Topics
- EnVision Mission
- G7 meet
- PASIPHAE Project
- Competition Commission of India
- Innovation for Defence Excellence
- EnVision Mission
#GS3 #Scienceandtechnology #Spacemissions
Context: Recently, European Space Agency (ESA) has announced a new mission- EnVision mission to Venus.
About:
- It is an European Space Agency (ESA) led mission with contributions from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
- It will be next Orbiter that will visit Venus sometime in the 2030s.
- Once launched on an Ariane 6 rocket, the spacecraft will take about 15 months to reach Venus and will take 16 more months to achieve orbit circularisation.
- The mission will carry a range of instruments to study the planet’s atmosphere and surface, monitor trace gases in the atmosphere and analyse its surface composition.
- EnVision will follow another ESA-led mission to Venus called ‘Venus Express’ (2005-2014) that focussed on atmospheric research and pointed to volcanic hotspots on the planet’s surface.
- The results from DAVINCI+ are expected to reshape the understanding of terrestrial planet formation in the solar system and beyond. Taken together, both missions are expected to tell scientists more about the planet’s thick cloud cover and the volcanoes on its surface.
Other Missions related to Planet Venus:
- Japan: Akatsuki spacecraft has been studying the planet’s atmosphere since 2015.
- NASA has announced two new robotic missions to Venus – DAVINCI+ and VERITAS. It will be launched between 2028-2030.
- Russia’s Venera series of space crafts 1967-1983, Vegas 1 and 2 in 1985.
- India plans to launch a new orbiter named Shukrayaan to Venus in 2024.
Why are scientists interested in studying Venus?
- At the core of the ESA’s mission is the question of how Earth and Venus evolved so differently from each other considering that they are roughly of the same size and composition.
- Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system because of the heat that is trapped by its thick cloud cover.
- It will help to learn what conditions exist on Earth-sized exoplanets (planets that orbit a star other than our sun).
- It will help in modelling Earth’s climate, and serves as a cautionary tale on how dramatically a planet’s climate can change.
- Scientists speculate about the existence of life on Venus in its distant past and the possibility that life may exist in the top layers of its clouds where temperatures are less extreme.
- It will help us understand whether planet Venus is still geologically active and even sustained life in past.
- In 2020, scientists detected the presence of phosphine (a chemical produced only through biological processes) in the atmosphere of Venus.
DAVINCI+
- DAVINCI+ is short for ‘Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging’ and is the first US-led mission to the planet’s atmosphere since 1978.
- It will try to understand Venus’ composition to see how the planet formed and evolved.
- It will also try to return the first high resolution photographs of a geological feature that is unique to Venus. This feature, which is called “tesserae” may be comparable to Earth’s continents.
- The presence of tesseraes may suggest that Venus has tectonic plates like Earth.
VERITAS
- VERITAS is short for ‘Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy’ and will map the Venus’s surface to determine its geologic history and understand the reasons why it developed so differently from Earth.
About Venus:
- For those on Earth, Venus is the second-brightest object in the sky after the moon.
- It appears bright because of its thick cloud cover that reflects and scatters light.
- It is called the Earth’s twin because of their similar sizes, the two planets have significant differences between them.
- Surface temperatures on Venus can go up to 471 degrees Celsius, which is hot enough to melt lead.
- Venus moves forward on its orbit around the Sun but spins backwards around its axis slowly. This means on Venus the Sun rises in the west and sets in the East.
- One day on Venus is equivalent to 243 Earth days because of its backward spinning, opposite to that of the Earth’s and most other planets.
- Venus does not have a moon and no rings.
- G7 meet
#GS2 #InternationalOrgansiations
Context: The leaders of seven nations — the U.S., Germany, the U.K., France, Canada, Japan and Italy met in Cornwall in south-west England, marking the 47th edition of the “Group of seven” summit.
- Recently, the Indian Prime Minister addressed the 47th G7 Summit 2021 through video conferencing.
Highlights of the Summit:
- This year’s summit was hosted by the UK.
- The last G-7 summit was in France in 2019, with last year’s event in the US cancelled due to the pandemic.
- The United Kingdom had invited India, Australia and South Korea to attend the G7 summit that was scheduled to be held in June as “guest countries”
- Earlier, the Finance Ministers from the G7 nations reached a landmark accord setting a Global Minimum Corporate Tax Rate (GMCTR).
- G-7 leaders agreed on Sunday to raise their contributions to meet an overdue spending pledge of $100 billion a year to help poorer countries cut carbon emissions and cope with global warming.
- Signed off on a joint statement (Democracies 11) by G-7 and guest countries on “open societies” that reaffirm and encourage the values of freedom of expression, both online and offline, as a freedom that safeguards democracy and helps people live free from fear and oppression.
- The statement also refers to politically motivated internet shutdowns as one of the threats to freedom and democracy.
- The G-7 statement which was not signed by India and other outreach countries hit out at China on “human rights and fundamental freedoms” in Xinjiang (Uyghur Muslims) and Hong Kong, and the unilateral attempts to change the status quo in the South China Sea.
- It also called for a transparent and timely World Health Organization’s Covid origins study in China.
- The G7 signed the?Carbis Bay Declaration. It is aimed at preventing future pandemics.
- The G7 also pledged over 1 billion coronavirus vaccine doses for poorer nations with half of that coming from the United States and 100 million from Britain.
- Build Back Better for the World Project:
- Which is aimed squarely at competing with China’s trillion-dollar Belt and Road infrastructure initiative.
- It will collectively catalyse hundreds of billions of infrastructure investment for low- and middle-income countries (in Asia and Africa) and offer a values-driven, high-standard and transparent partnership with G7.
India in G7 Summit:
- India signed the joint statement by G-7 and guest countries on “open societies” that reaffirm and encourage the values of “freedom of expression, both online and offline, as a freedom that safeguards democracy and helps people live free from fear and oppression”.
- Addressing the First Outreach Session of G7 summit, Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Saturday conveyed India’s commitment to “collective” solution to global health challenges.
- India is a natural ally for the G7 countries in defending the shared values from a host of threats stemming from authoritarianism, terrorism and violent extremism, disinformation and economic coercion.
- It sought the support of the grouping to lift patent protections for Covid-19 vaccines.
- India is the only G-20 country on track to meet its Paris commitments.
- In the session on climate change, the Prime Minister highlighted that the planet’s atmosphere, biodiversity and oceans cannot be protected by countries acting in silos, and called for collective action on climate change.
- Developing countries need better access to climate finance, and called for a holistic approach towards climate change that covers mitigation, adaptation, technology transfer, climate financing, equity, climate justice and lifestyle change.
- India also highlighted the revolutionary impact of digital technologies on social inclusion and empowerment in India through applications such as Aadhaar, Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) and JAM (Jan Dhan-Aadhaar- Mobile) trinity.
- Prime Minister Modi called for “one earth, one health” approach which aims for unity and solidarity among the states of the world to deal with the pandemic.
About G7:
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975.
- The bloc meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like global economic governance, international security and energy policy.
- The G-7 does not have a formal constitution or a fixed headquarters. The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
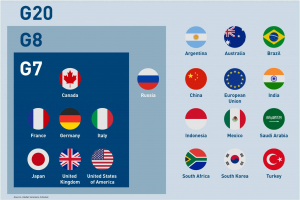
- G-7 is a bloc of industrialized democracies i.e. France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Japan, the United States, and Canada.
- The G7 was known as the ‘G8’ for several years after the original seven were joined by Russia in 1997.
- The Group returned to being called G7 after Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following the latter’s annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine.
- Summits are held annually and hosted on a rotation basis by the group’s members.
- The groundwork for the summit, including matters to be discussed and follow-up meetings, is done by the “sherpas”, who are generally personal representatives or members of diplomatic staff such as ambassadors.
- The leaders of important international organizations like European Union, IMF, World Bank and the United Nations are also invited.
- PASIPHAE Project
#GS3 #Scienceandtechnology #outerspace
Context: The Wide Area Linear Optical Polarimeter (WALOP), a vital instrument for the PASIPHAE Project, is being developed at Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA), India.
What is PASIPHAE:
- Polar-Areas Stellar-Imaging in Polarisation High-Accuracy Experiment (PASIPHAE) is an international collaborative sky surveying project.
- The name is inspired from Pasiphae, the daughter of Greek Sun God Helios, who was married to King Minos
- It is an opto polarimetric survey aiming to measure the linear polarization from millions of stars.
- The survey will use two high-tech optical polarimeters to observe the northern and southern skies, simultaneously.
- It will focus on capturing starlight polarisation of very faint stars that are so far away that polarisation signals from there have not been systematically studied. The distances to these stars will be obtained from measurements of the GAIA satellite.
- By combining these data, astronomers will perform a maiden magnetic field tomography mapping of the interstellar medium of very large areas of the sky using a novel polarimeter instrument known as WALOP (Wide Area Linear Optical Polarimeter).
- The Infosys Foundation, India, Stavros Niarchos Foundation, Greece and USA’s National Science Foundation have each provided a grant of $1 million, combined with contributions from the European Research Council and the National Research Foundation in South Africa.
Why is PASIPHAE important?
- Since its birth about 14 billion years ago, the universe has been constantly expanding, as evidenced by the presence of Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation which fills the universe.
- So far, there have only been theories and indirect evidence of inflation associated with the early universe.
- All previous attempts to detect this signal met with failure mainly due to the difficulty posed by our galaxy, the Milky Way, which emits copious amounts of polarised radiation.
- The Milky Way Galaxy contains a lot of dust clouds that are present in the form of clusters. When starlight passes through these dust clouds, they get scattered and polarised.
- The PASIPHAE survey will measure starlight polarisation over large areas of the sky. This data along with GAIA distances to the stars will help create a 3-Dimensional model of the distribution of the dust and magnetic field structure of the galaxy.
- Such data can help remove the galactic polarised foreground light and enable astronomers to look for the elusive B-mode signal.
- Beyond studies of the early Universe, the survey will lead to leaps forward in some of the most actively pursued areas in Astrophysics, including high-energy astrophysics, stellar astrophysics, and interstellar medium dynamics.
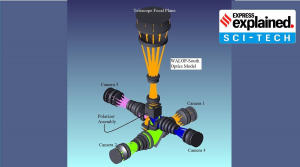
Wide Area Linear Optical Polarimeter (WALOP):
- Wide Area Linear Optical Polarimeter (WALOP) is an instrument, when mounted on two small optical telescopes, that will be used to detect polarised light signals emerging from the stars along high galactic latitudes.
- But the WALOP will be capable of observing hundreds of stars concurrently present both in the northern and the southern skies.
- In simple terms, the images will simultaneously have the finest of details of a star along with its panoramic background.
- A WALOP each will be mounted on the 1.3-metre Skinakas Observatory, Crete, and on the 1-metre telescope of the South African Astronomical Observatory located in Sutherland.
Astronomical Polarimetry:
- Polarimetry, a technique to measure the polarisation of light, is a powerful tool that allows astronomers to infer information about celestial objects, from passing comets to distant galaxies, that can not be obtained using other techniques.
- Polarization is a property of light that represents the direction that the light wave oscillates.
- Two decades ago, an Indian astrophysicist Sujan Sengupta, put forth an idea, that the light emitted by a cloudy brown dwarf, or reflected off an extrasolar planet, will be polarised.
- Competition Commission of India
#GS03 #e-commerce #FDI #internaltrade
Context: The Karnataka high court on Friday dismissed Amazon and Flipkart’s writ petitions challenging the probe ordered by the Competition Commission of India (CCI) against their business practices
Key Details:
- Last year, CCI had announced a probe into e-commerce companies, Amazon and Flipkart for alleged violation of competition Act and Foreign Direct Investment Act.
- However, two companies had managed to get stay on the investigation till now.
Allegations against the companies are:
- In 2019, the Delhi Vyapar Mahasangh (DVM), a group of owners of several micro, small and medium enterprises, submitted a plea with CCI against Flipkart and Amazon for abusing their market dominance and giving preferential listing and deep discounting on products sold by select vendors in which they control indirect stakes. This hurts small business in the country, it contended.
- The e-commerce giants are accused of making special agreements with select sellers, having stakes in Indian companies selling on their platforms, and deep discounting.
- Predatory pricing and cherry-picking sellers
- Circumventing foreign investment rules that effect e-commerce.
- FDI is not permitted in inventory-based model of e-commerce.
Government Policy regarding this:
- Government had earlier released draft e-commerce policy to provide a level playing field to all stakeholders, including consumers, MSMEs and start-ups.
- It will ensure e-commerce entities to ensure equal treatment of all sellers or vendors registered on their platforms and not adopt algorithms that result in prioritizing select vendors.
- As per the draft policy, E-commerce operators should ensure their algorithms unbiased. Algorithms must not prioritise any vendors; there should be transparent policies on discounts.
Competition Commission of India:
- Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002, it was duly constituted in March 2009.
- The Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act, 2002, on the recommendations of Raghavan committee.
- It aims at establishing a competitive environment in the Indian economy through proactive engagement with all the stakeholders, the government, and international jurisdiction.
- The commission is a quasi-judicial body which gives opinions to statutory authorities and also deals with other cases.
- The objectives of the Commission are:
- To prevent practices that harm the competition.
- To promote and sustain competition in markets.
- To protect the interests of consumers.
- To ensure freedom of trade.
Composition of CCI:
- The Commission consists of one Chairperson and six Members as per the Competition Act who shall be appointed by the Central Government.
- Eligibility of members: The Chairperson and every other Member shall be a person of ability, integrity and standing and who, has been, or is qualified to be a judge of a High Court, or, has special knowledge of, and professional
experience of not less than fifteen years in international trade, economics, business, commerce, law, finance, accountancy, management, industry, public affairs, administration or in any other matter which, in the opinion of the Central Government, may be useful to the Commission.
Why do we need Competition Laws?
- Competition laws perform three main functions in society.
- To uphold free-enterprise
- Security against market distortions
- Aid in the promotion of domestic industries.
Important Judgements of CCI:
- CCI imposed a fine of ?07 billion (US$910 million) on 11 cement companies for cartelisation in June 2012. It claimed that cement companies met regularly to fix prices, control market share and hold back supply which earned them illegal profits.
- CCI imposed a penalty of ?522 million (US$7.6 million) on the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) in 2013, for misusing its dominant position.
- CCI imposed a fine of ?10 million upon Google in 2014 for failure to comply with the directions given by the Director General (DG) seeking information and documents.
- CCI ordered a probe into the functioning of Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) following a complaint filed by Reliance Jio against the cartelization by its rivals Bharti Airtel, Vodafone India and Idea cellular.
- Innovation for Defence Excellence
#GS03 #Internalsecurity #innovation #AtmanirbharBharath
Context: Recently, the Defence Minister has approved the budgetary support of Rs. 498.8 crore to Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) challenge under the Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO) for the next five years.
Key Details:
- The funds will be used to provide financial support to nearly 300 start-ups, micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) and individual innovators with a larger goal of ensuring self-reliance in the defence sector.
- The scheme is in sync with the government’s push to cut imports of military hardware and weapons and make India a hub for defence manufacturing.
- In the last couple of years, the government has unveiled a series of reform measures and initiatives to make India a hub of defence manufacturing.
- India is one of the largest importers of arms globally.
- The government now wants to reduce dependence on imported military platforms and has decided to support domestic defence manufacturing.
- Self-reliance in manufacturing of defence equipment is a crucial factor for maintaining India’s strategic autonomy.
- India’s arms imports fell 33% between 2011-15 and 2016-20, said a report released by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI).
About iDEX initiative:
- The iDEX initiative was launched by the Prime Minister Modi in April 2018.
- It is an initiative taken by the government to contribute towards modernization of the Defence Industry.
What are the main objectives of iDEX?
- To frame ‘corporate Venture Capital’ models for Indian Defence needs thereby identifying emerging technologies, connecting innovators with military units, facilitating co-creation of new and appropriate technologies and so forth into weapon systems used by Indian Armed Services.
- To deliver military-grade products thereby solving the critical needs of the Indian defence set-up by developing or applying advanced technologies.
- To devise a culture of innovation in the Indian Defence and Aerospace by engaging startups and innovators for co-creation and co-innovation.
- It will provide the engaging industries with funding and other support to carry out Research & Development.
- iDEX is funded and managed by the DIO, and functions as the executive arm of Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO).
Defence Innovation Organisation:
- DIO is a ‘not for profit’ company registered under Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013.
- Its two founding members are Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) & Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) – Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs). HAL and BEL are navratna companies.
- DIO will provide high-level policy guidance to iDEX.
- However, iDEX will be functionally autonomous. The CEO of both DIO and iDEX will be the same. It will facilitate coordination and separation of functions also without any conflicts.
- iDEX has partnered with leading incubators in the country to provide hand holding, technical support and guidance to the winners of iDEX challenges.
Other Related Initiatives:
- To support the growth of the Defence sector and enhance manufacturing capacity in the sector, two Defence Industrial Corridors are being set up in India, one in Uttar Pradesh and another in Tamil Nadu.
- The FDI limit was increased from 49 per cent to 74 per cent under the automatic route in the defence sector.
- Strategic Partnership (SP) Model identifies a few Indian private companies who would initially tie up with global Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to seek technology transfers to set up domestic manufacturing infrastructure and supply chains.
- Last August, Defence Ministry had announced that India will stop the import of 101 weapons and military platforms like transport aircraft, light combat helicopters, conventional submarines, cruise missiles and sonar systems by 2024.
- A second negative list, putting import restrictions on 108 military weapons and systems such as next-generation corvettes, airborne early warning systems, tank engines and radars, was in June 2021.
- N Chadrasekharan Task Force was set up in 2018 to study implications of AI in national security.
- The ministry has set a goal of a turnover of USD 25 billion (Rs 1.75 lakh crore) in defence manufacturing in the next five years that included an export target of USD 5 billion (Rs 35,000 crore) worth of military hardware.
