Topics
- India European Union together in Agriculture Sector
- Authorised Economic Operators:
- Kappa And Lambda- Newest Sars-CoV-2 Variants
- China Declared as Malaria free country by World Health Organisation
- Central Information Commission
- Melanistic Leopard Spotted in Maharashtra
-
India- European Union together in Agriculture Sector:
#GS2 #Bilateral Relations #GS3 #Agriculture
Context: Recently, A Virtual meeting between Union Minister for Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Narendra Singh Tomar and Member of European Commission-Agriculture, Janusz Wojciechowski, was held.
Highlights of the meet:
- During the India European Union meeting, strong momentum of India-EU relations especially since the last India European Union Summit in July, 2020 was acknowledged
- Both discussed EU Common Agriculture Policy (CAP) and the recent India market reforms, UN Food System Summit, EU Farm to Fork Strategy and bilateral cooperation.
- India has asked the European Commission to fix the issue surrounding the Maximum Residual Limit (MRL) of Tricyclazole, a fungicide used for the control of rice blast but it is not approved for use in the European Union.
- As a result of this, Basmati rice exports to the EU are affected.
- The volume of annual basmati rice exports to the EU is around 10% of the country’s annual aromatic rice shipment.
- According to the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, all the required studies and documents have been submitted to the EU in May-2021 and MRL will be fixed by the second quarter of 2022 before next season.
- In the case of MRL for Tricyclazole, rice-importing countries do not have uniform tolerance limits. The US and Japan has fixed MRL at 3 PPM. However, the US does not allow the presence of pesticide residue like Isoprothiolane beyond 0.01 PPM.
- The Member of European Commission, Agriculture explained in detail the recent reforms undertaken by EU in Common Agriculture Policy as well as EU Farm to Fork Strategy in order to make agriculture green & sustainable.
- EU side also underlined that; EU has set a target of bringing 25 per cent of area in EU under Organic Farming by 2030.
- Indian side explained the scenario of agriculture in India, dominance of small farmers and commitment of Government of India for welfare of farmers in India.
- Recent initiatives taken by Government to increase farmer’s income, launch of Agriculture Infrastructure Fund with a corpus of Rs One Lakh Crore for development of farm gate and agriculture marketing infrastructure in rural areas, scheme of formation of 10000 FPOs were explained to EU.
- Indian side enlisted the steps being taken by the Government of India to make agriculture sustainable and environment friendly which included encouragement of application of nano-urea and Organic Farming under the Pramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana.
- And highlighted the initiative of encouraging organic farming on either sides of Ganga River up to 5 km through formation of clusters wherein 11 lakh farmers have already enrolled.
- Agriculture Minister of India also acknowledged India’s support to UN Food Systems Summit and informed EU delegation he will lead Indian delegation to Pre-Summit being organized from July 26th to 28th, 2021.
EU Common Agricultural Policy (CAP):
- Launched in 1962, it is a partnership between agriculture and society, and between Europe and its farmers.
- Support farmers and improve agricultural productivity, ensuring a stable supply of affordable food;
- Safeguard European Union farmers to make a reasonable living;
- Help tackle climate change and the sustainable management of natural resources;
- Maintain rural areas and landscapes across the EU;
- Keep the rural economy alive by promoting jobs in farming, agri-foods industries and associated sectors.
- It is a common policy for all EU countries.
- The CAP is financed through two funds as part of the EU budget:
- the European agricultural guarantee fund (EAGF) provides direct support and funds market measures;
- The European agricultural fund for rural development (EAFRD) finances rural development.
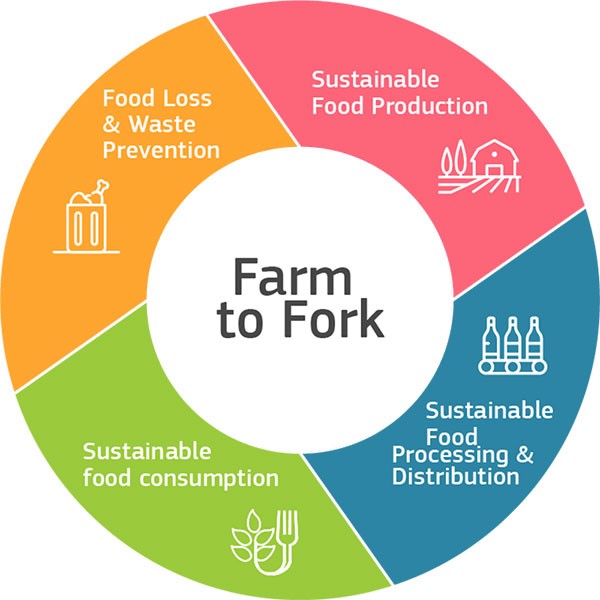
EU Farm to Fork Strategy:
The Farm to Fork Strategy aims to accelerate our transition to a sustainable food system that should:
- Have a neutral or positive environmental impact
- Help to mitigate climate change and adapt to its impacts
- Reverse the loss of biodiversity
- Ensure food security, nutrition and public health, making sure that everyone has access to sufficient, safe, nutritious, sustainable food
- Preserve affordability of food while generating fairer economic returns, fostering competitiveness of the EU supply sector and promoting fair trade
- The strategy sets out both regulatory and non-regulatory initiatives, with the common agricultural and fisheries policies as key tools to support a just transition.
-
Authorised Economic Operators:
#GS3 #Taxation system #Government Policies
Context: The Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) has inaugurated the online filing of Authorised Economic Operators (AEO) applications.
- The new version (V 2.0) of the web application is designed to ensure continuous real-time and digital monitoring of physically filed AEO T2 and AEO T3 applications for timely intervention and expedience.
Who are Authorised Economic Operators?
- The AEO concept is one of the main building blocks within the WCO SAFE Framework of Standards (SAFE).
- It aims to enhance international supply chain security and facilitate the movement of goods.
- SAFE sets out a range of standards to guide international Customs Administrations towards a harmonized approach based on Customs to Customs cooperation and Customs to Business partnership.
- Developing an Authorized Economic Operator programme is a core part of SAFE.
- Under this, an entity engaged in international trade is approved by WCO as compliant with supply chain security standards and granted AEO status.
- An entity with an AEO status is considered a ‘secure’ trader and a reliable trading partner.
- Benefits of AEO status include
- improved security and communication between supply chain partners,
- Customs will trust the operator and perform less or no inspections on goods imported or exported by or via the AEO.
- This benefits the mover of the goods as goods are available more quickly, which means lower transport costs.
- Customs benefits as scarce inspection capacity can be targeted better at cargo of unknown and potentially unsafe operators.
Indian AEO Programme:
- AEO is a voluntary programme.
- The AEO Programme was introduced as a pilot project in 2011.
- The security standards detailed in WCO SAFE Framework are the basis of the Indian AEO programme.
- There is a three tier AEO Status for Exporters and Importers. The three tiers are AEO T1, AEO T2, AEO T3, where AEO T3 is the highest level of accreditation.
- It enables Indian Customs to enhance and streamline cargo security through close cooperation with the principal stakeholders of the international supply chain viz. importers, exporters, logistics providers, custodians or terminal operators, customs brokers and warehouse operators.
- To provide business entities with an internationally recognized certification.
- To recognize business entities as “secure and reliable” trading partners.
- Enhanced border clearance.
- Customs advice/assistance if trade faces unexpected issues with Customs of countries.
Benefits:
- Harmonization of the advance electronic cargo information
- Ensure the integrity of the information, i.e. what is said to be in a container, really is in the container and nothing else, more, or less;
- Ensure the integrity of its employees, that they will not put goods in the container that should not be there; and
- Secure access to its premises, to prevent unauthorized persons to put goods in the container.
- Worldwide recognition as safe, secure and compliant business partners in international trade.
- India gets trade facilitation by a foreign country with whom India enters into a Mutual Recognition Agreement/Arrangement (MRA).
- It enables Indian Customs to enhance and streamline cargo security through close cooperation with the principal stakeholders of the international supply chain viz. importers, exporters, logistics providers, custodians or terminal operators, custom brokers and warehouse operators.
- Promote Ease of Doing Business: A liberalized, simplified and rationalized AEO accreditation process has potential to promote Ease of Doing Business and to emulate global best practices.
- Facility of Direct Port Delivery of import Containers and/or Direct Port Entry of Export Containers.
- It also fast tracking of refunds and adjudications.
- The Indian AEO Programme is a game-changer. It will not only achieve ‘Make in India’ but also substantially add to the vision and lead India to become a manufacturing and exporting power-house.
World Customs Organization (WCO)
- WCO is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium.
- The role of the World Customs Organisation (WCO) is multifaceted.
- To improve the effectiveness and efficiency of member customs administration.
- Help member customs administration in revenue collection, national security, trade facilitation, community protection, collection of trade statistics, combating counterfeiting in support of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), drugs enforcement, illegal weapons trading and integrity promotion.
- The WCO represents 179 Customs administrations that collectively process approximately 98% of world trade.
- India is a member and India was appointed as the Vice-Chair (Regional Head) of the Asia Pacific Region for a period of 2 years from 2018 to 2020.
- WCO is divided into 6 regions. Each region is represented by an elected Vice-Chairperson to the WCO Council.
- The WCO maintains the international Harmonized System (HS) goods nomenclature and administers the technical aspects of the World Trade Organization (WTO) Agreements on Customs Valuation and Rules of Origin.
-
Kappa and Lambda- Newest Sars-CoV-2 Variants:
#GS1 #Issues related to Health #GS3 #Disaster Management
Context: Kappa and Lambda variants have been labelled as Variants of Interest (VoI) by World Health Organisation.
Key Details:
Kappa Variant:
- It is a variant that is linked to the B.1.617 lineage of mutations that has also given rise to the Delta variant.
- 1.617 has been found to carry more than a dozen mutations of which two stand out: E484Q and L452R, which is why this variant has also been called the “double mutant”.
- But as it evolved, the B.1.617 branched out into new lineages. One of those, B.1.617.2 is called Delta and is the most prevalent variant at present in India. The other lineage, B.1.617.1, is called Kappa.
- Kappa was first detected in India and more than 3,500 of the close to 30,000 cumulative samples submitted by the country to the GISAID initiative (which maintains a global database of novel coronavirus genomes, are of this variant) are of this variant.
- In the last 60 days, the Kappa variant has made up 3 per cent of all samples submitted by India. India, in fact, leads the GISAID table for Kappa submissions.
What is Lambda?
- The C.37 variant, better known as Lambda, its name as per the WHO designations based on the letters of the Greek alphabet, is the newest VoI identified by the UN health agency.
- The strain was first identified in Peru in December 2020.
- Lambda is the dominant variant in the South American country with 81% samples found to be carrying it.
- It is so far been detected in samples from about 26 countries shared with GISAID.
- India has not yet reported any case of Lambda Varient.
- The Lambda variant belongs to the B.1.1.1 lineage, which has been identified in as many as 29 countries, including in North and South America, Europe and Oceania.
- WHO has said that this variant has multiple mutations in the spike protein, which could have implications for how easily the virus spreads between people.
- Health officials in the UK confirmed that Lambda is linked with symptoms that are common with other variants and that there is currently no evidence that it causes more severe disease or renders vaccines less effective.
What is a Variant of Interest (VoI)?
- According to WHO, a VoI is one that “has been identified to cause community transmission/multiple Covid-19 cases/clusters, or has been detected in multiple countries”.
- This means that the genetic changes involved are predicted or known to affect transmissibility, disease severity, or immune escape.
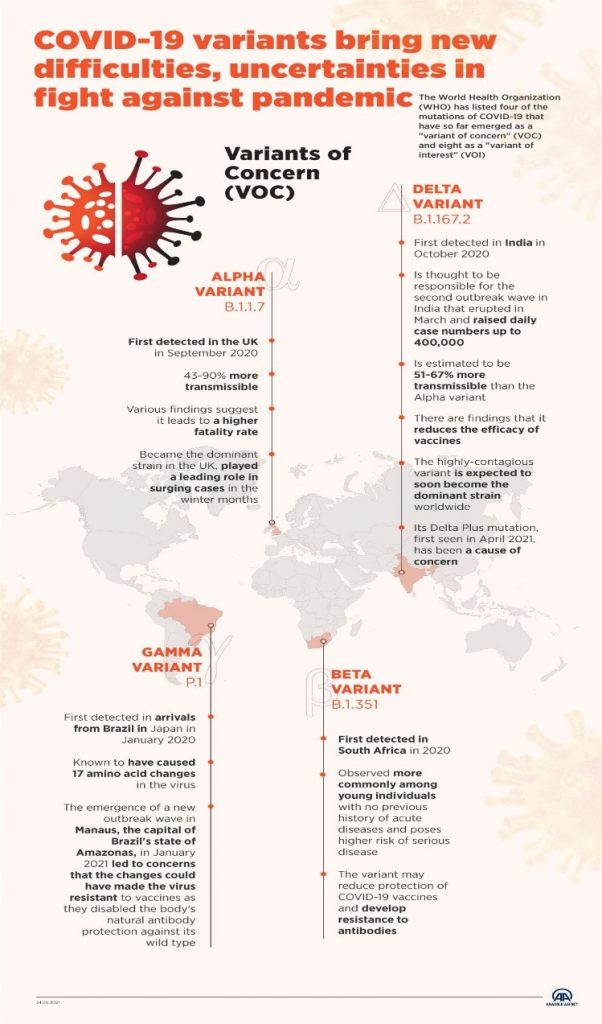
Variant of Concern:
- Various national and international organisations such as CDC (Centre for Disease Control and Prevention), COVID-19 Genomics UK Consortium and Canadian COVID Genomics Network use the following criteria:
- A variant for which there is evidence of an increase in transmissibility, significant reduction in neutralization by antibodies generated during previous infection or vaccination, decrease in susceptibility to antiviral drugs, or diagnostic detection failures, increase in mortality, Increase in morbidity, Ability to infect vaccinated individuals, the ability of the mutant to evade diagnostic test, ability to evade natural immunity, increased affinity towards a particular demographic group.
- When one or all these criteria are met, then the variant is named as “Variant of Interest” or “Variant under Investigation”.
- After validation or verification, it is named as “Variant of Concern”.
- There are four – Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta – which have been designated as “variants of concern”, and are considered a bigger threat.
Other Variants:
4.China Declared as Malaria free country by World Health Organisation
#GS1 #Health related issues #Policy Interventions
Context: With the effort of seven decade-long, multi-pronged health strategy China was able to entirely eliminate indigenous cases for four straight years.
About Malaria Free Status:
- China is the first country in the WHO Western Pacific Region to be awarded a malaria-free certification in more than 3 decades.
- China reported 30 million cases of Malaria annually in 1940s but no indigenous case was reported for four consecutive years.
- WHO grants the certification when a country has proven –with credible evidence, that the chain of indigenous malaria transmission by Anopheles mosquitoes has been interrupted countrywide for at least the past three consecutive years along with the capacity to prevent the re-occurrence of transmission?
- The final decision will be taken based on a recommendation by the independent Malaria Elimination Certification Panel (MECP).
- In Western Pacific region the countries that have achieved this status include Australia (1981), Singapore (1982) and Brunei Darussalam (1987).
- Globally, 40 countries and territories have been granted a malaria-free certification from WHO – including, most recently, El Salvador in 2021, Algeria in 2019 and Argentina also in 2019.
How did China achieve this feat?
- China started working out where malaria was spreading and began to combat in 1950s using preventative anti-malarial medicines.
- It reduced mosquito breeding grounds and sprayed insecticide in homes.
- In 1967, China had launched a scientific programme to look after new malaria treatments, which led to the discovery of artemisinin which are the most effective antimalarial drugs.
- Artemisinin is the core compound of artemisinin-based combination therapies, the most effective antimalarial drugs available today.
- In the 1980s, China began using insecticide-treated nets widely, distributing 2.4 million nets by 1988.
- 1-3-7 Strategy:
- A one-day deadline to report a malaria diagnosis
- Confirming a case and determining the spread by the third day, and
- Measures taken to stop the spread by the seventh day, along with continued surveillance in high-risk areas.
- Global Fund: With assistance from the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria starting in 2003, China “stepped up training, staffing, laboratory equipment, medicines and mosquito control
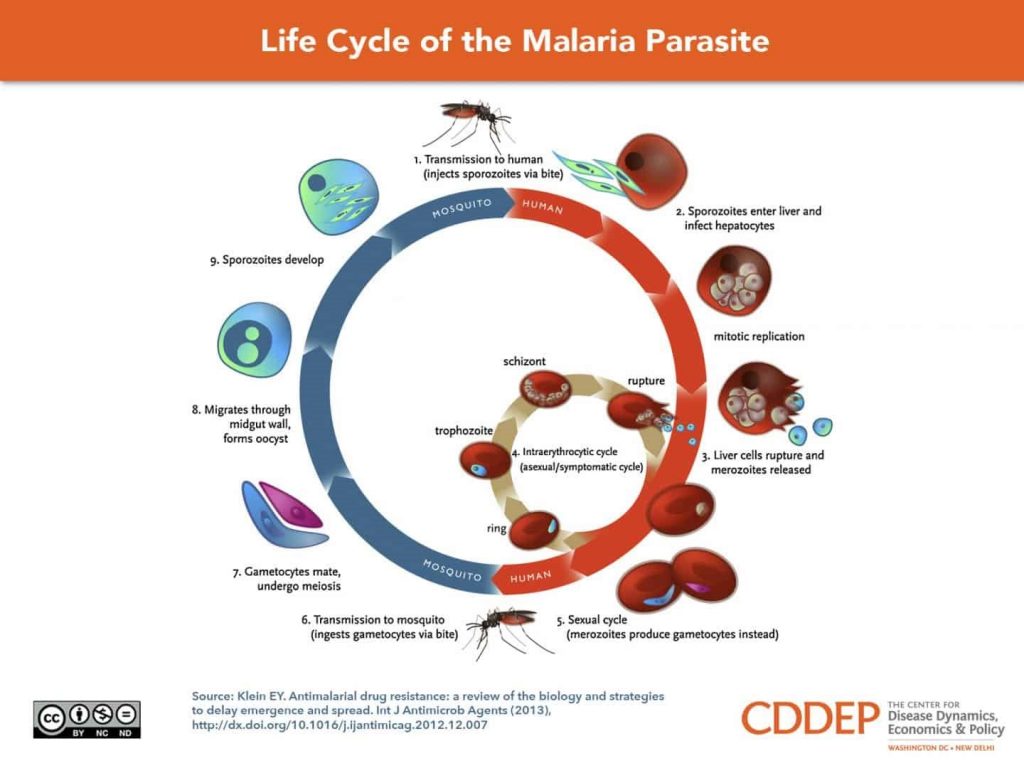
About Malaria:
- It is Caused by a parasite that commonly infects a certain type of mosquito which feeds on humans.
- Female Anophelesmosquitoes deposit parasite sporozoites into the skin of a human host and acts as disease vector.
- Four kinds of malaria parasites infect humans: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale, and P. malariae.
- In addition, P. knowlesi, a type of malaria that naturally infects macaques in Southeast Asia, also infects humans, causing malaria that is transmitted from animal to human (“zoonotic” malaria).
- Malaria is one of the major causes of preventable death in the world today. It affects more than 500 million people worldwide and causes 1 to 2 million deaths every year. It is a tropical infectious disease and almost 90 per cent of the cases are from Sub-Saharan Africa.
- There are two ways to deal with malaria – prevent the mosquito bite from happening (i.e preventative steps) or attack the parasites once they have infected the body.
-
Central Information Commission
#GS2 #Statutory Bodies #Right to Information
Context: The Supreme Court of India has directed the Union Government and all State Governments to file status reports on the latest developments regarding vacancies and pendency in their respective Information Commissions.
What’s the issue?
- A plea has sought directions to the government authorities for implementing the Supreme Court’s directions in the 2019 judgment.
- By its 2019 order:
- The apex court had passed a slew of directions to the Central and State governments to fill vacancies across Central and State Information Commissions in a transparent and timely manner.
- The court had given three months to the Centre to fill the vacancies that existed in the CIC.
About Central Information Commission (CIC):
- The CIC was constituted with effect from 12th October 2005 under the RTI Act 2005.
- Its jurisdiction extends to all central public authorities.
- It is not a constitutional body.
- The CIC is headed by the Chief Information Commissioner and not more than ten Information Commissioners are there for the assistance of CIC.
- They are appointed by the President on the recommendation of a committee consisting of the Prime Minister as Chairperson, the Leader of Opposition in the Lok Sabha and a Union Cabinet Minister nominated by the Prime Minister.
- The Chief Information Commissioner and an Information Commissioner shall hold office for such term as prescribed by the Central Government or until they attain the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- They are not eligible for reappointment.
Role of CIC:
- To receive and inquire into a complaint from any person regarding information requested under RTI, 2005.
- It can order an inquiry into any matter if there are reasonable grounds (suo-moto power).
- The commission has the power to examine any record under the control of the public authority. All such records have to be given to the Commission during the examination and nothing shall be withheld.
- Secure compliance of its decisions from any public authority.
- The CIC also submits an annual report to the GOI on the implementation of the provisions of the Act. This report is then placed before both the Houses of Parliament.
State Information Commission:
- It is constituted by the State Government.
- It has one State Chief Information Commissioner (SCIC) and not more than 10 State Information Commissioners (SIC) to be appointed by the Governor on the recommendation of the Appointments Committee headed by the Chief Minister.
- They should be persons of eminence in public life with wide knowledge and experience in law, science and technology, social service, management, journalism, mass media or administration and governance. They should not be a Member of Parliament or Member of the Legislature of any State or Union Territory. They should not hold any other office of profit or connected with any political party or carrying on any business
- The information commissioner is eligible for the post of state chief information commissioner but can be in office for a maximum of 5 years including his tenure of information commissioner.
Issues with Information Commisions:
- Delays and Backlogs: In October 2017, the CIC had 24,287 appeals and complaints pending before it. In October 2020, this figure had increased by 52% to 36,894.
- On average, the CIC takes 388 days (more than one year) to dispose of an appeal/complaint from the date it was filed before the commission.
- Inability to file an RTI or refusal to give information.
- Despite repeated directions from the court, there are still three vacancies in the CIC.
- Lack of Transparency: The criteria of selection, etc, nothing has been placed on record.
-
Melanistic Leopard Spotted in Maharashtra
#GS3 #Conservation #Endangered Species
Context: Recently, a rare Melanistic Leopard (commonly known as Black Panther) has been recorded in Navegaon-Nagzira Tiger Reserve (NNTR) of Maharashtra.
About Black Panther:
- A black panther is the melanistic colour variant of the leopard (Panthera pardus) and the jaguar (Panthera onca).
- Black panthers of both species have excess black pigments, but their typical rosettes are also present.
- They have been documented mostly in tropical forests, with black leopards in Kenya, India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia and Java, and black jaguars in Mexico, Panama, Costa Rica and Paraguay.
- Melanism is caused by a recessive allele in the leopard, and by a dominant allele in the jaguar.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Vulnerable.
- CITES: Appendix I.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I.

Courses we offer :
- UPSC Civil Services Coaching ( We are the best top rated IAS Academy in Vijayawada and Andhra Pradesh by Times of India Excellence award)
- Degree with IAS Coaching (BA and BSc plus UPSC Coaching)
- Inter with IAS Coaching (Sarat Chandra Junior College provides intermediate plus UPSC Coaching with HEC, MEC, CEC along with CLAT, IIT HSEE, IPMAT)
- APPSC Group 1 Coaching (Produced 37 ranks, Expert faculty from Hyderabad)
