UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 29th March 2022
Topics for the day:
- S – EU LNG Deal
- Bucharest Nine
- Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme
- NPPA hikes prices of 800 essential drugs from 1 April
- India, UAE Trade pact
- ODF plus villages
- Protest in LS as Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill envisages lifting biometrics of detainees
U.S – EU LNG Deal
Context :
- The U.S. President struck a deal with the European Union to supply liquefied natural gas (LNG) to meet the continent’s energy needs. The deal comes amidst efforts by European countries to wean themselves off Russian energy exports in the wake of the Russia-Ukraine war.
More on the news :
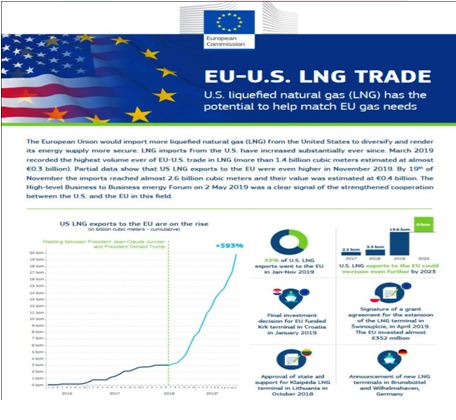
- Under the U.S-EU LNG deal, the United States will supply 15 billion cubic meters (bcm) of LNG to the EU this year this is equivalent to around 10 per cent of the gas imports from Russia.
- Further, the EU will import additional LNG of at least 50 bcm until 2030 from the U.S. This is expected to reduce Europe’s dependence on Russian energy exports and thus neutralise the Kremlin’s influence on Europe to a significant extent.
- It should be noted that Europe has been at the mercy of Russian energy exports which has limited its response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine due to the fear that Russia could cut off its energy exports to Europe.
- Gas prices in Europe rose sharply even before the Russian invasion and a drop in supplies from Russia could make the situation even worse. This has left the EU vulnerable, so much that the West hasn’t imposed sanctions on EU’s energy imports from Russia.
- Europe relies on Russian exports to meet about 40% of its natural gas requirements and about a quarter of its crude oil needs.
- Germany and many countries in Eastern Europe depend on Russia to meet more than 80% of their natural gas needs.
Analysis :
- As US LNG plants are already producing at full capacity, analysts believe most of the additional gas going to Europe would have to come from exports that would have gone to other parts of the world
- Such a relocation to Europe is already happening because European gas prices have in recent months mostly been the highest in the world
- This would tighten the supply of LNG to other parts of the world.
- This also comes in the wake of Moscow saying that “unfriendly” countries, including EU member states, must start paying in roubles for Russian oil and gas. This has heightened concerns of potential disruptions to Europe’s gas supply.
Bucharest Nine
Context :
- The envoys to India of nine Eastern European countries called Bucharest Nine jointly wrote to acquaint the Indian public with the basic facts on the ground about the “premeditated, unprovoked and unjustified Russian aggression in Ukraine”.
- The B9 countries have been critical of President Vladimir Putin’s aggression against Ukraine since 2014, when the war in the Donbas started and Russia annexed the Crimean peninsula.
What is Bucharest Nine?
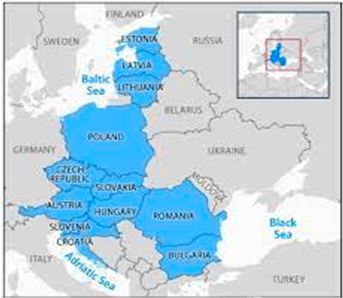
- The “Bucharest Nine” is a group of nine NATO countries in Eastern Europe that became part of the US-led military alliance after the end of the Cold War.
- The B9 was founded on November 4, 2015, and takes its name from Bucharest, the capital of Romania.
Members of the grouping :
- Romania, Poland, Hungary, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and the three Baltic republics of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- All members of the B9 are part of the European Union (EU) and North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO)
- All nine countries were once closely associated with the now dissolved Soviet Union, but later chose the path of democracy.
Functions of B9 :
- The B9 offers a platform for deepening the dialogue and consultation among the participant allied states, in order to articulate their specific contribution to the ongoing processes across the North-Atlantic Alliance.
- It works in total compliance with the principles of solidarity and indivisibility of the security of the NATO Member States.
Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme
Context:
- The Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme has been approved for continuation during 2021-2026.
The PACER scheme:
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER) scheme comprises the Antarctic program, Indian Arctic program, Southern Ocean program and Cryosphere and Climate program.
- It is being implemented successfully through National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
What is the cryosphere?
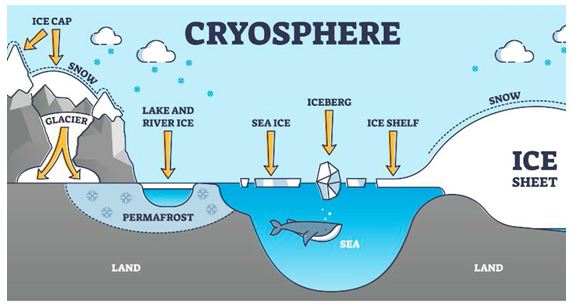
- The cryosphere is the frozen water part of the Earth system.
- These are places on Earth that are so cold that water is frozen solid
- These areas of snow or ice, which are subject to temperatures below 0°C for at least major part of the year, compose the cryosphere.
- This includes the largest parts of the cryosphere, the continental ice sheets found in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as ice caps, glaciers, and areas of snow and permafrost.
Significance of Cryosphere :
- The components of the cryosphere play an important role in the Earth’s climate.
- Snow and ice reflect heat from the sun, helping to regulate our planet’s temperature.
- Since polar regions are some of the most sensitive to climate shifts, the cryosphere may be one of the first places where scientists are able to identify global changes in climate.
PACER encompasses the following six components :
- Construction of polar research vessel
- Construction of the third research base in Antarctica
- Indian scientific endeavours in the Arctic
- Polar expeditions-Antarctica
- Replacement of Maitri station
- Southern Ocean Research
Major achievements of the PACER scheme in the recent years are:
- Executed 39th & 40th Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica. 41st Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica is ongoing.
- Clear-air atmospheric observatories containing automatic weather stations, a suite of sensors to measure aerosol and greenhouse gas concentrations have been established at Maitri and Bharati stations.
- Twenty-three research projects related to glaciology, marine science, polar biology, and atmospheric science were successfully carried out during 2019-20 Arctic Expedition.
- IndARC mooring system along with Hydrophone system was successfully deployed at Svalbard.
- Glaciological field campaigns were carried out in glaciers in Chandra basin of Lahaul-Spiti region of Western Himalaya.
NPPA hikes prices of 800 essential drugs from 1 April

Context:
- The National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) has announced a hike in prices of around 800 essential drugs from 1 April.
- These drugs are included in the National Essential List of Medicine (NELM).
- The rise in drug prices works out at around 10.76% based on the Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
- The Drugs Price Control Order 2013, allows NPPA to revise the ceiling price of scheduled formulations as per the annual wholesale price index (WPI) for the preceding calendar year on or before 1 April of every year and notify the same on the first day of April every year.
How are prices of drugs regulated in India?
- All medicines under the NLEM are under price regulation.
- As per the Drugs (Prices) Control Order 2013, scheduled drugs, about 15% of the pharma market, are allowed an increase by the government as per the WPI while the rest 85% are allowed an automatic increase of 10% every year.
- The NPPA was set up to fix/revise prices of controlled bulk drugs and formulations and to enforce price and availability of the medicines in the country, under the Drugs (Prices Control) Order
- The ceiling price of a scheduled drug is determined by first working out the simple average of price to retailer in respect of all branded and generic versions of that particular drug formulation having a market share of more than or equal to 1%, and then adding a notional retailer margin of 16% to it.
- The NPPA is also mandated to collect/maintain data on production, exports and imports, market share of individual companies, profitability of companies etc ,for bulk drugs and formulations.
What is the NPPA ?
- NPPA was set-up as an independent Regulator for pricing of drugs and to ensure availability and accessibility of medicines at affordable prices.
- NPPA is neither a Statutory nor a Constitutional Body. It is an attached office of the Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilizers.
- The functions of NPPA include fixation and revision of prices of Scheduled drugs under Drug (Price Control) Orders issued from time to time, as well as monitoring and enforcement of prices and ensuring availability and accessibility of all medicines and medical devices, including non-scheduled drugs
India, UAE Trade pact
Context :
- The free trade agreement between India and the UAE is likely to come into effect from May 1 this year,Commerce and Industry Minister said.
More on the deal :
- Under this, domestic exporters of as many as 6,090 goods from sectors such as textiles, agriculture, dry fruits, gem and jewellery would get duty-free access to the UAE market.
- The Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) was signed by India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in February which aims to boost bilateral trade to $100 billion in the next five years from current $60 billion.
- The two countries have agreed to set up a technical council on Investment, Trade Promotion and Facilitation, as part of the agreement signed.
- Overall, the UAE is offering duty elimination on over 97% of its products which account for 99% of Indian exports in value terms.
- Immediate duty-free access covers all labour-intensive sectors such as gems and jewellery, textiles and apparel, agricultural and fish products, leather, footwear, and sport goods, pharmaceuticals and medical devices, and many engineering products.
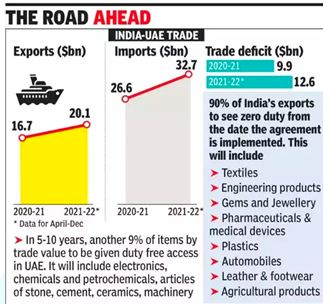
- Currently, India is exporting about $26 billion worth of goods to the UAE, almost 90% of them will get total tariff (or customs duty) elimination on Day 1 itself.
- In the coming 5-10 years the rest of the 9.5% (about 1,270 goods) will also get zero duty.
India UAE economic ties :
- India and the UAE established diplomatic relations in 1972.
- The greater push has been achieved in bilateral relations when the visit of India’s Prime Minister to the UAE in August 2015 marked the beginning of a new strategic partnership between the two countries.
- During the visit of the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi to India in January 2017 as the chief guest at India’s Republic Day celebrations, it was agreed that bilateral relations were to be upgraded to a comprehensive strategic partnership.
- Bilateral trade between India and the UAE stood at $43.3 billion in 2020-21. Exports from india were $16.7 billion, and imports, driven by oil, were $26.7 billion in 2020-21. However the India-UAE total trade merchandise has been valued at US $52.76 billion for the first nine months of the fiscal year 2021-22.This has made the UAE India’s third largest trading partner.
- The UAE’s investment in India is estimated to be around US $11.67 billion, which makes it the ninth biggest investor in India.
- Many Indian companies have set up manufacturing units either as joint ventures or in Special Economic Zones for cement, building materials, textiles, engineering products, consumer electronics, etc.
- Recently India, Israel, the United Arab Emirates and the United States have decided to launch a new quadrilateral economic forum.
- UAE hosts a large Indian community which numbers close to 3.5 million. The nation has been a consistent provider of jobs to Indian people.
- India had received over US $83 billion in remittances in 2020 which was one of the highest in the world. Amongst this, a substantial portion came from the UAE
- The UAE is one of India’s key energy providers and remains committed to meeting India’s growing energy India imported US $10.9 billion worth of crude oil from the UAE in 2019-20.
ODF plus villages
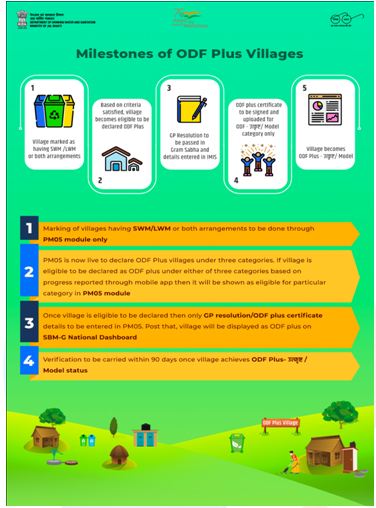
Context and news :
- India has crossed a milestone of 50 thousand open defecation-free (ODF) Plus
- ODF plus village is defined as “a village which sustains its Open Defecation Free (ODF) status, ensures solid and liquid waste management and is visually clean.”
- Among the top performing States are Telangana with 13,960 ODF Plus villages followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
- Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen Phase-II was launched in February 2020 with the aim to ensure that all villages in the country can declare themselves as ODF Plus by the end of 2024.
- The mission towards becoming ODF Plus has several components including biodegradable waste management including the GOBAR dhan Scheme, Grey water management, Plastic waste management and Faecal sludge management etc.
- ODF Plus villages have been divided into three categories, Aspiring, Rising, and Model, to showcase their progress.
What is ODF tag?
- The original ODF protocol, issued in 2016, said, “A city/ward is notified as ODF city/ward if, at any point of the day, not a single person is found defecating in the open.”
ODF+ v/s ODF++ :
- ODF+ and ODF++ were launched to scale up and sustain the work undertaken by the cities after achieving the ODF status under Phase I of the Swachh Bharat Mission.
- ODF+ protocol/Tag/Certification says that a city, ward or work circle could be declared?ODF+ if,at any point of the day, not a single person is?found defecating and/or urinating in the open, and all community and?public toilets?are functional and well-maintained.
- While the ODF++ protocol//Tag/Certification adds the condition that fecal?sludge/septage and sewage?is safely managed and treated, with no discharging and/or dumping of untreated fecal?sludge/ septage and sewage in drains, water bodies or open areas.
- While ODF+ focuses on toilets with water, maintenance and hygiene, ODF++ focuses on toilets with sludge and septage management.
- Also remember that ?ODF+ and?ODF++ statuses are given by ?ministry of housing and urban affairs(MoHUA)
Protest in LS as Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill envisages lifting biometrics of detainees

Context and more on the bill :
- The Criminal Procedure (Identifcation) Bill, 2022, that would allow the police and prison authorities to collect, store and analyse physical and biological samples, including retina and iris scans, was introduced in the Lok Sabha amid strong protests from Opposition members, who forced a vote on the issue and termed the Bill “unconstitutional”.
- The Bill also seeks to apply these provisions to persons held under any preventive detention law.
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) will be the repository of physical and biological samples, signature and handwriting data that can be preserved for at least 75 years.
- Opposition members argued that the Bill was beyond the legislative competence of Parliament as it violated fundamental rights of citizens, including the right to privacy.
Key Provisions:
- It seeks to repeal the Identification of Prisoners Act 1920. The said Act, in its present form, provides access to a limited category of persons whose body measurements can be taken.
- It authorises law enforcement agencies to collect, store and analyse physical and biological samples of convicts and other persons for the purposes of identification and investigation in criminal matters.
- The Bill also authorises police to record signatures, handwriting or other behavioural attributes referred to in section 53 or section 53A of the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973, for the purposes of analysis.
- As per the Bill, any person convicted, arrested or held under any preventive detention law will be required to provide “measurements” to a police officer or a prison official.
- Any state government of Union Territory administration may notify an appropriate agency to collect, preserve and share the measurements of a person of interest in their respective jurisdictions.
- Resistance to or refusal to allow the taking of measurements under this Act shall be deemed to be an offence under the Indian Penal Code (IPC).
- The bill also defines “measurements” to include finger impressions, palm-print and foot-print impressions, photographs, iris and retina scan, physical, biological samples and their analysis, etc.
- It empowers a Magistrate to direct any person to give measurements; a Magistrate can also direct law enforcement officials to collect fingerprints, footprint impressions and photographs in the case of a specified category of convicted and non-convicted persons.
Issues with the Act.
- Members argued that the Bill, which implied use of force in collection of biological information, could also lead to narco analysis and brain mapping, and claimed that it violates Article 20 (3) of the Constitution
- The Bill also supposedly goes against the Supreme Court judgment in the K.S. Puttaswamy case.
- The proposed law, that also provides for retaining the people’s measurements for 75 years from the date of collection, was in “violation of the Right to be Forgotten.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 29th March 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

