Topics
- India and Anaemia
- Indian Certification of Medical Devices Plus Scheme
- Flag Satyagraha / Jhanda Satyagraha
- National Maritime Heritage Complex
- Integrated Tri-service Theatre Commands
- India and European Union
- India and Anaemia
#GS1 #Health and Nutrition #Women and Children
Context: A recent study suggests anaemia is being over-diagnosed in India.
Key Details:
- The National Family Health Survey – 5 data has shown that India’s anaemia situation has remained unchanged from the high prevalence of nearly 60% reported in the NFHS-4 survey in 2015.
- It indicated that there was a high anaemic population of Indian women and children that had not responded to the various iron supplementation and food fortification programs implemented in the last five years.
- Some researchers said that anaemia is being over-diagnosed in India due to a wrong (higher than appropriate) haemoglobin diagnostic cut-off.
- In their recent paper published in the Lancet Global Health, these researchers asserted the need for re-examination of WHO haemoglobin cut-offs to define anaemia.
- WHO standard – Currently, the WHO haemoglobin (Hb) diagnostic cut-off to diagnose anaemia is –
- For children, a haemoglobin of less than 11 grams per decilitre (g/dl) indicated anaemia.
- For non-pregnant and pregnant women, it was less than 12 g/dl and 11g/dl respectively, and for men, it was less than 13 g/dl.
- Among children, prevalence was adjusted for altitude and among adults, it was adjusted for altitude and smoking status.
- These researchers used data from the Comprehensive National Nutrition Survey (CNNS) carried out in 2016-18 (by the Health Ministry in collaboration with UNICEF and the Population Council).
(CNNS is an exhaustive and quality-controlled survey that measures a number of biomarkers of health and nutrition with great precision in venous blood sampled from a very large number of children across India).
- The prevalence of anaemia in these children was 35%, when using the WHO cut-off, lower than what the NFHS surveys have found.
- The extreme low value in a representative healthy population of children (in CNNS), or the 2.5th centile of the distribution of Hb values, was chosen as the Hb cut-off to diagnose anaemia.
- The Indian cut-offs based on the CNNS were lower than the current WHO cut-off, across all ages from 1-19 years in boys and girls.
- If the proposed anaemia cut-offs were used, the burden of anaemia in Indian children would fall from present value (35%) to one-third (11%).
Difference in blood sampling method
- The study also pointed to differences in the way blood is drawn for sampling in CNNS and NFHS.
- NFHS survey measured haemoglobin in a drop of capillary blood that oozes from a finger prick.
- This can dilute the blood and give a falsely lower value, and consequently it will appear that there was a higher prevalence of anaemia in the population.
- The CNNS survey used the recommended method of venous blood sampling and gave accurate values.
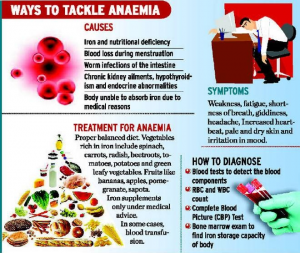
What is anaemia?
- The condition of having a lower-than-normal number of red blood cells or quantity of haemoglobin. It can make one feel tired, cold, dizzy, and irritable and short of breath, among other symptoms.
- A diet which does not contain enough iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 is a common cause of anaemia.
- Some other conditions that may lead to anaemia include pregnancy, heavy periods, blood disorders or cancer, inherited disorders and infectious diseases.
Other reasons for high prevalence of Anaemia in India:
- Iron-deficiency and vitamin B12-deficiency anaemia are the two common types of anaemia in India.
- Among women, iron deficiency prevalence is higher than men due to menstrual iron losses and the high iron demands of a growing foetus during pregnancies.
- Lack of millets in the diet due to overdependence on rice and wheat
- Insufficient consumption of green and leafy vegetables, and dominance of packaged and processed foods which are low in nutrition.
- Indian Certification of Medical Devices plus Scheme
#GS3 #Industrial policy #Growth and Development
Context: The Quality Council of India (QCI), and the Association of Indian Manufacturers of Medical Devices (AiMeD) have added further features to the ICMED Scheme for Certification of Medical Devices.
- ICMED 13485 PLUS scheme was launched by the QCI and AiMeD for Certification of Medical Devices in 2016.
ICMED 13485 PLUS
- ICMED Plus will verify the quality, safety and efficacy of medical devices.
- It integrates the Quality Management System components and product related quality validation processes through witness testing of products with reference to the defined product standards and specifications.
- Association of Healthcare Providers (AHPI) will encourage implementation of ICMED Plus among its members and stake holders.
Significance:
- ICMED PLUS is the first scheme around the world in which quality management systems along with product certification standards are integrated with regulatory requirements.
- This scheme will be an end-to-end quality assurance scheme for the medical devices sector in India.
- It provides the much-needed institutional mechanism for assuring the product quality and safety.
- It will assist the procurement agencies to tackle the challenges relating to the menace of counterfeit products and fake certification.
- This will also help in eliminating the circulation and use of sub-standard medical products or devices of doubtful origin that could prove to be serious health hazards.
About ICMED Scheme:
- The ICMED Scheme is a voluntary quality certification scheme for the medical device industry rolled out by the QCI and the National Accreditation Board for Certification Bodies (NABCB) in collaboration with the Association of Indian Medical Device Industry (AIMED).
- The Scheme has been launched with two levels of certification:
- ICMED 9000 certification which is ISO 9001 plus additional requirements.
- ICMED 13485 which is ISO 13485 plus additional requirements
- Flag Satyagraha / Jhanda Satyagraha
#GS1 #Indian Freedom Struggle
Context: The Ministry of Culture recently organised a programme to observe the Flag Satyagraha in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
About Flag Satyagraha:
- It was on March 18, 1923 that the first Tricolour was hoisted in Jabalpur, marking the start of ‘Jhanda Satyagraha’.
- According to the records, the outline of the Jhanda Satyagraha was prepared in the year 1922 in a meeting held in the Town Hall of Jabalpur.
- Despite the deployment of heavy police force, ignoring the orders of the British government, the brave immortal martyrs of Jabalpur had hoisted the flag in Victoria Town Hall without caring for their lives.
- The tussle began when Congress members on 8 March 1923, when the flag was waved at the municipal building, the European Deputy Commissioner was enraged and ordered to take down the flag.
- In violation of the government ban, some volunteers along with Subhadra Kumari Chauhan, Nathuram Modi, took out a procession with a flag.
- The Flag Satyagraha movement by the freedom fighters shook the British government and it infused a new life into the freedom movement.
- The news of flag hoisting in Jabalpur spread like fire in the country and after flags were hoisted at several places across the country.
Significance:
- The Flag Satyagraha is a campaign of peaceful civil disobedience during the Indian independence movement that focused on exercising the right and freedom to hoist the nationalist flag and challenge the legitimacy of the British Rule in India through the defiance of laws prohibiting the hoisting of nationalist flags and restricting civil freedoms.
Outcomes:
- The arrest of nationalist protestors demanding the right to hoist the flag caused an outcry across India especially as Gandhi had recently been arrested.
- Nationalist leaders such as Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, Jamnalal Bajaj, Chakravarthi Rajagopalachari, Dr. Rajendra Prasad and Vinoba Bhave organised the revolt and thousands of people from different regions travelled to Nagpur and other parts of the Central Provinces to participate in civil disobedience.
- The flag became a symbol of India’s aspiration for freedom.
- In the end, the British negotiated an agreement with Patel and other Congress leaders permitting the protestors to conduct their march unhindered and obtaining the release of all those arrested.
- National Maritime Heritage Complex
#GS1 #Art and Culture #Ancient India
Context: The Ministry of Culture and Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for ‘Cooperation in Development of National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) at Lothal, Gujarat’
Key Details:
- It is to be developed as a first of its kind in the country dedicated to the legacy of Maritime Heritage of India from ancient to modern times, to showcase India’s rich and diverse maritime glory.
- It would be developed as an international tourist destination that would be showcased for edutainment purpose.
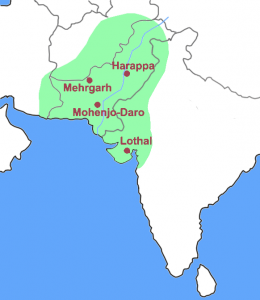
- The unique feature of NMHC is the recreation of ancient Lothal city – one of the cities of the Indus valley civilization (2400 BC).
- NMHC would have structures such as National Maritime Heritage Museum, Light House Museum, Heritage Theme Park, Museum Themed Hotels & Maritime themed eco-resorts, Maritime Institute etc.
- Various theme parks would be developed through public-private partnership.
- Ministry of Culture will facilitate in the fundraising for NMHC through the National Culture Fund (NCF).
- The services of National Culture Fund (NCF) shall be utilized to receive funds by way of grant, donation, CSR and foreign contribution.
- MoC will also provide needed collaboration to NMHC for all maritime heritage subjects under its project ‘Mausam’.
- Lothal was chosen because it has lots of archaeological remains, showcasing the trade route through water. It was a major maritime activities centre of Harappans.
- Lothal displays engineering standards used in creating an artificial dock that shows high standards of scientific and engineering skills, far more advanced than anywhere else in the world in the 3rd millennium BC

About Lothal:
- Lothal was one of the southernmost cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization located in Gujarat.
- Construction of the city began around 2200 BCE.
- According to the ASI, Lothal had the world’s earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati River on the trade route between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra.
- Lothal was a vital and thriving trade Centre in ancient times, with its trade of beads, gems, and valuable ornaments reaching the far corners of West Asia and Africa.
- The techniques and tools they pioneered for bead-making and in metallurgy have stood the test of time for over 4000 years.
- The Lothal site has been nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and its application is pending on the tentative list of UNESCO.
- Integrated Tri-service Theatre Commands
#GS3 #Security #GS2 #Governmentpolicies
Context: Recently, a high-level committee has been formed for wider consultations on the creation of integrated tri-service theatre commands.
Key Details:
- The panel includes the Vice-Chiefs of the three services, the Chief of Integrated Defence Staff to the Chairman, Chiefs of Staff Committee, and representatives from Ministries such as Home Affairs, Finance and Law.
- Some aspects like bringing in paramilitary forces, which are under the Home Ministry, under the purview of the theatre commands and financial implications that may arise in the process of integration has necessitated the move.
- The proposed Air Defence Command plans to integrate all air assets of the armed forces while the Maritime Theatre Command plans to bring in all assets of Navy, Coast Guard as well as coastal formations of Army and Air Force under one umbrella.
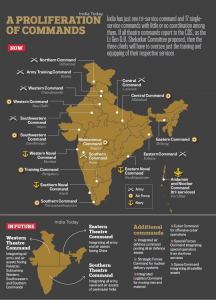
- On land, the Army’s Northern command and Western Command would be converted into 2-5 theatre commands.
Mandate of the committee:
- The committee will examine all issues and find a way forward before a formal note on their creation is sent to the Cabinet Committee on Security.
- The issue is about fine-tuning the proposals and forming a consensus on the integrated tri-service theatre commands.
Integrated Theatre Command:
- An integrated theatre command envisages a unified command of the three Services, under a single commander, for geographical theatres (areas) that are of strategic and security concern.
- The commander could either be from the Army, Air Force or the Navy.
- Theaterisation means putting specific units of personnel from the three services — Army, Navy and Air Force — under a common theatre commander so they fight as a cohesive unit.
- Both the US and China follow a theatre command doctrine.
- The integrated theatre commander will not be answerable to individual Services.
- Integration and jointness of the three forces will avoid duplication of resources. The resources available under each service will be available to other services too.
- The Shekatkar committee (in 2015) had recommended the creation of 3 integrated theatre commands — northern for the China border, western for the Pakistan border, and southern for the maritime role.
Views in favour of Integration:
- The integrated theatre commander will not be answerable to individual Services, and will be free to train, equip and exercise his command to make it a cohesive fighting force capable of achieving designated goals.
- The logistic resources required to support its operations will also be placed at the disposal of the theatre commander so that it does not have to look for anything when operations are ongoing.
- This is in contrast to the model of service-specific commands which India currently has, wherein the Army, Air Force and Navy all have their own commands all over the country. In case of war, each Service Chief is expected to control the operations of his Service through individual commands, while they operate jointly.
Views against Integration:
- There has been no occasion, during actual warfare, when the three services have not operated with commendable cooperation.
- Faraway land war and medium to high intensity wars are a distant possibility.
- With increased communication networks, interaction between three organizations is easy, they can come on board, can plan without much consideration of spatial distance, so there is no need for a new organisation.
- Domain knowledge of the integrated force commander is likely to be limited in respect of the other two Services components under his command, thereby limiting his ability to employ them in the most suitable manner and at the appropriate time.
Current Situation:
- There are about 19 military commands in the country and only two of them are tri-service commands – Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) and the Strategic Forces Command, which looks after nuclear assets.
- Each command is headed by a 3-star rank military officer.
Recent Developments:
- The appointment of the CDS (Chief of Defence Staff) and the creation of the Department of Military Affairs (DMA) are momentous steps towards the integration and advancement of defence forces.
- CDS: It is the single-point military adviser to the government as suggested by the Kargil Review Committee in 1999.
- Department of Military Affairs: Work exclusively pertaining to military matters will fall within the purview of the DMA. Earlier, these functions were the mandate of the Department of Defence (DoD).
- India and European Union
#GS2 #Internationalrealtions #GS3 #Security
Context: The maiden Indian Navy – European Union Naval Force (IN-EUNAVFOR) Exercise is being conducted in Gulf of Aden.
Key Details:
- Main objective is to enhance and sharpen their war-fighting skills and their ability as an integrated force to promote peace, security and stability in the maritime domain.
- Along with Indian Navy, other naval forces are from Italy, Spain and France.
- The naval exercise included advanced air defence and anti-submarine exercises, tactical manoeuvres, cross deck helicopter operations, Search & Rescue, and other maritime security operations.
- Indian Naval Ship Trikand, currently deployed for anti-piracy operations, is participating in the first ever exercise with EUNAVFOR
Significance:
- EUNAVFOR and the Indian Navy see eye-to-eye on multiple issues including counter piracy operations and protection of vessels deployed under the charter of World Food Programme (UN WFP).
- This engagement showcases increased levels of synergy, coordination and inter-operability between IN and EUNAVFOR.
- The two navies also have regular interaction through SHADE (Shared Awareness and Deconfliction) meetings held annually at Bahrain.
- SHADE is an international operational counter piracy platform, convened in Bahrain.
- It aimed to encourage partners for sharing information, assessing the evolution of trends, best practices and to de-conflict operations amongst counter-piracy actors in the Gulf of Aden, the Gulf of Oman and the Western Indian Ocean.
- It also underscores the shared values in ensuring freedom of seas and commitment to an open, inclusive and a rules-based international order.
- Concurrently, a virtual “Information sharing Exercise” is also being conducted between the Indian Navy Information Fusion Centre – Indian Ocean Region and Maritime Security Centre-Horn of Africa, an integral part of EUNAVFOR.
Courses we offer
UPSC Civil Services Coaching ( We are the best top rated IAS Academy in Vijayawada and Andhra Pradesh by Times of India Excellence award)
Degree with IAS (BA and BSc plus UPSC Coaching)
Inter with IAS (Sarat Chandra Junior College provides intermediate plus UPSC Coaching with HEC, MEC, CEC along with CLAT, IIT HSEE, IPMAT)
