Sarat Chandra IAS Academy brings to you the daily current affairs keeping in mind the changing pattern of the UPSC civil services exam. UPSC Prelims and Mains exams mix the current affairs with static core concepts. So, we give the background explanation for every current topic.
Topics of the day:
- MALABAR maritime exercise
- Office of p profit
- India and Luxembourg bilateral meet
- Five EYES
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):
- Digital Nation
1) MALABAR maritime exercise:
Relevant to: GS Prelims
Context: The 24th edition of MALABAR maritime exercise, hosted by Indian Navy (IN) in two phases, concluded in the Arabian Sea on 20 November.
- Phase 1 of the exercise involving participation by Indian Navy (IN), United States Navy (USN), Japan Maritime Self Defense Force (JMSDF) and Royal Australian Navy (RAN), was conducted off Visakhapatnam in Bay of Bengal from 3-6 November 2020.
- The second phase was conducted in the Arabian Sea from 17-20 November 2020.Phase-1 of MALABAR 2020 witnessed participation of Indian Navy units with United States Ship (USS) John S McCain, Her Majesty’s Australian Ship (HMAS) Ballarat with integral MH-60 helicopter, and Japan Maritime Self Defence Ship (JMSDF) Onami, with integral SH-60 helicopter.
- ‘Dual Carrier’ operations, advanced surface and anti-submarine warfare exercises, seamanship evolutions and weapon firings were also undertaken during both phases of MALABAR 2020, demonstrating the synergy, coordination and inter-operability between the four friendly navies.
- The Malabar series of exercises, which began as an annual bilateral naval exercise between India and the US in 1992, has seen increasing scope and complexity over the years. The 24th edition of MALABAR, conducted in a ‘non-contact at sea only’ format in the backdrop of Covid-19 pandemic, was reflective of the commitment of the participating countries to support a free, open, inclusive Indo-Pacific as well as a rules-based international order.
2) Office of profit:
Relevant to: GS prelims and Mains GS 2.
Context: The Joint Parliamentary Committee on Office of Profit is deliberating on whether an MP can continue to teach at a university and if this draws the provisions of “Office of Profit” rules.
What is an ‘office of profit’?
- If an MLA or an MP holds a government office and receives benefits from it, then that office is termed as an “office of profit”.
- A person will be disqualified if he holds an office of profit under the central or state government, other than an office declared not to disqualify its holder by a law passed by Parliament or state legislature.
What is the underlying principle for including ‘office of profit’ as criterion for disqualification?
Makers of the Constitution wanted that legislators should not feel obligated to the Executive in any way, which could influence them while discharging legislative functions.
In other words, an MP or MLA should be free to carry out her duties without any kind of governmental pressure. The intent is that there should be no conflict between the duties and interests of an elected member.
The office of profit law simply seeks to enforce a basic feature of the Constitution- the principle of separation of power between the legislature and the executive.
Reasons for controversies:
- The expression “office of profit” has not been defined in the Constitution or in the Representation of the People Act, 1951.
- It is for the courts to explain the significance and meaning of this concept. Over the years, courts have decided this issue in the context of specific factual situations.
Role of Judiciary in defining the ‘office of profit:
The Supreme Court in Pradyut Bordoloi vs Swapan Roy (2001) outlined the four broad principles for determining whether an office attracts the constitutional disqualification.
- First, whether the government exercises control over appointment, removal and performance of the functions of the office
- Second, whether the office has any remuneration attached to it
- Third, whether the body in which the office is held has government powers (releasing money, allotment of land, granting licenses etc.).
- Fourth, whether the office enables the holder to influence by way of patronage.
3) India and Luxembourg bilateral meet:
Relevant to: Mains GS 2
Context: The first meeting between India and Luxembourg in 20 years was held recently.
The meeting resulted in three new bilateral agreements.
- All three agreements are in the financial space to promote trade ties between India and Luxembourg.
- Luxembourg is the third largest foreign investor in India.
The three agreements that have been signed are:
- Luxembourg Stock Exchange with State Bank of India (SBI).
- Luxembourg Stock Exchange with the India International Stock Exchange (INX).LuxInnovation and Invest India.
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI )India also invited Luxembourg to join the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
About CDRI:
- Launched by Modi in September 2019 at the UN Secretary-General’s Climate Action Summit in New York, US.
- It is a platform where knowledge is generated and exchanged on different aspects of disaster and climate resilience of infrastructure.
- It will create a mechanism to assist countries to upgrade their capacities and practices, with regard to infrastructure development in accordance with their risk context and economic needs.
Benefits and significance:
- This initiative will benefit all sections of society.
- Economically weaker sections of society, women and children, are the most vulnerable to the impacts of disasters and hence, will be benefitted from the improvement of knowledge and practice in creating disaster resilient infrastructure.
- It will also benefit all areas with high disaster risk.
- In India, the north-eastern and Himalayan regions are prone to earthquakes, coastal areas to cyclones and tsunamis and central peninsular region to droughts.
4) Five EYES:
- It is an intelligence alliance comprising Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- These countries are parties to the multilateral UKUSA Agreement, a treaty for joint cooperation in signals intelligence.
Origin: It began in 1946 when the United States and the United Kingdom agreed to an open exchange of intelligence on the communications of foreign nations. It was expanded when Canada joined the alliance in 1948, followed by Australia and New Zealand in 1956.

5) Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC):
Relevant to: GS Prelims
Context: The latest Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) forum was held online this year because of the pandemic.
APEC: It is a regional economic forum established in 1989 to leverage the growing interdependence of the Asia-Pacific.
Aim: To create greater prosperity for the people of the region by promoting balanced, inclusive, sustainable, innovative and secure growth and by accelerating regional economic integration.
Functions:
- APEC works to help all residents of the Asia-Pacific participate in the growing economy. APEC projects provide digital skills training for rural communities and help indigenous women export their products abroad.
- Recognizing the impacts of climate change, APEC members also implement initiatives to increase energy efficiency and promote sustainable management of forest and marine resources.
- The forum adapts to allow members to deal with important new challenges to the region’s economic well-being. This includes ensuring disaster resilience, planning for pandemics, and addressing terrorism.
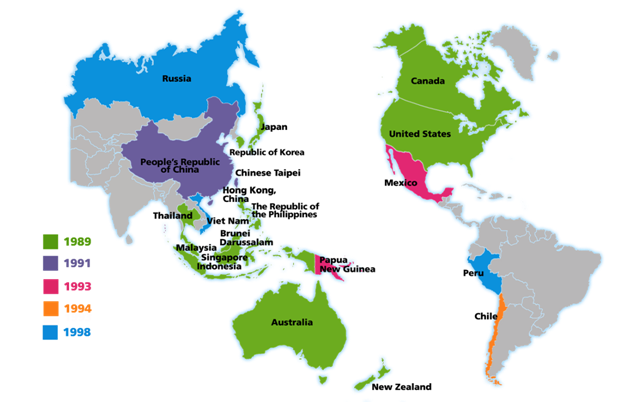
- Members: APEC’s 21 member economies are Australia; Brunei Darussalam; Canada; Chile; People’s Republic of China; Hong Kong, China; Indonesia; Japan; Republic of Korea; Malaysia; Mexico; New Zealand; Papua New Guinea; Peru; The Philippines; The Russian Federation; Singapore; Chinese Taipei; Thailand; United States of America; Viet Nam.

6) Digital Nation:
Relevant to: Mains GS 2 and 3
Context- Role of digital technology in governance
Key points:
- Affordable smartphones and Internet access have made India a digital nation with an estimated 750 million connections and a thriving financial technology sector.
- Digital platforms providing goods and services, including online education and telemedicine, have grown vigorously during the COVID-19 pandemic, while many professionals have maintained productivity by working from home.
- The true measure of digital nations is the readiness of governments to use technology to create open, participatory public systems that citizens consider trustworthy. What governance must achieve is a reliable system of digital welfare.
- A beginning has, no doubt, been made through government-to-citizen services using Common Service Centres, advice to agriculturists, digital payments of welfare benefits through bank accounts and, even legal advice online to four lakh people under the Tele-Law scheme. In health sector:
- Successive governments failed to grasp the promise of achieving universal health coverage (UHC) by 2022, for which the erstwhile Planning Commission presented a road map a decade ago. Now, the nucleus plan is Ayushman Bharat, with a digital health identity for all.
- With the emphasis on digitalization, it should be possible to achieve measurable progress early on at least on one UHC component – access to free, essential prescription drugs.
- A digital health ID would help prescribe and dispense essential medicines free.
- At a broader level, efficient digital government depends on transforming internal processes, and fixing deadlines for service delivery. Conclusion: If digital has to become a way of life, redefining the irregular functioning of citizen-centric services would be a good place to start, with deadlines for government departments.
Sarat Chandra IAS Academy provides civil services coaching not only for graduates but also for students pursuing their graduation. You can visit our website, telegram channel, facebook account, instagram for regular current affairs, daily questions on UPSC prelims and Mains for practice. Also we provide test series for prelims and mains, both Online classes and Offline classes (Vijayawada)