12th May 2022
Topics
1. Russia – Ukraine war – an eye-opener for India and others
GS – 2: International Relations
2. Asani – A Tropical Cyclone
GS – 1: Geography
3. National Family Health Survey (NFHS – 5), 2019–21
GS – 2: Governance and Social Issues
4. Param Vishisht Seva Medal
GS – 3: Internal Security
5. Thrissur Pooram – Biggest festival in Kerala
GS -1: Art & Culture
1. Russia – Ukraine war –an eye-opener for India and others
Context:Recent, Ukraine wide fall-out has taught many lessons for India and other countries.
- In international relations there are no permanent friends, there are only permanent interests
- Comprehensive National Power
-
- India’s wars of tomorrow would have to be fought with Indian equipment only. The Russia-Ukraine crisis has clearly shown the vulnerability of depending upon another nation for military equipment.
- CNP is indicative of a nation’s deterrence capability and its ability to fight if deterrence fails.
- The lesson for India’s political and entrepreneurial class is to understand better our vulnerabilities and double down on “aatmanirbharta”.
-
Self-defending:
- The Ukraine war clear shows that India must defend on its own in its issues with neighboring countries like China as West is not likely to enter into war with China for India’s sake. While a lot of international condemnation is expected, as is happening against Russia, nobody would provide military support or enter into war for another country’s sake.
- Alliance do matter in the inter-connected world no matter how big the country might be
-
- Ukraine relation with the Western countries helped it in resisting Russia’s military.
- Intelligence is the key to power
-
- Developing high-resolution satellites imaginary is crucial for any country to contribute a bit in modern warfare
- Nuclear weapons are clearly not a deterrence against economic warfare, real economic muscle is necessary for that.
-
- Russia has been humiliated over the years, its security has been threatened with the relentless expansion of NATO and dismissal of its protests.
- The structures of the existing “international order” are breaking down further.
-
- The UN is again demonstrating its impotency to establish peace, which is not the same as countries scoring diplomatic points against each other in the UN Security Council or the General Assembly.
- The lesson to learn is that the West controls the global financial system
-
- The hegemony of the US $ has been powerfully demonstrated in Russia’s case.
-
Substantial powers
- Even though Russia has been a close ally of India for decades, the growing proximity between Moscow and Beijing is public. Therefore, any possibility of Russia playing the active role of a mediator between India and China is unlikely.
- Moreover, even though India has succeeded in a neutral global stand until now, it might not be able to continue this for long.
- US, Russia and China are amongst the most substantial powers, and even if India does not join a bloc, it would have to accept which country it was closer to.
-
Boost technology
- Modern warfare has more tech-friendly. Therefore, massive investments to boost technology in the country would be one of the essential steps, rather than re-inventing the old wheel.
- Inspite of all these, India got a huge market to scaleup its Wheat production as global attention is towards India in this regard.
Asani – A Tropical Cyclone
- Asani is the first cyclonic storm in this season that occurred in Bay of Bengal.
- Srilanka has given the name Asani which means wrath (means great anger) in Sinhalese.
- The next cyclone name will be Sitrangas given by Thailand.
Tropical Cyclone
- Tropical cyclones are low pressure systems that form over warm tropical waters.
- They typically form when the sea-surface temperature is above 26.5°C.
- A cyclone will dissipate once it moves over land or over cooler oceans.
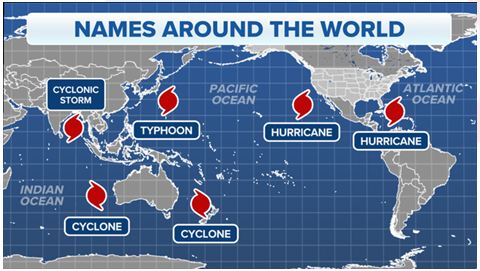
Tropical cyclones are referred to by different names depending on where they originate in the world.
- Hurricanes occur in the Atlantic Ocean and the eastern north Pacific Ocean.
- Typhoons occur in the western Pacific Ocean.
- Tropical cyclones occur in the south Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean.
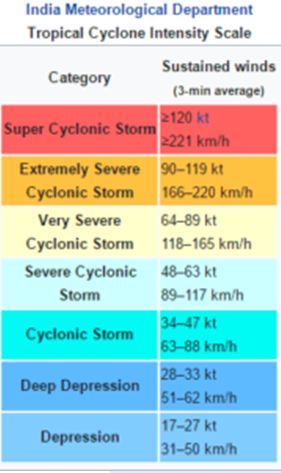
Intensity scale of Tropical Cyclone by IMD:
Cyclones in India
- From March to May and from October to December are the cyclonic periods in India but exceptional cases cyclones appear in June and September.
- Intense storms are seen from May to June and from October to November in India
India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- The India Meteorological Department(IMD) is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.
- IMD is headquartered in Delhi
- It has the responsibility for forecasting, naming and distribution of warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northern Indian Ocean region, including the Malacca Straits, the Bay of Bengal, the Arabian Sea and the Persian Gulf.
National Family Health Survey (NFHS – 5), 2019–21
Context: Recently, NFHS-5 has been released by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India, with the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) Mumbai, serving as the nodal agency.
Key Findings
-
HOUSEHOLD POPULATION AND HOUSING CHARACTERISTICS
-
Drinking water:
- Ninety-six percent of households use an improved source of drinking water.
- In India, almost all urban households (99%) and rural households (95%) have access to an improved source of drinking water
- The main sources of drinking water for urban households are water piped into their dwelling, yard, or plot (54%), tube wells or boreholes (16%), and public taps or standpipes (12%)
- In contrast, rural households rely most on tube wells or boreholes (46%), followed by water piped into their dwelling, yard, or plot (23%). In rural areas, 68 percent of households have water on their premises or delivered to their dwelling, compared with 86 percent in urban areas.
-
Sanitation
- Sixty-nine percent of households use an improved sanitation facility that is not shared with other households and 8 percent use a facility that would be considered improved if it were not shared.
- Nineteen percent of households have no facility, which means that the household members practice open defecation
- Eighty-three percent of households have access to a toilet facility.
-
Electricity
- Ninety-seven percent of households have electricity (95% of rural households and 99% of urban households).
-
Cooking fuel
- Only fifty-nine percent of households use clean fuel for cooking
-
CHARACTERISTICS OF RESPONDENTS
- Literacy: Seventy-two percent of women and 84 percent of men are literate.
-
Employment:
- Men are more likely to be employed than women
- 25 percent of women are currently employed, compared with 75 percent of men.
- Eighty-three percent of employed women earn cash for their work.
-
Occupation:
- Forty-six percent of women and 32 percent of men who were employed in the 12 months preceding the survey are engaged as agricultural workers, whereas only 11 percent of women and 9 percent of men work in the service sector.
- Internet usage: One-third of women and slightly over half (51%) of men age 15-49 have ever used the internet.
-
FERTILITY AND FERTILITY PREFERENCES
- Total fertility rate: The total fertility rate is 2.0 children per woman, which declined from 2.2 children in 2015- 16 and is currently below the replacement level of fertility of 2.1 children per woman.
OTHER PROXIMATE DETERMINANTS OF FERTILITY
- Eleven percent of marriages are consanguineous marriages, which are more common in all of the southern states except Kerala.
- Almost half of women with an abortion (48%) sought their abortion due to an unplanned pregnancy
-
FAMILY PLANNING
- Modern contraceptive use by currently married women has increased from 48 percent to 56 percent between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- Female sterilization is still the most popular contraceptive method, used by 38 percent of currently married women.
-
INFANT AND CHILD MORTALITY
- For the five years preceding the survey, the under-five mortality rate was 42 deaths per 1,000 live births, and the infant mortality rate was 35 deaths per 1,000 live births.
- The neonatal mortality rate was 25 deaths per 1,000 live births.
-
MATERNAL HEALTH
- The proportion of women age 15-49 in India who received Antenatal care (ANC) has risen from 84 percent in NFHS-4 (2015-16) to 94 percent in NFHS-5 (2019-2021), and 85 percent received ANC from a skilled provider in NFHS-5.
-
CHILD HEALTH
- Nighty-one percent of live births in the five years preceding the survey had a written record of the child’s weight at the time of birth or the mother was able to recall the child’s weight. Eighteen percent of these births had a low birth weight (less than 2.5 kg), the same as in 2015-16.
- Sixty-eight percent of children received any service from an anganwadicentre. Sixty-two percent received food supplements.
-
NUTRITION AND ANAEMIA
- Thirty-six percent of children under age five years are stunted (short for their age); 19 percent are wasted (thin for their height); 32 percent are underweight (thin for their age); and 3 percent are overweight (heavy for their height). Children born to mothers with no schooling and children in the lowest wealth quintile are most likely to be undernourished.
- Sixty-seven percent of children age 6-59 months have anaemia (haemoglobin levels below 11.0 g/dl), which is higher than the NFHS-4 estimate of 59 percent.
- In adult’s Fifty-seven percent of women and 25 percent of men age 15-49 have anaemia.
-
MORBIDITY AND HEALTH CARE
- The prevalence of tuberculosis is higher among men (283 per 100,000) than among women (162 per 100,000).
- At least one usual household member is covered under any health insurance or health scheme in over two-fifths (41%) of households.
- Twenty-one percent of women and 24 percent of men age 15 and over have hypertension.
- The proportion of deaths that are due to non-medical reasons (accidents, violence, poisoning, homicides, or suicides) is higher among men (11%) than women (6%).
- The proportion of deaths due to nonmedical reasons peaks at ages 15-29 for both men and women, reaching a high (47%) of all deaths for men age 20-29.
-
HIV/AIDS-RELATED KNOWLEDGE, ATTITUDES, AND BEHAVIOUR
- One-fifth (22%) of women and nearly one-third of men (31%) age 15-49 in India have comprehensive knowledge of HIV/AIDS.
-
WOMEN’S EMPOWERMENT and DOMESTIC VIOLENCE
- Thirty-two percent of currently married women age 15- 49, and 98 percent of currently married men age 15-49 are employed. Among employed women, 83 percent earn cash and 15 percent are not paid at all. More than four-fifths of employed women (85%) participate in decisions about the use of their own earnings.
- Thirty percent of women age 18-49 have experienced physical violence since age 15, and 6 percent have ever experienced sexual violence in their lifetime. Three percent of ever-pregnant women age 18-49 have experienced physical violence during any pregnancy.
- Six percent of ever-married women age 18-49 have experienced spousal sexual violence.
About NFHS
- The National Family Health Survey (NFHS) is a large-scale, multi-round survey conducted in a representative sample of households throughout India.
- Three rounds of the survey have been conducted since the first survey in 1992-93.
- The survey provides state and national information for India on fertility, infant and child mortality, the practice of family planning, maternal and child health, reproductive health, nutrition, anaemia, utilization and quality of health and family planning services.
Each successive round of the NFHS has had two specific goals:
- to provide essential data on health and family welfare needed by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and other agencies for policy and programme purposes, and
- to provide information on important emerging health and family welfare issues.
Param Vishisht Seva Medal
Context: Recently, Southern Army Commander Lt Gen JS Nain awarded Param Vishisht Seva Medal
- The PVSM is awarded in recognition of peace-time service of the most exceptional order.
- It was constituted in 1960 and since then till date
- It may be awarded posthumously.
The following categories of personnel shall be eligible for the medal: –
- All ranks of the Army, the Navy and the Air Force including Territorial Army Units, Auxiliary and Reserve Forces (when embodied) and other lawfully constituted Armed Forces.
- Nursing officers and other members of the Nursing Services in the Armed Forces.
Thrissur Pooram – Biggest festival in Kerala
Context: After two years of Covid restrictions, the festival is back in its original form with grand processions
- Kerala’s biggest temple festival Thrissur Pooram is celebrated every year with a lot of pomp and fervor at Vadakkunnathan Temple in the city of Thrissur.
- This festival is held in various temples of the state, though the centre of attraction is the Vadakkunnathan temple.
- Thrissur Pooram, the largest and most famous of all Poorams, is observed in the month of Medam on Pooram day when the moon rises with the Pooram star.
- On this day, various temples are invited to the city of Thrissur to pay homage to Lord Vadakkunnathan at the Vadakkunnathan temple
- The highlight of the festival is the huge procession which comprises of over 50 elephants decorated with golden ornaments.
- The annual temple festival is more than 200 years old and was started by SakthanThampuran or Rama Varma IX, the Maharaja of Kochi, who first organized this festival and invited 10 temples – Paramekkavu, ThiruvambadiKanimangalam, Karamucku, Laloor, Choorakottukara, Panamukkampally, Ayyanthole, Chembukkavu and Neythilakavu.
- Another tradition is called PooraVilambharam where an elephant pushes open the south entrance gate of the Vadakkunnathan Temple, the venue for Thrissur Pooram, with the idol of ‘Neithilakkavilamma’ atop it.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 12th May 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube