CURRENT AFFAIRS 30-10-2021
Topics
- The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969
- Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act
- Coronavirus Variant A-Y4.2
- Autosomal DNA
- OPV Sarthak
1.The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969
#GS2- Health
Context
- The Centre recently recommended changes to the 1969 Registration of Births and Deaths Act (RBD).
- It will allow it to “keep the national database of registered births and deaths.”
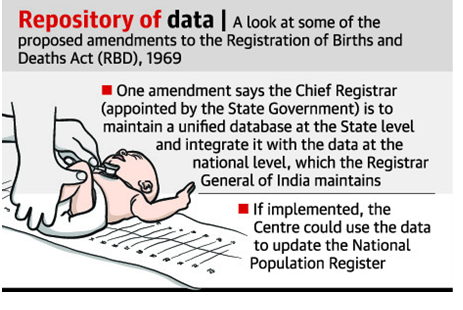
In depth information
- Registration of Births and Deaths: With the enactment of the Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD), Act 1969, registration of births and deaths became mandatory in India. Registration is done according to the place where the event occurs.
- The change has been proposed in order to simplify the provisions of several sections of the existing RBD Act, 1969 and to make it more user-friendly.
The Centre has proposed the following amendments:
- It is proposed that the Chief Registrar (chosen by the States) maintain an uniform database at the State level, which would be integrated with data maintained by the Registrar General of India at the “national level” (RGI).
- The revisions will make the Centre a data repository in its own right.
- In the event of a disaster, “Special Sub-Registrars” shall be appointed with some or all of his powers and duties for on-the-spot registration of fatalities and issuing of extracts, as may be prescribed.”
Sub-Registrars with special responsibilities:
- The appointment of “Special Sub-Registrars, with some or all of his powers and duties for on-the-spot registration of fatalities and issue of extract therefrom, as may be stipulated” in the event of a calamity.
Data Expected to Be Used:
- To modernise the National Population Register (Citizenship Act, 1955) and electoral register (Registration of Electors Rules, 1960), as well as Aadhaar (Aadhaar Act, 2016), ration card (National Food Security Act, 2013), passport (Passport Act), and driving licence databases (Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019).
- The NPR already has a database of 119 crore residents, and it is the first step toward the construction of the National Register of Citizens under the Citizenship Rules of 2003. (NRC).
- The NPR update and the first phase of Census will be conducted simultaneously by the RGI.
What are the advantages of birth and death registration?
- For school admissions.
- For job purposes, as proof of age.
- As proof of age at the time of marriage.
- To determine who the parents are.
- To determine one’s age in order to be enrolled on the electoral rolls.
- To determine one’s age for the sake of insurance.
- In order to be included in the National Population Register, you must first register (NPR).
- Production of a death certificate is required for the purposes of inheritance and demanding dues from insurance companies and other businesses.
2. Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act
#GS2- India & Foreign Relations
Context
- Key senators continue to back a sanctions relief for India in exchange for its acquisition of Russia’s S-400 missile defence system.
In depth information
What exactly is the problem?
- The S-400 is expected to be delivered to India in November 2021.
- It could trigger sanctions imposed by the US under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
CAATSA
- The Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act was enacted in the aftermath of three incidents that would have major geopolitical ramifications. The following are the details:
- Iran’s Nuclear Missile Program: The US government feared that any advancement in Iran’s nuclear missile programme would further destabilise the Middle East, as Iran has repeatedly threatened Israel, a vital NATO and US ally. The CAATSA grants the President of the United States the right to impose penalties on anybody involved in the sale or transfer of military technology to Iran.
- Russian influence is being stifled in the United States. The CAATSA against Russia was sparked by Russia’s invasion of Crimea in 2014 and suspicions of meddling in US elections in 2016.
- If the state or private people are proven to be involved in activities such as cybersecurity, crude oil projects, financial institutions, corruption, human rights abuses, and so on, sanctions can be imposed on Russia under the act.
- North Korea and the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction: North Korea has a nuclear weapons programme, and its missile arsenal is anticipated to contain 30-40 warheads by 2020, with enough fissile materials to launch 6-7 missiles per year. North Korea has issued numerous threats against its neighbour, South Korea, as well as the United States.
Exemptions: The US President may waive the sanctions if the following conditions are met:
- A country is taking steps to limit its connections with Russia in terms of weapons acquisitions or sales.
- A country has improved collaboration with the United States on other security issues that are essential to the United States’ strategic interests.
- If the delivery of Russian weaponry to the country does not pose a major threat to US defence systems and operational capabilities.
India’s concerns
- Indo Russian Aviation Ltd, Multi-Role Transport Aircraft Ltd, and Brahmos Aerospace are all joint ventures that could be affected.
- Weapon Systems of Russian Origin
- It will also have an impact on India’s ability to obtain spare parts, components, raw materials, and other help.
- India employs a considerable number of Russian-made defence systems, including the nuclear submarine INS Chakra and the Kilo-class conventional submarine.
CAATSA is being chastised.
- The Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act has been roundly criticised by North Korea, Russia, and Iran. However, the unfavourable sentiment is not limited to the United States’ foes; major partners such as the European Union believe that the CAATSA casts a negative light on US-EU ties because many of them have inked gas line contracts with Russia.
- The CAATSA, according to geopolitical research tanks, will make it more difficult for the US to defend its Asian allies against expanding Chinese dominance. Another implication is that this would deter other countries from developing defensive relationships with the US in order to avoid future strategic autonomy sacrifices. According to these analysts, if the CAATSA is applied clumsily, it will likely backfire on US policy in the near future.
Ahead of Schedule
- CAATSA Waiver Criteria: In 2018, the President of the United States was given the power to waive CAATSA sanctions on a case-by-case basis.
- Either at the Congressional level or at the 2+2 level, India and the United States must keep the dialogue going.
- Strategic Objectives
- In the wake of fatal skirmishes with China on the Line of Actual Control, India’s defence procurement has grown significantly (LAC).
- Aside from that, another hostile neighbour, Pakistan, must be dealt with.
- In terms of balancing foreign relations, Russia is India’s all-weather defence partner.
- Russia aided India’s admission to the SCO and the development of the RIC philosophy.
- However, India must strike a balance in its relations with both Russia and the United States to ensure that its national interests are not jeopardised.
- Building a peaceful international order Today, India is in a fortunate position to have good relations with all major powers.
- As a result, India must take use of its position to aid in the establishment of a peaceful world order.
3. Coronavirus Variant A-Y4.2
#GS3- Developments, Applications & Effects on Everyday Life
Context
- According to a report by the India SARS-CoV-2 Genome Consortium, the latest mutation of the coronavirus variety, AY4.2, is “extremely unusual” in India (INSACOG).
In depth information
- The principal Variant of Concern (VOC) in India is still Delta (B.1.617.2) and its related sublineages (AY numbered up to 35). According to the INSACOG, no new VOIs or VOCs have been discovered in India. Many instances previously classified as AY.4 have recently been reclassified as AY.33.
The AY4.2 coronavirus is a kind of coronavirus.
- In the United Kingdom, it has been connected to an increase in instances.
- It is also found in a variety of other countries, as well as among visitors visiting the United Kingdom from a variety of countries.
- It’s unclear when or where AY4.2 first appeared.
- The mutations of Delta (the prevalent global variation) and AY.4 are found in this coronavirus lineage (a sub-lineage).
- S: A222V on the spike protein, and Y145H on the coronavirus’s N terminal domain, or the part that doesn’t interact to human cells, were the two most common mutations.
- It’s still as potent as Delta in terms of severity.
What is a Concern Variant?
- A rise in transmissibility, an increase in fatality, and a considerable drop in the effectiveness of vaccines, therapy, and other health interventions, according to the World Health Organization.
- A VOI is a SARS CoV-2 variant with a genetic capacity that influences virus features such as illness severity, immunological escape, transmissibility, and diagnostic escape, according to the WHO. The World Health Organization also found that a VOI results in a significant amount of community transmission. A global surge in instances poses a significant threat to global public health.
4. Autosomal DNA
#GS3- Developments, Applications & Effects on Everyday Life
Context
- For the first time, a technology based on ‘Autosomal DNA’ was utilised to identify Sitting Bull’s great-grandson and closest living cousin.
- Sitting Bull was a famous Native American chieftain in the nineteenth century.
- He is well known for defeating US General George Armstrong Custer at the Little Bighorn River Battle in 1876.
Autosomal DNA Information
What Is Autosomal DNA and How Does It Work?
- Chromosomes are lengthy sections of DNA, and most people have 23 pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46. Autosomal and sex chromosomes are the two main types of chromosomes. X and Y chromosomes make up a person’s chromosomes, and most people have either a pair of X chromosomes or a pair of X and Y chromosomes.
- The remaining 22 pairs are autosomal chromosomes, which almost everyone has a full set of. Only the DNA from these 22 chromosomal pairs is examined in an autosomal DNA test.
What Is Autosomal DNA Testing and How Does It Work?
- Autosomal DNA tests look at the autosomes, which are the 22 pairs of chromosomes that are found in almost everyone. The most typical way is to examine hundreds of thousands of locations, or markers, across all 22 pairs using a DNA array.
- Scientists can use this information to search a database for significant areas of common DNA between you and others to locate near relatives. The more DNA you have in common with another person, the closer you are linked.
- Scientists can also compare your DNA to DNA from people who have ancestors from all around the world. For example, if a portion of your DNA resembles that of people from France, that portion is considered to be French. This is how we figure out where your forefathers and mothers lived hundreds, if not thousands, of years ago.
- Y-DNA and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) testing, which cannot provide as much information about close relatives or recent ancestry, yield more genetic information than autosomal DNA tests.
5.OPV Sarthak
#GS3-Various Security Forces & Agencies & Their Mandate
Context
- The Indian Coast Guard has commissioned and dedicated an Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV), the Indian Coast Guard Ship (ICGS) Sarthak, to the nation in Goa.
In depth information
- It’s a 105-meter-long ship with a displacement of 2,450 tonnes that’s propelled by two 9,100-kilowatt diesel engines that can reach 26 knots.
- It’s the fourth of five OPVs in the series. And it will considerably improve the nation’s maritime safety and security.
- OPVs are long-range surface ships that may operate in India’s maritime zones, including island territories that have helicopter operations.
- Coastal and offshore patrols, policing India’s marine zones, control and surveillance, anti-smuggling and anti-piracy activities, and limited warfare missions are among its responsibilities.
- M/s Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL) designed and built it in-house in accordance with the government’s vision of “Make in India.”
- It has roughly 70% indigenous content, giving the Indian shipbuilding sector a much-needed boost and a huge step toward reaching ‘Atmanirbar Bharat.’
What distinguishes ICGS Sarthak from other schools?
- To begin with, the ship is outfitted with cutting-edge equipment, machinery, sensors, and weapons, allowing it to perform tasks such as search and rescue, combating maritime crimes, and maintaining and protecting the marine environment.
- Second, it can transport a twin-engine helicopter, four high-speed boats, and one inflatable boat for rapid boarding and Search and Rescue missions.
- Finally, it has the capability of carrying minimal pollution response equipment to respond to oil spills at sea.
Utility:
- It will be used extensively for EEZ monitoring, Coastal Security, and other responsibilities outlined in the Coast Guard charter of duty in order to protect the nation’s marine interests.

