Daily Current Affairs 09th September -2021
- Shiksha Parv 2021
- Financial Powers to Armed Forces
- Increasing Complaints of Crimes against women
- Tamil Nadu set to make ‘right to sit’ a workplace law
- Pollution of River Bhogdoi
1.Shiksha Parv 2021
#GS2 #Issues related to Education and Children #Government policies and Interventions
Context: PM Modi launches 05 new initiatives for accessible education on the occasion of Shiksha Parv.
- Union Ministry of Education is celebrating Shiksha Parv from 5th-17th September to recognize the contributions of teachers and to take New Education Policy (NEP) 2020 a step forward.
Initiatives launched:
-
School Quality Assessment and Accreditation Framework (SQAA) of CBSE:
- SQAA is a quality initiative proposed by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) to provide global parameters of attainment as standards in schools affiliated to it.
- The CBSE aspires to lay down a set of standards and best practices as paradigms for attaining the best benchmark in an individual institution for the upliftment of learning outcomes in the domain of school education imparted to children.
- It is holistic as it covers all aspects of a school functioning, namely its Scholastic and Co-scholastic Domains, Infrastructural Areas, Human Resources, Management and Administration, Leadership and Beneficiary Satisfaction.
-
Vidyanjali 2.0 Portal:
- Vidyanjali is an initiative taken by the Union Ministry of Education, with the aim to strengthen Schools through community and private sector involvement in schools across the country.
- This initiative would connect schools with varied volunteers from the Indian Diaspora namely, young professionals, school alumni, in service and retired teachers / Government officials / professionals and many others.
- Vidyanjali has two aspects:
- “Participate in school Service/Activity” and
- “Assets/Material/Equipment” in which volunteer can support and strengthen the government and government aided schools.
-
Indian Sign Language Dictionary:
- It was launched for the Children and persons with hearing impairments with 10,000 words in it.
-
Talking Books:
- Audiobooks for the visually challenged students.
-
NISHTHA Teachers’ Training programme for NIPUN Bharat:
- National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement (NISHTHA) is a capacity building programme for improving the quality of school education through integrated teacher training.
- Ministry of Education has launched a National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy (NIPUN Bharat), for ensuring that every child in the country necessarily attains foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN) by the end of Grade 3, by 2026-27.
- It is launched under the aegis of the centrally sponsored scheme of Samagra Shiksha.
- It will focus on providing access and retaining children in foundational years of schooling; teacher capacity building; development of high quality and diversified Student and Teacher Resources/Learning Materials; and tracking the progress of each child in achieving learning outcomes.
Other Related Initiatives:
- The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs has approved the school education programme Samagra Shiksha Scheme 2.0 till the 2025-26 financial year.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) recently notified the Academic Bank of Credits (ABC), an academic service mechanism for storing and transferring of academic credits of a student.
- It is a national-level facility to promote flexibility of curriculum framework and interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary academic mobility of students across higher education institutions in the country.
- The scheme is in line with the new National Education Policy.
- New Education policy was introduced in 2020

2.Financial Powers to Armed Forces
#GS3 #Various Security Forces & Agencies & Their Mandate
#Security infrastructure #GS2 # Government Policies & Interventions
Context: Recently, Union Defence Minister approved the delegation of financial powers to the armed forces for revenue procurement.
Key Details:
- Delegation of Financial Powers to Defence Services (DFPDS) 2021 provide enhanced delegation of Revenue Procurement powers for the Army, Navy and Air Force.
- Revenue procurement entails procurement of already sanctioned assets in service including renewals and replacements.
- Main objective of DFPDS 2021 is to empower field formations; focus on operational preparedness; promote ease of doing business and enhance jointness among the Services.
- The last DFPDS was released in 2016.
Highlights of DFPDS 2021:
- The DFPDS 2021 has guidelines on the Schedules of powers for the Army, the Navy, the Air Force and the Integrated Defence Staff (IDS).
- Under the new financial powers delegated, there is a
- General enhancement of up to 02 times has been approved for the Competent Financial Authorities (CFA),
- In certain schedules “this enhancement at field formations is in the range of up to 5-10 times on account of operational requirements.
- Additionally, new CFAs have also been added, which include the Deputy Chief of Army Staff, Master General Sustenance, ADG (Procurement)/DG Air Operations/DG Naval Operations, among other in the service headquarters, and in the field formations on account of reorganisation, restructuring or functional requirements.
- The Vice Chiefs of the services will get a 10 per cent increase in the financial powers delegated to them, with a ceiling of Rs 500 crore.
- The Chief of the Integrated Defence Staff and the Chairman Chiefs of Staff Committee, will also get financial powers aligned with the vice chiefs.
- Under the new rules, critical equipment, like air-to-air refuellers for the Air Force, can be hired for short periods as compared to buying them or a long-term lease, which is not only considerably expensive, but also takes a long time.
- While the Vice Chief of the Air Force will have powers capped at Rs 200 crore, commanders will have powers till Rs 100 crore for such hiring.
- Along with introducing the concept of short-term hiring of equipment, financial powers have also been delegated to new officers among the services, depending on requirements.
- New schedule on hiring of aircraft and associated equipment has been introduced for Indian Air Force which includes hiring of Air to Air re-fuellers”
- For the Navy, “powers for replenishment of Disaster Management Bricks have been delegated to Command Level for immediate response to Natural Disasters/HADR Operations”.
Significance of DFPDS 2021:
- The armed forces acquire capital assets according to the Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020, which was introduced last September.
- Along with buying equipment from Indian or international players, DAP 2020 had also introduced a chapter on leasing of equipment for a limited time.
- Hiring for shorter-durations, under the new delegated powers, will allow the forces to plug immediate gaps.
- The enhanced delegation of Financial Powers to functionaries in Service Headquarters and lower formations would result in quicker decision making at all levels leading to better planning and operational preparedness of the Services in a quicker time frame and optimal use of resources.”
- To empower Field Commanders and below to procure equipment/war-like stores in a speedy manner for urgent operational necessities and meeting essential sustenance requirements.
- To strengthen the security infrastructure of the country.
- Substantial enhancement has been approved in the Schedules related to Indigenisation/Research & Development up to 03 times of the existing powers, in line with ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ vision of the union government.
- To overcome procedural delays, bring greater decentralisation and operational efficiency.
Other initiatives regarding Arm procurement:
- Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP), 2020: For timely acquisition of military equipment, systems and platforms as required by the Armed Forces in terms of performance, capabilities and quality standards, through optimum utilisation of allocated budgetary resources.
- Defence Investor Cell: To provide info including addressing queries related to investment opportunities, procedures and regulatory requirements for investment in the sector.
3.Increasing Complaints of Crimes against women
#GS2 #Social Justice #Issues related to Women # Mechanisms, Laws, Institutions & Bodies Constituted for Protection & Betterment of These Vulnerable Sections
Context: An analysis of the National Commission for Women (NCW) statistics showed that there has been a 46% rise in complaints of crimes against women during January-August, 2021, over the corresponding period of last year.
Key Statistics:
- The NCW received a total of 19,953 complaints of crimes against women from January to August this year, it was 13,618 in the corresponding period of 2020.
- Of the 19,953 complaints, the highest number of 7,036 were recorded under the right to live with dignity clause, followed by 4,289 complaints of domestic violence and 2,923 complaints of harassment of married women or dowry harassment.
- The right to live with dignity clause takes into account the emotional abuse of women.
- Total of 1,116 complaints have been received concerning the offence of outraging modesty of women or molestation, followed by 1,022 complaints of rape and attempt to rape and 585 complaints of
- Among states and union territories, the highest number of complaints was received from Uttar Pradesh (10,084), followed by Delhi (2,147), Haryana (995) and Maharashtra (974).
Violence against Women:
- The United Nations states violence against women as “any act of gender-based violence that results in, or is likely to result in, physical, sexual, or mental harm or suffering to women, including threats of such acts, coercion or arbitrary deprivation of liberty, whether occurring in public or in private life.”
- Violence against women – particularly intimate partner violence and sexual violence – is a major public health problem and a violation of women’s human rights.
- Estimates published by WHO indicate that globally about 1 in 3 (30%) of women worldwide have been subjected to either physical and/or sexual intimate partner violence or non-partner sexual violence in their lifetime.
- Violence can negatively affect women’s physical, mental, sexual, and reproductive health, and may increase the risk of acquiring HIV in some settings.
Important Constitutional and legal safeguards for women in India:
- The principle of gender equality is enshrined in the Indian Constitution in its Preamble, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties and Directive Principles.
- The Constitution also empowers the State to adopt measures of positive discrimination in favour of women.
- India has ratified various international conventions and human rights instruments committing to secure equal rights of women. Key among them is the ratification of the Convention on Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW) in 1993.
LEGAL PROVISIONS:
- To uphold the Constitutional mandate, the State has enacted various legislative measures intended to ensure equal rights, to counter social discrimination and various forms of violence and atrocities and to provide support services specially to working women.
- Although women may be victims of any of the crimes such as ‘Murder’, ‘Robbery’, ‘Cheating’ etc, the crimes, which are directed specifically against women, are characterized as ‘Crime against Women’. These are broadly classified under two categories.
(1) The Crimes Identified Under the Indian Penal Code (IPC)
(i) Rape (Sec. 376 IPC)
(ii) Kidnapping & Abduction for different purposes (Sec. 363-373)
(iii) Homicide for Dowry, Dowry Deaths or their attempts
(Sec. 302/304-B IPC)
(iv) Torture, both mental and physical (Sec. 498-A IPC)
(v) Molestation (Sec. 354 IPC)
(vi) Sexual Harassment (Sec. 509 IPC)
(vii) Importation of girls (up to 21 years of age)
The Crimes identified under the Special Laws (SLL)
- Although all laws are not gender specific, the provisions of law affecting women significantly have been reviewed periodically and amendments carried out to keep pace with the emerging requirements.
- Some acts which have special provisions to safeguard women and their interests are:
- The Family Courts Act, 1954
- The Special Marriage Act, 1954
- The Hindu Marriage Act, 1955
- Immoral Traffic (Prevention) Act, 1956
- Dowry Prohibition Act, 1961
- The Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO), 2012
- The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
- The Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 1983
- Indecent Representation of Women (Prohibition) Act, 1986
- The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005
Special initiatives towards women:
(i) National Commission for Women: In January 1992, the Government set-up this statutory body with a specific mandate to study and monitor all matters relating to the constitutional and legal safeguards provided for women, review the existing legislation to suggest amendments wherever necessary, etc.
(ii) Reservation for Women in Local Self -Government: The 73rd Constitutional Amendment Acts passed in 1992 by Parliament ensure one-third of the total seats for women in all elected offices in local bodies whether in rural areas or urban areas.
(iii) The National Plan of Action for the Girl Child (1991-2000): The plan of Action is to ensure survival, protection and development of the girl child with the ultimate objective of building up a better future for the girl child.
(iv) National Policy for the Empowerment of Women, 2001: The Department of Women & Child Development in the Ministry of Human Resource Development has prepared a “National Policy for the Empowerment of Women” in the year 2001. The goal of this policy is to bring about the advancement, development and empowerment of women.
4.Tamil Nadu set to make ‘right to sit’ a workplace law
#GS2 #Indian constitution and significant provisions – Directive Principles of State Policy
Context: The Tamil Nadu government has tabled a Bill to amend Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act, 1947 making it mandatory for establishments to provide seating facilities for employees.
- It is popularly being called the “Right to Sit”.
Key Provisions of the bill:
- It is intended to help employees of large and small establishments, particularly those working in textile and jewellery showrooms.
- The proposed addition of Section 22-A to the Act reads that the premises of every establishment shall have suitable seating arrangements for all employees so that they may take advantage of any opportunity to sit.
Significance of “Right to sit”
- Persons working in most shops and establishments are made to stand throughout their duty time resulting in several types of health issues.
- Most owners of shops and other retail outlets forbid women, the bulk of the shop workforce, to sit. Even leaning against a wall was punished. They had developed varicose veins and joint pain from standing.
- Right to Sit would avoid the ‘on their toes’ situation throughout the working hours.
- The Right to Sit is a fresh step in pursuance of Article 42 of Indian Constitution (Directive principles of State Policy) which prompts the State to make provision for securing just and humane conditions of work and for maternity relief.
Similar legislation in Kerala which inspired Tamil Nadu government:
- The Kerala Shops and Commercial Establishments (Amendment) Act, 2018, was passed in December 2018, guaranteeing improved working conditions in commercial shops.
- This came as a result of prolonged protests by workers textile showrooms in Kerala demanding the ‘Right to Sit’.
Provisions of The Kerala Shops and Commercial Establishments (Amendment) Act, 2018:
- Amended act brings shops, hotels and restaurants under its purview.
- The Bill will have necessary rules to ensure protection for women working between 9 pm and 6 am.
- In a group of 05 members, there should be at least 02 women to be put on a night shift and the employer will have to keep in mind the dignity, pride and security of women staff.
- The women should also be facilitated with transport for being dropped at their residences.
- The Bill, while includes provisions for their safety, also includes women-friendly initiatives, including providing seating arrangements for saleswomen during working hours.
5.Pollution of River Bhogdoi
#GS3 # Environmental Pollution & Degradation – Sources and prevention of pollution
Context: The extensive coal mining in Nagaland, along with waste discharge from tea estates and encroachment are polluting waters of River Bhogdoi in Assam.
- In June this year, dead fish were sighted in several areas along the banks. These deaths were linked to contamination.
About the river:
- The Bhogdoi River is a south bank tributary of the Brahmaputra in India.
- It originates in Naga hills and flows through the City of Jorhat and merges with another river and its name becomes Gelabill.
- It is an inter-state river (flowing between Assam and Nagaland) and the total catchment area of the river is 1,545 square kilometres and travels 160 kilometres before joining Dhansiri river near its confluence with Brahmaputra.
Issues:
- In 2019, Union Environment ministry declared Bhogdoi as one of the most polluted rivers in Assam and 351st among the polluted rivers in the country.
- Manganese Contamination in the river by Coal mining industries in Nagaland.
- Chemical waste from the tea gardens is turning the river poisonous and polluted.
- Tocklai, one of the major drains, as well as some other smaller drains carry municipal waste from Jorhat and into the river.
- The drains carry industrial and residential wastes
- The river has also become heavily silted, reducing its carrying capacity.
- There have been no systematic studies done regarding the conservation of the river,
- The high BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) indicates low water quality and less oxygen for aquatic life.
- BOD of Bhogdoi was 04 milligrams per litre (mg / l) in September 2018, up from 1.1 mg / l in 2016, as per the River Rejuvenation Committee (RRC) set up by the state government.
- The massive infringements along the river bank have been making the river narrower and increasing the filth and garbage.
- Jorhat city has urbanised rapidly due to its strategic location near Nagaland border that facilitates transit of goods. The work requires an increase in manpower.
- Disposing human excreta and cremating dead bodies along the river bank are gradually contaminating the soil and water of the region. This is increasing the threat of water-borne diseases.
Action Plan for pollution control:
- The action plan for rejuvenation, protection and management of the identified polluted river stretch of Assam has been prepared as per direction of National Green Tribunal.
- This includes:
- Industrial Pollution Control.
- Identification, Channelization, Treatment and Utilization of Treated Domestic Sewage.
- River catchment/Basin Management-Controlled ground water extraction and periodic quality assessment.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand:

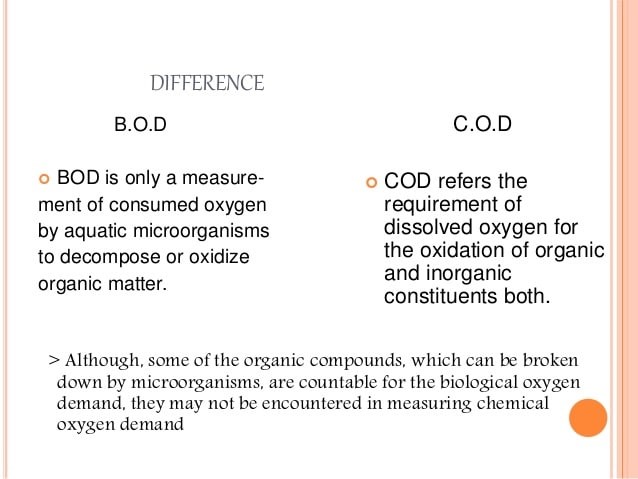
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 09th September -2021
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on Youtube

