CURRENT AFFAIRS 29-10-2021
Topics
- 16th East Asia Summit- virtual summit
- Augmented Reality (AR)
- SC on Pegasus Case
- Gray Hanuman Langur
- The Nag River and its Revitalization Project
1.16th East Asia Summit- virtual summit
#GS2- Agreements Involving India
Context
- On the sidelines of the ASEAN meeting with the leaders, the Indian Prime Minister spoke about Global Value Chains during an ASEAN – East Asia Summit virtual summit. Brunei, as EAS and ASEAN Chair, is hosting the event.
In depth information
The Big Picture:
- The significance of a resilient global value chain was stressed.
- Important regional and international problems were discussed, including the Indo-Pacific, the South China Sea, the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, terrorism, and the situation on the Korean Peninsula and Myanmar.
- Three statements on mental health, economic recovery through tourism, and sustainable recovery were adopted by EAS leaders, including India as a co-sponsor.
- India’s Focus: India emphasised the necessity of a Free, Open, and Inclusive Indo-Pacific and proposed the development of global cybersecurity standards.
- EAS was reaffirmed as the top leaders-led platform in the Indo-Pacific, bringing governments together to discuss critical strategic concerns.
- Reiterated its $1 million donation to the “ASEAN Covid Recovery Fund” and proposed the development of global cyber security standards
- India reaffirmed its promise to offer Quad-sponsored vaccines to Indo-Pacific nations.
- The ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ campaign was discussed as a means of assuring post-pandemic recovery and robust global value chains.
- A greater balance between economy and ecological, as well as a climate-friendly lifestyle, is required.”
- The Indo-“ASEAN Pacific’s centrality” was reinforced, as were the synergies between the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) and India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
The East Asia Summit’s History
- Mahathir Mohamad, Malaysia’s former Prime Minister, was the one who first proposed the East Asia Summit.
- During the ASEAN Plus Three Summit in 2004, the leaders reached an agreement to organise the East Asian Summit (EAS).
- Since its inception, ASEAN has played a key leadership role in the conference. EAS meetings follow the annual ASEAN leaders’ summit and serve a key role in Asia-Pacific regional architecture. On December 14, 2005, the first summit was place in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Membership
- The EAS is made up of ten ASEAN nations – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam – as well as eight non-ASEAN members: Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States.
- The EAS membership accounts for around 54 percent of the world’s population and 58 percent of global GDP.
- The EAS is a forum focused on ASEAN, and it can only be led by an ASEAN member.
East Asia’s Importance:
- The Asian nations of Greater China (which includes the Chinese mainland, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan), Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, and South Korea make up the eastern area of Asia.
- Economic benefit: It encompasses 16 countries that account for about half of the world’s population and 20 percent of global trade, and it represents nearly half of the world’s population.
- Given the tensions on the Korean Peninsula, in South China, and across the Taiwan Strait, it is critical for Japan, China, and South Korea to retain a single posture and share a similar concern for the East Asian region’s security.
- Global Implications: An East Asia community would play a significant role in developing a feeling of responsibility in Asian countries and in guiding them collectively in contributing to global issue resolution.
Ahead of Schedule
- ASEAN will continue to play a pivotal role in Southeast Asia’s and neighbouring regions’ growing regional architecture.
- The East Asia Summit (EAS), for example, should be considered a potential regional architecture platform for the Indo-Pacific region.
- Through the strategic context of competing interests, ASEAN countries must endeavour to reestablish “ASEAN centrality and unity.”
2.Augmented Reality (AR)
#GS3- Science & Technology
Context
- Snap, the parent company of Snapchat, sees Augmented Reality (AR) as the market’s next key driver for growth and acceptance.
In depth information
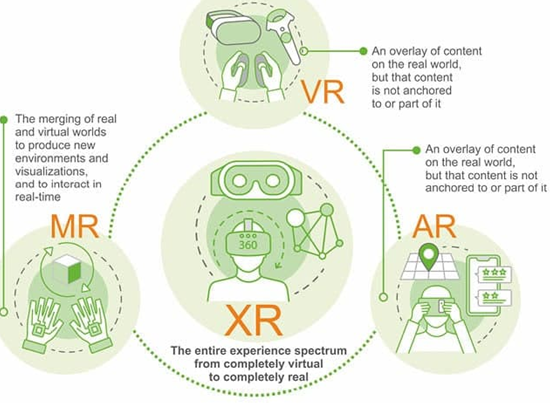
What is Augmented Reality and How Does It Work?
- Developers can design visuals within programmes that blend in with contents in the real world, resulting in augmented reality, which combines virtual reality with real life. AR allows users to engage with virtual content in the real environment while maintaining the ability to discern between the two.
Sectors in which AR could be used
- Education:
- Augmented reality can be utilised as a teaching tool and a means for people to learn more about the world around them.
- In the subject of language translation, augmented reality is applied.
- Law enforcement authorities can utilise augmented reality technology to identify criminals in large crowds.
- It will boost the soldiers’ situational awareness.
- Tactical Augmented Reality is the name of the technology (TAR).
- Night vision goggles will be replaced with TAR in the future, as this technology can assist warriors in the dark.
- It will take the place of the handheld GPS units that soldiers currently use to find their positions.
- Advertising:
- Flipkart and other e-commerce companies can utilise augmented reality to assist customers in shopping for and visualising things before purchasing them.
- Retailers utilise augmented reality to help customers see aesthetics when remodelling interiors.
- Without having to visit a dealership, Jaguar Land Rover puts potential automobile customers in the virtual driver’s seat of its latest models.
- Through transparent windows, customers sat in the driver’s seat may see the outside view.
- Traditional handheld ultrasound scanners would be replaced by AR technology in the healthcare industry.
- It will assist in precisely finding blood vessels in a shorter amount of time.
- AR is built right into Google Glass and other Head-up Displays (HUDs).
- These glasses could be used as medicine reminders for patients.
- Pharmaceuticals:
- AR would allow medication developers to peer inside a molecule to determine how the drug moves and reacts to various stimuli and situations.
- This will cut down on mistakes and shorten the years-long medication development process.
- Warehouse operations, transportation, last-mile delivery, and enhanced value-added services are all areas where logistics can be improved.
- Scanning the QR code on the merchandise could bring up useful information on the screen.
- Social media:
- Snapchat and Instagram’s various filters are nothing more than Augmented Reality.
- Pokemon is one of the most well-known video games ever released.
What is a Lens Studio, and how does it work?
- One of the most significant advantages of Lens Studio is that it is a tool and platform that enables anyone to create an AR experience. They may then distribute it across both iOS and Android user bases without any further effort.
3.SC on Pegasus Case
#GS2-Cyber Security,Judgements & Cases
Context
- The Supreme Court has stated that the government’s power to pry into people’s “sacred private space” in the name of national security is not absolute.
- As a result, it has formed an expert technical committee, chaired by retired Supreme Court judge R.V. Raveendran, to investigate claims that the Centre utilised Israeli software Pegasus to spy on Indians.
- The court further stated that indiscriminate espionage cannot be permitted in a democratic country governed by the rule of law unless adequate statutory safeguards are in place.
- The government’s use of technology for surveillance must be evidence-based.
In depth information
- Pegasus is a sort of spyware that is categorised as malicious software or malware.
- It is designed to get access to devices without the users’ awareness, collect personal information, and feed it back to whoever is spying on them using the software.
- Pegasus was created by the Israeli company NSO Group, which was founded in 2010.
- Researchers identified the first version of Pegasus in 2016, and it infected phones via a technique known as spear-phishing, which involves sending text messages or emails that deceive a target into clicking on a malicious link.
- NSO’s offensive capabilities, on the other hand, have improved since then.
- Pegasus infections can be spread using “zero-click” attacks, which require no input from the phone’s owner to succeed.
- These will frequently take use of “zero-day” vulnerabilities, which are faults or problems in an operating system that the phone’s manufacturer is unaware of and so unable to repair.
What is a zero-click attack, and how does it work?
- A zero-click attack allows viruses such as Pegasus to take control of a device without the need for human intervention or error.
- So, if the objective is the system itself, all understanding about how to avoid phishing attacks or which links not to click is useless.
- The majority of these assaults target software that receives data before determining whether or not it is trustworthy, such as an email client.
What can Pegasus accomplish?
- Pegasus may “return the target’s personal information, such as passwords, contact lists, calendar events, text messages, and live phone calls from popular mobile messaging apps.”
- The camera and microphone on the target’s phone can be turned on to record all activities in the area, broadening the scope of the surveillance.
India’s Recent Initiatives:
- The Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative was started in 2018 with the goal of raising awareness about cybercrime and increasing the capacity of Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) and frontline IT personnel across all government ministries to implement safety measures.
- The National Cyber Security Coordination Centre (NCCC) was established in 2017 to scan internet traffic and communication metadata (little bits of information concealed inside each communication) entering the country in order to detect real-time cyber threats.
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra: This portal was launched in 2017 to help internet users clean their computers and devices by removing viruses and malware.
- The government recently launched the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C).
- In addition, the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal has been launched across India.
- CERT-IN (Computer Emergency Response Team of India) is the nodal agency for cybersecurity threats such as hacking and phishing.
4.Gray Hanuman Langur
#GS3-Environmental Pollution & DegradationConservation
Context
- A group of Gray langurs (Semnopithecus entellus) with blue pelage (fur or hair) was recently discovered in an industrial area of Ankleshwar, Gujarat.
In depth information

The Himalayan grey langur (Semnopithecus ajax), also known as the Chamba holy langur and Kashmir grey langur, is a critically endangered species.
- According to a study undertaken by Wildlife Information Liaison Development Society after an 84-year delay, the langur population has dwindled to less than 250 mature individuals.
- The IUCN red list of vulnerable species listed this species of leaf-eating primates found between Kashmir and the Chamba area of Himachal Pradesh as endangered in 2008.
- The last research of the Chamba langur took place in 1928, and no precise information about them was available.
- This species was first reported in 1928 from a skin specimen by Reginald Innes Pocock of Chamba, but it has remained virtually unknown to Indian primatologists since then.
- The species has been limited to the Chamba Valley by detailed and well-informed range studies, implying endemism.
- The adult male’s shoulder mane is a remarkable and distinguishing feature of the Himalayan Grey Langur. Males and females have lengthy fur that makes them look plump and bushy.
- Deforestation, mining, and pollution are all threats.
- The IUCN Red List classifies this species as Least Concern.
- Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
- Schedule-I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972
5.The Nag River and its Revitalization Project
#GS2- Government Policies & Interventions
Context
- The Expenditure Finance Committee has approved the Nag River rehabilitation project (EFC).
In depth information
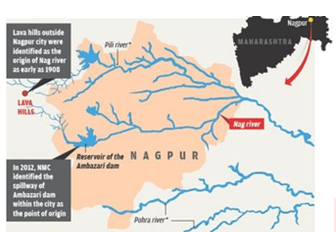
- The Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways conceptualised the Nag River Revitalization Project, which is an ambitious project for the Nagpur region.
- Nagpur is named after the Nag river, which flows through the city.
- It is presently a sewage and industrial waste-polluted water channel.
- The National River Conservation Plan has approved it, and the National River Conservation Directorate will implement it (NRCD).
- It will lower pollution levels in the Nag River and its tributaries by reducing untreated sewage, flowing solid waste, and other contaminants.
Nag River
- The Nag River is a river that flows through Nagpur, Maharashtra.
- It is well-known for being the source of the word Nagpur’s etymology. The Kanhan-Pench river system includes it.
- The Kanhan River is a major right-bank tributary of the Wainganga River in central India, draining a huge area south of the Satpura hills.
- It gets its greatest tributary, the Pench River, which is a key water source for Nagpur’s metropolis, throughout its 275-kilometer journey across Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.
- It merges with the Wardha River, becoming the Pranahita River, which discharges into the Godavari River at Kaleshwaram, Telangana.

