UPSC Civils Services 29th January Current Affairs
Topics :
- Bank Frauds
- The COMPETES Act
- Chakmas and Hajongs Communities
- Tipu Sultan
- The Great Nicobar Island
1. Bank Frauds
#GS3-Indian Economy
Context
- In the first half of 2021-22, there were more banking frauds in India than in the same period the previous year.
In depth information
India’s Banking Sector Frauds
- An effort to syphon or remove funds or other assets from a financial or banking organisation is known as banking fraud.
- This can range from data theft, cybercrime, and simple bookkeeping manipulation to falsified documentation.
They can be grouped into a variety of categories, including:
- Misappropriation of cash and criminal breach of trust
- Encashment of falsified instruments in a fraudulent manner
- Manipulation of accounting records
- Foreign exchange transaction irregularities
- Unauthorized credit facilities provided for the purpose of unlawful gratification, deceit, and forgeries.
- Negligence and a monetary crunch
The magnitude of the deceptions
- According to the RBI’s Trend and Progress of Banking in India, 2020-21 report, banking fraud cases increased to 4,071 in April–September FY22 from 3,499 the previous year.
- According to the RBI’s Trend and Progress of Banking in India report, the amount involved in the frauds decreased from 64,621 crore to 36,342 crore.
Reasons for such deception
- Remote working methods, clients increasingly preferring non-branch banking channels, and inadequate usage of forensic techniques are all contributing to an increase in fraud.
- Banks are unable to keep track of the loans they make to small and medium-sized firms on a consistent basis.
- The retail banking industry is a major source of fraud.
What is the impact of the growing number of frauds?
- Frauds degrade client trust and put the financial system at risk in terms of reputation, operational risk, and business risk.
- Regardless of rules or vested interests, loans granted rightfully belong to depositors.
- It has the potential to cause bank failure or to weaken their balance sheets, forcing bad banks to consolidate with stronger banks.
- Credit assistance, which is the backbone of any business, would be taken away from productive activity.
a path forward
- State-owned banks’ only option is functional autonomy, with limited room for bureaucratic or political intervention.
- The requirement of the hour is for strict adherence to kyc rules (know-your-customer) as well as responsibility among the banking employees involved.
- Banks must also be alert and monitor all accounts on a regular basis.
- People with corporate ties should, in theory, be precluded from serving on bank boards.
2.The COMPETES Act
#GS2-Indian Diaspora
Context
- The United States has launched the Creating Opportunities for Manufacturing, Preeminence in Technology, and Economic Strength (COMPETES) Act of 2022, which proposes a new start-up visa that would open up new horizons for brilliant individuals from all over the world.
In depth information
What is the COMPETES Act?
- The plan includes $52 billion in incentives to increase semiconductor manufacture in the United States, as well as $45 billion in grants and loans to boost supply chain resilience and manufacturing, among other things.
- It also contains money to combat social and economic inequity, climate change, and immigration.
- It exempts STEM PhDs from the green card cap, for example, and creates a special green card for entrepreneurs.
- The bill also authorises $600 million per year in manufacturing facilities to reduce reliance on solar components made in Xinjiang, China, in the United States.
The Act’s most important provisions
- The Act modifies the Immigration and Nationality Act to create a new “W” non-immigrant classification for entrepreneurs with a stake in a startup company.
- It aims to create procedures enabling foreign people having a stake in a startup company to apply for lawful permanent resident status as an immigrant entrepreneur on their own.
- Certain foreign nationals (and their wives and children) who have achieved a PhD degree in STEM are exempt from the numerical limits on immigrant visas under the bill.
Consequences for Indians
- It would mean greater chances for Indian talent and talented workers in the United States.
- The US government issues 85,000 H-1B work visas each year.
- Every year, Indians and Indian-owned businesses receive the lion’s share of the H-1B work visas issued.
- With this new category, Indian professionals will have a better chance of taking use of the Act’s opportunities.
3. Chakmas and Hajongs Communities
#GS2-Issues Related to Minorities
Context
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has issued an order directing the Ministry of Home Affairs and Arunachal Pradesh to submit an action report within six weeks in response to allegations of racial profiling and the forced evacuation of Chakmas and Hajongs from the state.
- Both authorities were also told to “guarantee that the Chakmas and Hajongs’ human rights are safeguarded in all respects.”
- Hate crimes, police brutality, and denial of rights and benefit programmes have allegedly been perpetrated against members of the two communities.
In depth information
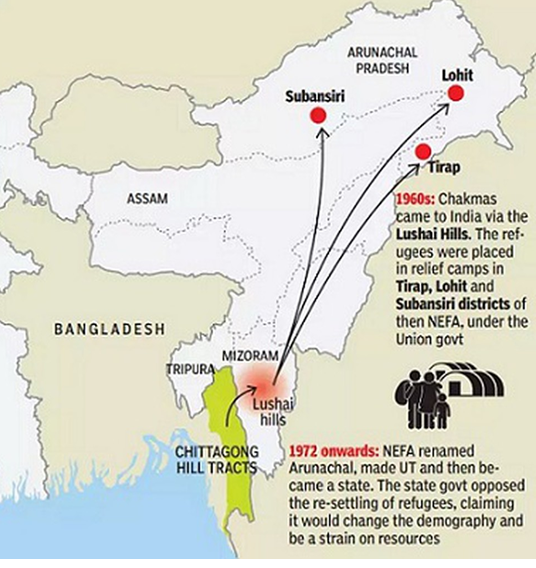
Background:
- The Supreme Court ordered the state to grant them citizenship in 2015, but this has yet to happen.
- The Court ruled in a 1996 ruling that “any Chakma residing within the State will have his or her life and personal freedoms protected.”
- Given these orders, and the fact that the majority of Chakma/Hajong people were born in the state and have lived peacefully there for generations, the Arunachal Pradesh Chief Minister’s announcement in August 2021 that they would be relocated outside the state and that steps would be taken to conduct a “census” of the communities was clearly unwarranted.
- Following that, the Chakma Development Foundation of India (CDFI) requested the NHRC’s urgent intervention in the racial profiling of 65,000 Chakma and Hajong tribals in Arunachal Pradesh through an illegal census scheduled to begin on December 31, 2021 (later, the census plan was dropped) in order to deport, expel, or relocate them from the state.
- Ethnic profiling is a government or police practise of identifying people to investigate based on their racial and cultural features.
Problems with the Special Census include:
- The census, according to Chakma organisations, was nothing more than racial profiling of the two communities based on their ethnic origins, violating Article 14 of the Indian Constitution and Article 1 of the International Convention on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination, both of which India has ratified.
- Within India’s territory, no one shall be denied equal treatment before the law or equal protection under the law, according to Article 14.
- In October 1966, the United Nations General Assembly declared the 21st of March to be the International Day for the Elimination of Racial Discrimination, to be observed annually.
Hajongs and Chakmas:
- The Buddhist Chakmas have a sizable population in Mizoram and Tripura, whereas the Hindu Hajongs are predominantly found in Meghalaya’s Garo Hills and the surrounding territories of Assam.
- The Chakmas and Hajongs of Arunachal Pradesh are descendants of East Pakistan’s Chittagong Hill Tracts, now Bangladesh.
- They sought shelter in India after being displaced by the Kaptai dam on the Karnaphuli River in the 1960s. They were settled in relief camps in the southern and south-eastern areas of Arunachal Pradesh from 1964 to 1969.
- The majority of them now reside in the state’s Changlang district (Arunachal Pradesh).
Status of Citizenship:
- About 60,500 Chakmas and Hajongs are citizens by birth, as defined by Section 3 of the Citizenship Act of 1955, after being born before July 1, 1987, or as descendants of individuals who were born before that date.
- Following the 1996 Supreme Court order, the remaining 4,500 surviving migrants’ applications have yet to be processed.
- Since the Chakma-Hajongs were permanently settled by the Union of India in the 1960s, the Citizenship (Amendment) Act of 2019, which changed two parts of the 1955 Act, has nothing to do with them.
- Because 95 percent of the migrants were born in the North-East Frontier Agency or Arunachal Pradesh, the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation of 1873, which requires outsiders intending to visit the State to get an Inner Line Permit, does not apply to them.
Next Steps
- The answer to the decades-old problem resides in the State’s respect for the rule of law and Supreme Court decisions.
- The use of the Chakma-Hajong issue by politicians and political aspirants must come to an end.
4. Tipu Sultan
#GS1-personalities
Context:
- The BJP claims a Congress leader is proposing to rename a playground in a Muslim-dominated neighbourhood after the Mysore monarch, which has sparked outrage in Mumbai.
In depth information

What was Tipu Sultan’s name?
- He was the eldest son of Sultan Hyder Ali of Mysore and monarch of the Kingdom of Mysore.
- In the larger national narrative, Tipu Sultan has been portrayed as a visionary and courageous leader, a skilled military strategist who, in a short 17-year reign, overcame the Company’s most significant challenge in India.
Tipu Sultan’s contributions include:
- At the age of 17, fought in the first Anglo-Mysore War (1767-69) and later against the Marathas in the Second Anglo-Mysore War (1780-84).
- During the Fourth Anglo Mysore War, he fought Company forces four times between 1767 and 1799, and was murdered defending his city Srirangapatnam.
- Tipu reorganised his army following European lines, using modern equipment such as the world’s first war rocket.
- Developed a land revenue system based on precise surveys and classification, in which the tax was levied directly on the peasant and collected in cash through hired agents, therefore increasing the state’s revenue base.
- Agriculture was modernised, tax breaks were given for developing wasteland, irrigation infrastructure was developed and ancient dams were restored, and agricultural manufacturing and sericulture were fostered. To support trade, a navy was built.
- To establish factories, the government established a “state commercial corporation.”
Why is he surrounded by so many controversies?
- On practically every historical figure, there are complaints expressed against Tipu Sultan, and viewpoints range.
- Outside of Mysore, Haider and Tipu had tremendous territorial ambitions, and they conquered and annexed regions. They burned down entire towns and villages, demolished hundreds of temples and churches, and forced Hindus to convert.
- Tipu boasted in the historical record about forcing “infidels” to convert to Islam and destroying their houses of worship.
- The debate thus is between those who consider the “Tiger of Mysore” as a bulwark against colonialism and a wonderful son of Karnataka, and those who accuse him of tyranny and fanaticism based on his demolition of temples and forced conversions of Hindus and Christians.
5.The Great Nicobar Island
#GS3-Environmental Impact Assessment
Context
- The draft environment impact assessment (EIA) report for the mega-development project on Great Nicobar Island, which was recently issued, has generated severe concerns about the submission of erroneous or incomplete information, scientific inaccuracy, and failure to follow the proper procedure.
In depth information
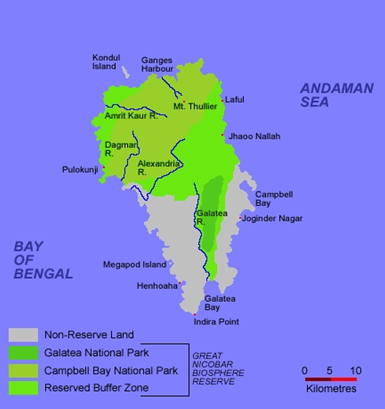
Concerning the Project
- The 72,000-crore integrated project in Great Nicobar, which is being launched by the NITI Aayog, includes the construction of a mega port, an airport complex, a township stretched over 130 square kilometres of virgin forest, and a solar and gas-based power plant.
- The project’s proponent is the Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Ltd. (ANIIDCO).
- The Gurugram-based consultant AECOM India Pvt. Ltd. prepared the project’s pre-feasibility report in March 2021.
- In May 2021, a committee of the Ministry of Environment, Forestry, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) announced terms of reference (ToR) for the preparation of the EIA report.
Significance
- Connectivity: The project will increase air and maritime connectivity, allowing the island to develop holistically.
- Job opportunities: Building world-class infrastructure will necessitate labour at all levels, resulting in a plethora of job opportunities.
- Tourism: Infrastructure development will lead to high-end eco-tourism, which will bring in more cash for the government.
- Cultural exchanges will occur as a result of the increased entry and outflow of people, as well as the island’s population development.
- Strategic
- Overall, the expansion would result in improved logistics and ongoing monitoring of marine operations.
- Even as China seeks to increase its naval reach, it will assist India in securing its borders and protecting its economic routes.
Concerns have been raised.
- For over a year, ecologists and scholars have expressed alarm about this project because it ignores tribal and ecological concerns, and the current draught EIA has failed to assuage those misgivings.
- Only one empanelled expert on ecology and biodiversity is part of the team of consultants hired to carry out the draught EIA, and it is unclear what his area of competence is.
- When it comes to the facts supplied, there are also severe concerns about scientific correctness and integrity.
- There are in-text citations but no references in Section 3.9, which is on ecology and biodiversity.
- Tables containing lists of flora and animals found on the island are sparse and lack sources.
- Other sources of information are internally contradictory and/or wrong.
- The island’s size is given as 1,045 square kilometres in one place and 910 square kilometres (the current official figure) in another.
- The executive summary claims that there are no coral reefs in the Galathea port region, however the ZSI research attached to the EIA claims that there is a coral reef covering 116 hectares in Galathea Bay.
- There are 330 species of fauna reported on the island, according to the report, whereas the same ZSI study puts the number at 695.
- The EIA claims that no migratory birds have been documented from Great Nicobar, despite the fact that these islands are located along two internationally major bird flyways and have been home to more than 40 species of migratory birds.
- In this EIA procedure, it is clear that there are severe procedural flaws, a lack of openness, and a lack of seriousness.
Suggestions
- The area must be safeguarded from an ecological, environmental, and biological standpoint, keeping in mind the complex ecological, social, and geological vulnerabilities.
- The official Shompen Policy of 2015, which said that the welfare and integrity of these people should be given priority in large-scale development initiatives and that these should be taken care of, has to be emphasised further.
- The geological instability of these islands must be taken into account, as well as investigations of alternate port locations.
- The rationale behind the NITI Aayog vision paper, as well as the mechanisms that underpin it, should be re-examined.
- Details on ANIIDCO’s corporate environmental policy, a prescribed standard operating procedure for dealing with environmental and forest issues, and a compliance management system should be made public.
- The tribal rights shall be well maintained and cared for” and if any exemption from existing regulations, policies, or laws of the land is required for the project’s execution.
UPSC Civils Services 29th January Current Affairs
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

