UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 18th January 2022
IAS institute in Hyderabad and Vijayawada
- “Inequality Kills”: The Oxfam Report
- Design Linked Incentive for Semiconductors
- Web3: A vision for the future
- Alan Hills (ALH) 84001: Meteorite
- Volcanic Eruption in Tonga
1. “Inequality Kills”: The Oxfam Report
#GS3-Inclusive Growth & Related Issues
Context
- According to a recent Oxfam research, the income of 84% of households in the country fell in 2021.
In depth information

Important Findings
Billionaires:
- The number of billionaires in India increased from 102 to 142, despite a widening economic gap exacerbated by the Covid epidemic.
- According to the research, India has the world’s third-highest number of billionaires, just behind China and the United States, with more billionaires than France, Sweden, and Switzerland combined – a 39 percent growth in the number of billionaires in India by 2021.
Wealth of the richest and poorest people:
- The combined wealth of India’s 100 wealthiest people reached a new high of Rs 57.3 lakh crore in 2021. (USD 775 billion).
- In the same year, the share of national wealth held by the bottom half of the population was only 6%.
- The wealth of Indian billionaires increased from Rs 23.14 lakh crore (USD 313 billion) to Rs 53.16 lakh crore (USD 313 billion) during the epidemic (from March 2020 to November 30, 2021). (USD 719 billion).
- According to the research, economic disparity contributes to the deaths of 21,000 people per day as a result of a lack of access to healthcare, gender-based violence, starvation, and climate change.
- Extreme poverty:
- In 2020, it is anticipated that over 4.6 crore Indians will be living in extreme poverty.
Healthcare budget:
- From RE (revised estimates) of 2020-21, India’s healthcare budget has decreased by 10%.
Budget for education:
- The funding for education was reduced by 6%.
Budget for Social Security:
- The budgetary allocation for social security programmes fell from 1.5 percent to 0.6 percent of the entire Union budget, accounting for nearly half of the world’s new poor.
Gender Parity:
- Gender parity has been pushed back from 99 years to 135 years as a result of the epidemic.
- In 2020, women lost Rs 59.11 lakh crore in earnings (USD 800 billion), with 1.3 crore fewer women working than in 2019.
- It has never been more critical to begin correcting the wrongs of this egregious inequality by taxing extreme wealth and reinvesting the proceeds in the real economy to save lives.
Taxes:
- The rise in indirect taxes as a percentage of Union government revenue lasted four years, while the proportion of corporation taxes fell. In the first six months of 2020-21, the additional gasoline tax increased by 33% over the previous year, and is now 79 percent higher than pre-Covid levels.
- At the same time, in 2016, the wealth tax “for the super-rich” was repealed.
Expenses paid out of pocket:
- Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in private hospitals is over six times greater than in public hospitals for inpatient care, and two or three times higher for outpatient care, according to data from the National Sample Survey (NSS) (2017-18).
- In India, the average OOPE is 62.67 percent, compared to 18.12 percent globally.
Structure of the Federal Government:
- Despite the country’s federal system, the revenue structure kept the reins of resources in the hands of the federal government, and the pandemic was left to the states, who lacked the financial and human resources to deal with it.
Ahead of Schedule
- A one-time 99 percent windfall tax on the Covid-19 wealth gains of the top ten richest men would raise $812 billion.
- These funds may cover the cost of producing enough vaccines for the entire planet, as well as filling funding shortages in climate action, universal health and social protection, and efforts to combat gender-based violence in over 80 countries.
- The world can build an economy in which no one lives in poverty and where billionaires have inconceivable wealth—an economy in which inequality no longer kills.
2.Design Linked Incentive for Semiconductors
#GS3-Growth & Development
Context
- Under the Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme, the Ministry of Electronics and Information (MeitY) is inviting submissions from 100 domestic semiconductor chip design firms, corporations, start-ups, and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- The DLI programme is part of MeitY’s overall Plan for the Development of Semiconductors and Display Manufacturing Ecosystems in China.
- There has recently been an acute and cascading scarcity of semiconductors over the world.
In depth information
- Domestic enterprises, startups, and MSMEs will benefit from financial incentives and design infrastructure support under the DLI Scheme.
- Over a five-year period, the incentives will be offered at various stages of semiconductor design development and deployment for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores, and semiconductor linked design.
Eligibility:
- Approved applicants who claim incentives under the scheme will be encouraged to keep their domestic status (i.e., more than 50% of the capital is beneficially owned by resident Indian citizens and/or Indian companies that are ultimately owned and controlled by resident Indian citizens) for three years after claiming incentives.
- To be eligible for incentives under the Scheme, an applicant must fulfil the Threshold and Ceiling Limits.
- In addition, a special gateway has been established.
Aim:
- At least 20 local semiconductor design companies would be nurtured, with the goal of achieving a turnover of more than Rs.1500 crore in the following five years.
Approach:
- The DLI Scheme will also take a graded and proactive approach to identifying national priorities and developing strategies for complete or near-complete indigenisation and deployment, thereby advancing import substitution and value addition in strategic and social sectors.
Agency in charge of nodes:
- The DLI programme will be implemented by C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing), a scientific society that operates under MeitY.
- DLI’s components are as follows:
- Chip Design infrastructure support, Product Design Linked Incentive, and Deployment Linked Incentive are the three components of the scheme:
- Support for Chip Design Infrastructure:
- C-DAC will establish the India Chip Centre to house state-of-the-art design infrastructure (such as EDA Tools, IP Cores, and support for MPW (Multi Project Wafer fabrication) and post-silicon validation) and make it available to supported enterprises.
- Product Design Linked Incentive:
- Approved applicants who are involved in semiconductor design will receive a reimbursement of up to 50% of eligible expenditures up to a maximum of Rs.15 crore per application as fiscal support.
- Approved applicants whose semiconductor design for Integrated Circuits (ICs), Chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), Systems & IP Cores, and semiconductor linked design are deployed in electronic products will receive an incentive of 6% to 4% of net sales turnover over 5 years, subject to a ceiling of Rs.30 Crore per application.
Initiatives that are related:
- Semiconductor and Display Fabrication Units:
- The government will grant financial assistance of up to 50% of the project cost for the establishment of semiconductor and display fabrication units.
- SCL (Semiconductor Laboratory):
- MeitY will take the necessary efforts to modernise and commercialise the Semiconductor Laboratory (SCL).
- Compound Semiconductors:
- The government will provide financial assistance to authorised Compound Semiconductors units in the amount of 30% of capital expenditure.
- A specialised and independent India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) would be established in order to push long-term plans for establishing a sustainable semiconductors and display ecosystem.
- Production Linked Incentives:
- Under the Product Linked Incentive (PLI) for Largest Scale Electronics Manufacturing, PLI for IT Hardware, SPECS Scheme, and Modified Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMC 2.0) Scheme, incentive support worth Rs.55,392 crore (7.5 billion USD) has been granted.
3. Web3: A vision for the future
#GS3-Science & Technology
Context
- In 2021, the term “Web3” was coined to describe a possible next phase of the internet, and it generated a lot of discussion.
In depth information
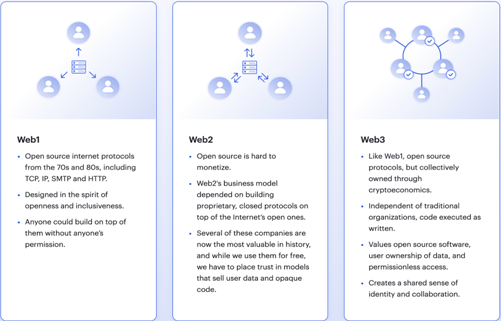
Versions from the past
- Version 1.0
- In 1989, the worldwide web, also known as the internet, was created.
- It gained popularity in 1993. The internet in the early days of Web 1.0 was primarily static web pages, with people visiting a website and then reading and interacting with static material.
- Even if there were e-commerce websites in the beginning, it was still a closed environment, with consumers unable to generate content or leave reviews on the internet.
Web 1.0 lasted until 1999.
Web 2.0
- It began in some form in the late 1990s, but it wasn’t until 2004 that the majority of its features were completely functional.
- We are still in the Web 2.0 era.
- Web 2.0 distinguishes itself from Web 1.0 by allowing users to produce their own content.
- They can participate and contribute by leaving comments, registering likes, sharing and uploading photographs and videos, and other similar activities.
- The distinguishing feature of Web 2.0 is, first and foremost, a social media type of engagement.
Why was the need for Web3 felt?
- In Web 2.0, a small number of giant firms possess or handle the vast majority of online data and traffic. This has resulted in difficulties with data privacy, data security, and data abuse.
- Web3 provides an answer to these issues.
- There’s a sense of regret that the internet’s basic purpose has been twisted.
- The hype about Web3 is particularly noticeable in this context.
What is Web3?
- Web 3.0 is another name for it.
- It is a decentralised internet that will use Blockchain technology to operate.
- Web3 was coined by Gavin Wood, the founder of Ethereum (a blockchain technology startup), in 2014, and many others have since added to the concept.
- It would be distinct from the current Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 versions.
- Unlike now, when tech companies control platforms, users will have ownership shares in web3 platforms and applications.
Benefits
- Web3 will provide a “decentralised and fair internet where users own their own data,” according to the company.
- Web3 eliminates the need for an intermediary, allowing peer-to-peer (seller-to-buyer) transactions.
- Currently, in order for a seller to do business with a customer, both the buyer and the seller must be registered on a “shop” or “platform” such as Amazon, Ebay, or another e-commerce gateway.
- The platform verifies that the buyer and seller are legitimate participants in the transaction.
- Web3 attempts to do away with the concept of a “platform.”
- The philosophy of Web3 is Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), which means that all business and governing norms in every transaction are transparently available for anyone to view, and software will be created in accordance with them.
- There is no need for a central authority to validate or authenticate with DAO.
Its current state of development
- Web3 is still in its early stages, and no one knows if it will take off as Web 1.0 or Web 2.0 did.
- Top tech minds in the industry and academia are sceptical of Web3, claiming that it does not answer the challenges it claims to tackle.
- Elon Musk and Jack Dorsey, for example, do not believe Web3 has a future.
- Web3 will necessitate a departure from the current architecture, which consists of a front-end, intermediate layer, and back-end.
- Backend solutions for processing blockchain, persisting and indexing data in the blockchain, peer to peer communications, and so on will be required for Web3’s design.
- Similarly, the middle layer, often known as the business rules layer, will have to deal with a blockchain-based backend.
- Although it is unknown if Web3 will become the dominant way of internet access, the problems it raises are important.
4. Alan Hills (ALH) 84001: Meteorite
#GS3-Space
Context
- The presence of organic molecules on the surface of Meteorite ALH 84001 is explained by a recent study.
In depth information
Alan Hills (ALH) 84001
- A US meteorite hunting group discovered it on a snowmobile ride in the Far Western Icefield of Allan Hills in Antarctica in December 1984. It was recognised as the most peculiar rock collected at the time of its discovery.
- It was reported as being shaped like a rounded brick or a huge potato, measuring about 6 inches long by 4 inches wide by 3 inches tall, and partially covered with black glass at the time (like it was dipped in tar).
- When meteorites burn through the Earth’s atmosphere, a glass called fusion crust emerges.
- Scientists have debated for nearly four decades whether organic chemicals discovered on the surface of the meteorite (ALH) 84001 were evidence of old, rudimentary life on Mars.
- The possibility that the molecules came through volcanic activity, impact events on Mars, or hydrological exposure was also discussed.
A recent study’s key findings
- The organic molecules identified in the meteorite are thought to have formed as a result of water and rock interactions on Mars, according to the study. These interactions resembled those that occur on Earth.
- These non-biological geological events produce a reservoir of organic carbon compounds from which life could have arisen, and they represent a background signal that must be considered when looking for signs of past life on Mars.
- Despite the fact that no human has ever set foot on Mars and no rocks have been examined, it was reported.
- However, NASA’s Perseverance rover took the first sample of Martian rock in 2021.
- Because the meteorite contains evidence of particular gases that are similar to those found in the Martian atmosphere, it can be declared with certainty that it came from the Red Planet.
The importance of studying
- Scientists are interested in meteorites because they can provide information about the origins of the solar system and possibly even the Earth.
- Specific missions to asteroids have been launched by space agencies in order to investigate them.
- One example is NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission, which was launched in 2018 with the goal of reaching asteroid Bennu and returning a sample.
5.Volcanic Eruption in Tonga
#GS1-Physical Geography
Context
- A volcano erupted recently on Tonga’s southern Pacific island, triggering Tsunami waves across the Pacific.
- The Tonga Islands are located on the Ring of Fire, which encircles the Pacific Ocean basin and is marked by increased volcanic and seismic activity.
In depth information
- Hunga-Ha’apai and Hunga-Tonga are two small uninhabited islands that make up an Undersea Volcanic Eruption.
- Over the last few decades, the Hunga-Tonga-Hunga-Ha’apai volcano has erupted on a regular basis.
- Hot magma and steam jets erupted through the waves during incidents in 2009 and 2014/15. However, these eruptions were minor in comparison to the January 2022 eruptions.
- This is one of the volcano’s major eruptions, which occur every thousand years or so.
- The interaction between the fuel and the coolant is one of the reasons it is very explosive.
Impact:
- As sulphur dioxide is blasted into the stratosphere, large volcanic eruptions can induce temporary global cooling. In the case of the Tonga eruption, however, preliminary satellite data indicated that the amount of sulphur dioxide produced would only have a negligible influence on global average cooling, perhaps 0.01 degrees Celsius.
- The eruption changed atmospheric pressure, which may have helped clear the fog around Seattle, Washington, for a short time.
- The waves smashed into Peru, killing two people and causing minor damage from New Zealand to Santa Cruz, California.
- According to the US Geological Survey, the eruption triggered a magnitude 5.8 earthquake.
UPSC Civils Daily Current Affairs 18th January 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

