CURRENT AFFAIRS 02-12-2021
Daily Current Affairs – Topics
- Barbados: World’s Newest Republic
- World AIDS Day
- Char Dham Devasthanam Management Act
- Abundance of Lithium in Stars
- Hydrogen-enriched compressed natural gas (HCNG):
1. Barbados: World’s Newest Republic
#GS2-Groupings & Agreements Involving India
Context
- Barbados has recently deposed Queen Elizabeth II as the country’s head of state, making it the world’s newest republic nearly 400 years after becoming a British colony.
- By breaking away from Britain 55 years after gaining independence, the Caribbean island nation was able to cleanse itself of the remains of colonial authority.
- Barbados, on the other hand, will remain one of the 54 Commonwealth countries.
In depth information
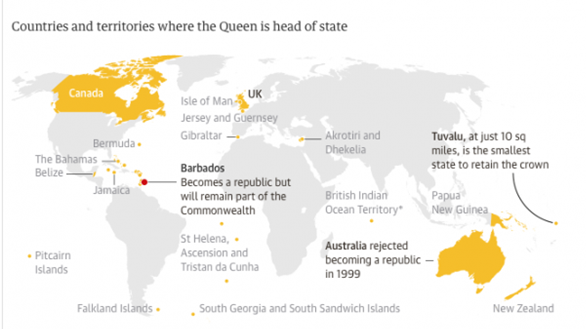
Barbados:
- It is a small island country in the Caribbean Sea’s south-eastern corner.
- Saint Lucia to the north, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines to the west, and Trinidad and Tobago to the south are its neighbours.
- Bridgetown is the capital.
- Barbados obtained independence from the United Kingdom on November 30, 1966.
- Leadership:
- Barbados’ current President is Dame Sandra Prunella Mason.
- Barbados’ current Prime Minister is Mia Amor Mottley.
- Barbados is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM), which was founded in 1973.
Barbados’ history is as follows
- Barbados became an English colony for the first time in 1625. It was a link in the lines of trade, commerce, and tyranny that English mercantilism and colonialism cultivated for centuries, and it was a part of the British Empire for over 400 years.
- Slavery, indentured labour, and a lack of democracy – the Caribbean witnessed some of history’s most institutionalised and invisibilised evils.
- Relations between India and Barbados:
- Shared Platforms: India and Barbados have friendly relations and participate actively in the United Nations (UN), Commonwealth, Non-Aligned Movement (NAM), and other international organisations.
- Barbados is also a member of the International Solar Alliance, which it ratified in January 2021. Air Services Agreement: In 2015, India and Barbados signed an Air Services Agreement to make travel arrangements easier for citizens and to allow for direct air connectivity and chartered flight operations between the two countries.
- In 2015, Bridgetown, Barbados hosted the first ever Foreign Office Consultations (FOC) between India and Barbados.
- UNSC Reform: In 2007, Barbados voted in favour of a G-4 resolution to increase the UN Security Council.
- In 2011–12, the country voted in favour of India’s candidacy for a non-permanent seat on the UN Security Council, and it continues to back India’s bid for a permanent seat.
Bilateral Trade:
- Vehicles, pharmaceuticals, textiles, iron and steel, organic chemicals, and other Indian exports total USD 12.76 million in 2019-20.
- Electrical machinery, optical photography, and cinematographic equipment are among the items imported by India (USD 1.48 million in 2019-20).
- Sports and Culture: Cricket has a strong link in India, and Barbadian cricketers from the past and present are well-known among Indian sports fans.
- Many Barbadian cricketers play for teams in the Indian Premier League.
- About 2500 persons of Indian ancestry have settled in Barbados, and the majority of them have now gained local nationality.
What does it mean to be a republic?
- “A state in which the supreme authority rests in the body of citizens able to vote and is exercised by representatives chosen directly or indirectly by them,” according to the definition of a republic.
- Many modern democracies are republics as well, and are referred to as democratic republics. As a result, the United States and France are both regarded democracies and republics—both terms imply that the people own the power of administration, and that this authority is exercised through some form of electoral representation.
- The essential principle behind the term republic is that the leader of this government (or state) is a president, who is elected or installed rather than a hereditary king.
- This basic concept explains why dictatorial regimes such as North Korea are formally known as the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Its residents vote for a single candidate (or “vote”).
- A republican example from history is also instructive. The Republic of Venice was a Middle Ages trading city-state commanded by a doge who was elected by affluent merchants and served until his death. Neither of these governments can be described as democratic.
2. World AIDS Day
#GS2- Health
Context
- The world observes World AIDS Day every year on December 1st.
In depth information
- The World Health Organization (WHO) first noticed it in 1988.
- The goal is to raise awareness about the condition.
- ‘End inequality. End AIDS’ is the theme for 2021.
- Aids (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) is a condition in which a person (AIDS)
- It is a chronic, potentially fatal illness caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which destroys the human immune system.
Transmission:
- Through direct contact with HIV-positive people’s bodily fluids (blood, sperm, rectal fluid, vaginal fluid, or breast milk).
Symptoms:
- Stage 1: Symptoms of a flu-like illness (Fever, chills, rashes, night sweats)
- The second stage is clinical latency (No particular symptoms)
- AIDS, Stage 3 (Weakening of Immune System)
Treatment & Prevention:
- Using safe procedures, non-contaminated needles, and preventing mother-to-child transmission, prevention is better than cure.
- During pregnancy, delivery, and breastfeeding, effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) prevents HIV transmission from mother to child.
- Antiretroviral therapy, which consists of one or more drugs, is used to treat HIV.
- ART does not cure HIV, but it does stop the virus from replicating in the blood, lowering the viral load to undetectable levels.
- People living with HIV can live healthy, productive lives thanks to antiretroviral therapy (ART). It also serves as a preventative measure, with a 96 percent reduction in the probability of onward transmission.
- ART should be used on a daily basis throughout the rest of a person’s life. If people stick to their treatment, they can continue to get safe and effective ART.
- People will need to transition to different drugs to protect their health if ART becomes ineffective owing to circumstances such as lost communication with health care professionals or drug stock outs.
- Someone who is virally suppressed and on antiretroviral medication will not spread HIV to their sexual partners.
- Condoms and prophylaxis employ antiretroviral drugs to prevent HIV and other sexually transmitted illnesses.
- According to the AIDS Society of India, India has the third-highest HIV burden in the world, with 2.35 million people infected.
- In India, 69,220 new HIV infections and 58,960 AIDS-related deaths were reported in 2019.
- Over the last decade, the Asia Pacific area has seen a 12% decrease in new HIV infections and a 29% decrease in AIDS-related fatalities, according to the UNAIDS Report 2020.
Efforts on a Global Scale
- UNAIDS is an international organisation dedicated to preventing new HIV infections, ensuring that everyone living with HIV has access to treatment, supporting human rights, and gathering statistics for decision-making.
- The organisation leads and motivates people all across the world to work toward a common goal of zero new HIV infections, zero prejudice, and zero deaths from AIDS.
- Every person who may be at risk of contracting HIV should get tested, according to the World Health Organization.
- Antiretroviral treatment should be offered and linked to HIV patients as soon as possible after their diagnosis. This therapy also inhibits HIV transmission to others if taken on a regular basis.
- Steps done by the Indian government
- India has accomplished the 6th Millennium Development Goal (MDG 6) of arresting and reversing the HIV epidemic through the National AIDS Control Programme (NACP) (Central Sector Scheme).
- The HIV/AIDS Prevention from Parent to Child Transmission (PPTCT) programme is mandated under the 2017 HIV/AIDS Act (prohibits discrimination or unfair treatment of HIV-infected people on any grounds)
- System PALS (PPTCT ART Linkages Software) (Repository of HIV positive pregnant women)
- UNAIDS’ 90:90:90 approach (90 percent (diagnosed, treated (by antiretroviral medication (ART)), and suppressed) by 2020.
- With a goal post of 95-95-95, the time limit has been extended by ten years.
- Workshops to raise social awareness.
- Facilities for Viral Load Testing: They’ve been scaled up, and HIV counselling, testing, and community-based screening for early diagnosis have all been increased in order to meet the goal of eliminating HIV transmission from mother to child.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare announced Project Sunrise in 2016 to combat the rising HIV prevalence in the north-eastern states.
Challenges
- Human rights breaches, social exclusion, and removing social stigma
- AIDS is caused by inequalities.
- Medicines for HIV, such as lopinavir/ritonavir, are in short supply.
- There is a scarcity of financial resources.
Ahead of Schedule
- To eradicate AIDS by 2030, action against disparities, coordination between the centre and the states, involvement of NGOs, and increased budget allocation are all needed.
3.Char Dham Devasthanam Management Act
#GS2- Government Policies & Interventions
Context
- The Char Dham Devasthanam Management Act was recently repealed by the Uttarakhand government.
In depth information
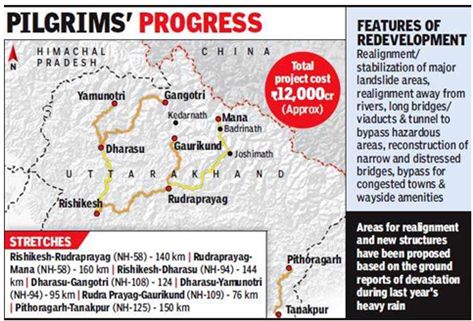
- The Char Dham Devasthanam Board Act intended to expand control over 51 Hindu sites, but seers and shrine managements fought it tooth and nail.
- The decision was made on the advice of a high-powered committee appointed by Shri Manohar Kant Dhami.
Char Dham Devasthanam Board Act
- The Uttarakhand Char Dham Shrine Management Bill, 2019, was introduced in the state Assembly in December 2019 by the Uttarakhand administration, which was then led by Trivendra Singh Rawat.
- The bill’s goal was to bring the Char Dham pilgrimage sites of Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri, as well as 49 other temples, under the jurisdiction of a proposed shrine board.
Board of Uttarakhand Char Dham Devasthanam:
- The Uttarakhand Char Dham Devasthanam Management Act, 2019, was passed by the Assembly and became the Uttarakhand Char Dham Devasthanam Management Act, 2019.
- On January 15, 2020, the Trivendra government established the Uttarakhand Char Dham Devasthanam Board under the same Act.
- The Chairman of the Board is the Chief Minister, and the Vice-Chairman is the Minister of Religious Affairs, according to the Act.
- The board includes two Gangotri and Yamunotri MLAs, as well as the Chief Secretary. The Chief Executive Officer is a senior IAS officer.
- There are 53 temples under this board, including four shrines – Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri – as well as temples surrounding these shrines.
- The board was formed for the following purposes:
- The shrine board was established as the temple’s highest governing body, with the authority to set policies, carry out the Act’s provisions, formulate budgets, and approve expenditures, among other things.
- The board was also given authority to offer instructions for the secure custody, prevention, and management of cash, valuable securities, jewellery, and other temple assets.
Prior to the Act:
- The Shri Badrinath-Shri Kedarnath Act, 1939, was in force prior to the formation of the Board for the management of two shrines – Badrinath and Kedarnath – and the Shri Badrinath-Shri Kedarnath Mandir Samiti for 45 temples.
- The Samiti was chaired by a government official, and the CEO was a member of the All India Service.
Independence from the State:
- That group made all decisions about the use of donations, funds, and development projects in and around those 45 temples, including Badrinath and Kedarnath, with no intervention from the government.
- However, the government attempted to exert control over financial and policy decisions through the Devasthanam board.
The Move’s Importance
- Stakeholders’ interests are protected: People’s feelings and interests, priests’ honour, and the dignity and respect of all stakeholders are all preserved.
- Benefiting the ruling party’s political agenda: The move is hugely significant in terms of state politics, as the BJP has been facing a lot of backlash and threats of protests in the state from Hindu religious groups like saints and seers, as well as the RSS-affiliated Vishwa Hindu Parishad.
Issues with the Project
- Since 2017-18, project work and tree felling on various stretches totaling more than 250 km has been carried out without formal authorisation.
- The state Forest Department issued a work order in September 2018 that was not just retroactive but also legally unsound.
Taking advantage of ancient clearances:
- On the basis of former forest clearances provided to the Border Roads Organisation between 2002 and 2012, work on stretches totaling more than 200 km began.
- This is prohibited and defies the aim of the regulations because the scope of work has changed dramatically as a result of the “enormous hill cutting” that has been done.
- False Statement:
- Tree felling, hill cutting, and muck dumping on sections of more than 200 km began with bogus declarations that these stretches did not lie inside the Eco Sensitive Zones of Kedarnath Wildlife Sanctuary, Rajaji National Park, Valley of Flowers National Park, and other protected areas.
- Working without obtaining permission:
- After withdrawing petitions for forest removal without providing reasons, work proceeded on numerous portions totaling at least 60 kilometres.
Supreme Court Directive Violations:
- Despite the fact that the state administration stated in an affidavit in April 2019 that areas where work had not yet commenced would be subject to the SC’s instruction, work began on stretches totaling at least 50 kilometres.
4. Abundance of Lithium in Stars
#GS3-Science & Technology
Context
- The issue surrounds the cause for the great abundance of Lithium in stars, which, according to models, should be annihilated in the star’s heated plasma.
- Lithium is a trace element found on Earth that is used to make rechargeable batteries.
In depth information
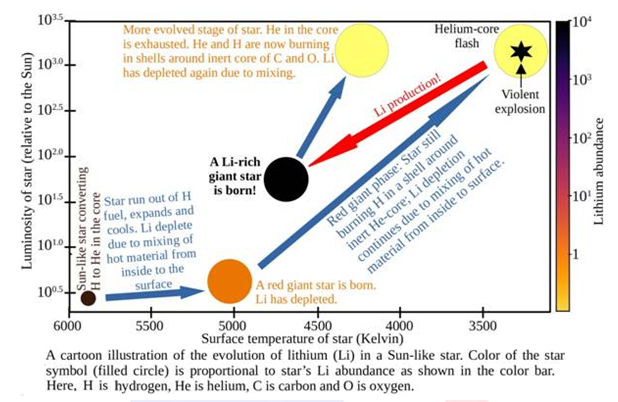
- The analysis of lithium among red giants revealed that only about 1% of sun-like red giants have a lithium-enriched surface.
- Methodology: The study looked at a collection of around 500,000 stars with well-defined physical and chemical features, including lithium abundances (dubbed GALAH after a common Australian bird).
- Research Findings: For the first time, scientists have confirmed that all lithium-rich stars are burning helium in their cores, which is the cause of lithium formation.
- They theorised that the powerful helium-core flash is linked to lithium synthesis.
- It’s thought to be a brief and straightforward chain of nuclear processes involving a collision between two stable helium isotopes, leading to the formation of a stable lithium isotope.
- All of the Sun-like low-mass stars had lithium-rich giants, according to the survey.
Lithium Facts
Lithium has the following properties:
- It has the symbol Li and is a chemical element.
- It’s a silvery-white metal with a delicate texture.
- It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element under normal conditions.
- It must be stored in mineral oil because it is very reactive and combustible.
- As the need for high-performance rechargeable batteries grows, lithium has become the new “white gold.”
- The so-called ‘lithium triangle,’ which encompasses sections of Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile, has sparked renewed interest due to rising global lithium demand and rising prices.
- Lithium metal can be utilised to create useful alloys.
- For instance, lead is used to manufacture ‘white metal’ bearings for engines, aluminium is used to make aircraft parts, and magnesium is used to make armour plates.
- Thermonuclear reactions are a type of thermonuclear reaction.
- In order to create electrochemical cells. Lithium is used in electric vehicles, laptops, and other electronic devices.
- Chile> Australia> Argentina are the countries with the largest reserves.
India’s Lithium Industry:
- In a small plot of land recently studied in Southern Karnataka’s Mandya district, researchers from the Atomic Minerals Directorate (under India’s Atomic Energy Commission) estimated lithium deposits of 14,100 tonnes.
- It’s also the first Lithium deposit site ever discovered in India.
Other Possible Locations in India:
- Rajasthan, Bihar, and Andhra Pradesh have substantial mica belts.
- In Odisha and Chhattisgarh, there are pegmatite (igneous rock) belts.
- Rajasthan’s Sambhar and Pachpadra sand dunes, as well as Gujarat’s Rann of Kachchh.
- Initiatives by the government:
- India had struck an agreement with an Argentinian corporation to jointly prospect lithium in Argentina through a newly formed state-owned company, Khanij Bidesh India Ltd.
- Khanij Bidesh India Ltd was formed with the goal of acquiring strategic mineral assets such as lithium and cobalt from other countries.
5. Hydrogen-enriched compressed natural gas (HCNG):
#GS3-Infrastructure- energy.
Context: .
- The use of “hydrogen-enriched compressed natural gas (HCNG)” is becoming more popular. This comes as India prepares to launch its National Hydrogen Energy Mission, which might force the fertiliser, steel, and petrochemicals industries to switch to green hydrogen.
In depth information
- The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has also published requirements for hydrogen-enriched compressed natural gas (H-CNG) for use as a fuel in automobiles (IS 17314:2019).
What exactly is HCNG?
- When hydrogen is combined with compressed natural gas, the result is HCNG.
- It can be used in place of gasoline, diesel fuel, and propane (C3H8) / LPG, and it emits fewer harmful gases during combustion.
- HCNG has the following benefits:
- CO emissions are reduced by up to 70% with HCNG.
- Fuel savings of up to 5% are possible.
- The first step in the direction of a future hydrogen economy.
- It is possible to adjust engines to release less NO.
- To run on HCNG, engines only require minor modifications.
- High-load applications and heavy-duty vehicles benefit from this gasoline.
- H2 has a higher Octane rating, which means it performs better.
Concerns:
- Physically blending CNG with hydrogen requires a series of energy-intensive procedures, making H-CNG more expensive than CNG.
- While the NITI Aayog-CII Action Plan for Clean Fuel recommends the use of H-CNG as an alternative fuel, it also points out that physical blending of CNG and hydrogen requires a series of energy-intensive procedures, making H-CNG more expensive than CNG.
- The research and development arm of IOCL has created a method that eliminates the need for physical blending. Its ‘Compact Reforming Process’ uses a single step to make a hydrogen-CNG mixture from natural gas. According to the EPCA research, the cost of production is much lower than physical mixing.
- With current technology, automobiles and autos would be unable to use H-CNG because hydrogen is “extremely volatile,” posing a risk of increased combustion temperature and risk.
- Higher hydrogen blend levels necessitate end-use system adaptation.
- Changes to the engine’s structural characteristics are required, as well as the development of new infrastructure for the preparation of HCNG.
- Calculating the optimal H2/NG (Natural Gas) ratio.
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

