does it work?
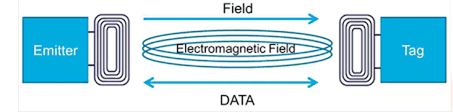
- NFC is a short-range wireless connectivity technology that allows NFC-enabled devices to communicate with each other and transfer information quickly and easily with a single touch – whether to pay bills, exchange business cards, download coupons, or share a document.
- NFC transmits data through electromagnetic radio fields, to enable communication between two devices.
- Both devices must contain NFC chips, as transactions take place within a very short distance.
- NFC-enabled devices must be either physically touching or within a few centimetres from each other for data transfer to occur.
What are the other applications of NFC technology?
- NFC tech has a wide range of applications besides driving payment services like Google Wallet and Apple Pay.
- Contactless cards and readers use NFC in several applications from securing networks and buildings to monitoring inventory and sales, preventing auto theft, keeping tabs on library books, and running unmanned toll booths.
- NFC is behind the cards that we wave over card readers in subways and on buses to check tickets.
- It is present in speakers, household appliances, and other electronic devices that we monitor and control through our smartphones.
- It also has an application in healthcare, to monitor patient stats through NFC-enabled wristbands.
- NFC is used in wireless charging too.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 4th April 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

