CURRENT AFFAIRS
TOPICS
1) India registers success with BP treatment, control:
2) Learning loss will dent India’s GDP: ADB
3) App based attendance hits rural workers
4) More deaths from respiratory causes
5) First Movers Coalition to drive zero-carbon tech demand
India registers success with BP treatment, control:
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death among adults in India. One of the major drivers of heart attack and stroke is untreated high blood pressure or hypertension. Hypertension is a silent killer as most patients do not have any symptoms.
Magnitude of the problem:
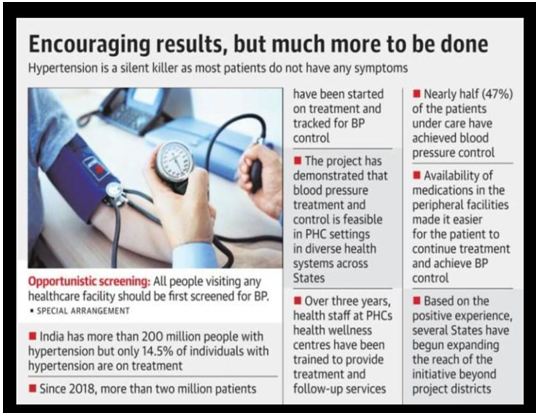
? India has more than 200 million people with hypertension
? Only 14.5% of individuals with hypertension are on treatment.
? Despite the fact that hypertension is easy to diagnose and can be treated with low cost generic drugs.
Initiatives are taken to control
- India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI) is a multipartner initiative involving the Indian Council of Medical Research, WHO India, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, and State governments to improve blood pressure control for people with hypertension.
- The project initiated in 26 districts in 2018 has expanded to more than 100 districts by 2022. More than two million patients were started on treatment and tracked to see whether they achieved BP control.
- The project demonstrated that blood pressure treatment and control are feasible in primary care settings in diverse health systems across various States in India.(primary level, block level, district level training provided to treat Hypertension)
Five scalable strategies
- First, a simple treatment protocol with three drugs was selected in consultation with the experts and non communicable disease programme managers.
- Second, the supply chain was strengthened to ensure the availability of adequate antihypertensive drugs.
- Third, patient centric approaches were followed, such as refills for at least 30 days and assigning the patients to the closest primary health centre or health wellness centre to make follow up easier.
- Fourth, the focus was on building capacity of all health staff and sharing tasks such as BP measurement, documentation, and follow up.
- Finally, there was minimal documentation using either paper based or digital tools to track follow up and BP control
Data driven approach;
- Data help to fallow up patients who did not returned for treatment.
- One of the challenges is the involvement of the private sector, where a large number of people with hypertension currently seek care. We must overcome the challenges to ensure early detection and treatment of hypertension to reduce preventable deaths and disability due to heart attack, stroke, and chronic kidney disease.
Learning loss will dent India’s GDP: ADB
- According to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of India, which is among the countries with the longest school closures during the COVID19 pandemic, will see the highest decline in South Asia due to learning losses for the young.
- School closures lead to declines in global GDP and employment.
- Declines in global GDP amount to 0.19% in 2024, 0.64% in 2028, and 1.11% in 2030
India case
- 3.2 % of the GDP reduction likely due to COVID school closures
Rural areas:
- India has notable enrolment in secondary education and among students in rural areas, and also pandemic induced school closures have also been more extensive there.
- They lack access to stable Internet connection needed to study online.
Economy:
- India may thus account for over 10% of the global GDP decline of $943 billion estimated by the ADB on account of earning losses in 2030, with jobs for skilled labour expected to decline by 1%, and unskilled labour by 2% that year.
- Learning and earning losses are significant because a notable portion of the impacted population will migrate to the unskilled labour force (large part of India’s work force is constituted by unskilled labour — 408.4 m acc. to ADB.)
- According to the ADB report In terms of absolute change, India experiences the highest GDP decline in South Asia, at $98.84 billion in 2030.
- In percentage terms, its GDP decreases by 0.34% in 2023, 1.36% in 2026, and 3.19% in 2030.
- Governments need to direct adequate funding and resources to young populations most affected by closures.
App based attendance hits rural workers
Context:
- The Union government has made capturing of attendance through its app, National Mobile Monitoring System, compulsory at worksites where 20 or more workers are employed under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
Problems:
- Patchy Internet connectivity in rural areas and little or no technical support.
- In a majority of cases, the employees’ families are averse to giving phones to women, especially smart phones. Hence, many women have dropped out.
- Mandatory capturing of attendance through the app has led to their exclusion from the process.
- The app certainly brings transparency and that is appreciated. However, the speed of the application and the strength of the server create troubles.
- The supervisors of the worksites are expected to have a smartphone with Internet connection, but they are not given added incentives to pay for the smartphones or Internet connections.
Advantages
- The Ministry’s directive claims that the app, which requires two timestamped and geotagged photographs of the workers in a day, encourages transparency and increases citizen oversight.
- Wages are directly connected to attendance
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS).
- The scheme envisages providing 100 days of guaranteed wage employment in a financial year to adult member volunteers for unskilled manual work.
- The scheme is a demand-driven wage employment scheme, which functions under the Ministry of Rural Development.
- Social security scheme in India.
Problems:
- Low wages, delay in wage payment, Inadequate financing, inadequate role of panchayats (very little autonomy), fabrication of cards.
More deaths from respiratory causes
Context:
- The first year of COVID19 lockdown saw the highest incidence of deaths from respiratory illnesses in a decade, the 2020 report on medical certification of cause of death (MCCD) compiled by the Registrar General of India (RGI).
- As per RGI as many as 1,81,160 deaths were due to respiratory diseases such as pneumonia, asthma and bronchitis, higher than the 1,52,311 in 2019 from those causes.
- According to the MCCD report, those above the age of 70 were the worst affected by the respiratory diseases accounting for the highest incidence of deaths — 47,292 deaths or 29.4% of total registered medically certified deaths.
- This was followed by the 55-64 age group reporting 23.9% deaths.
- The major number of deaths is concentrated in the age group of 45 and above constituting 82.7 % of total deaths in the group.
- The recent World Health Organization report on excess mortality rate pegged India’s excess mortality (people who probably would not have died if there was no pandemic) for 2020 and 2021 at 47.4 lakh.
- As of May, India’s official COVID19 death toll is 5.2 lakh.
- The report is based on 18,11,688 total medically certified deaths.
- Excess mortality includes deaths associate with COVID19 directly or indirectly (due to the pandemic’s impact on health systems and society).
First Movers Coalition to drive zero-carbon tech demand
Context :
- India has joined the first movers coalition steering group
- The Coalition has been launched at the COP26 Summit being held in Glasgow by USA and WEF (world economic forum)
- First Movers Coalition is a platform for the world’s leading global companies to make purchasing commitments to create early markets for critical technologies needed to achieve net-zero by 2050
- Members of the coalition have committed to using emerging technologies including sustainable aviation fuels (SAF) with significant emissions reductions, electric, and hydrogen propulsion for air travel by 2030.
- This initiative improve the purchasing power of companies to decarbonise seven hard to abate industrial sectors.
- These are Aluminium, Aviation, Chemicals, concrete, Shipping, Steel, and Trucking sector accounting for 30% of global emissions.
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 27th May 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube