21st May 2022 CURRENT AFFAIRS
Topics:
Need for increase in Biospheres in South Asia
- GS – III Environment & Ecology
Pegasus
- GS – III Cyber Security
Guidelines easing norms for GM Crops research
- GS – III Agriculture
Food security in space
- GS – III Space
Endosulfan
- GS – III Pollution
Need for increase in Biospheres in South Asia
Context: On the occasion of the International Day for Biological Diversity (22nd May 2022) one of the directors of the UNESCO raised the importance of increasing the number of Biospheres in South Asia.
- Biosphere: Biosphere reserves are places where humans live in harmony with nature, and where there is an effective combination of sustainable development and nature conservation.
- The aim is to detect changes and find solutions to increase climate resilience.
History of Biosphere’s in South Asia and its scope
- South Asia has a very diverse set of ecosystems. To begin with, Bhutan, India and Nepal combined have thousands of glaciers, surrounded by lakes and alpine ecosystems.
- In South Asia, over 30 biosphere reserves have been established.
- The first one was the Hurulu Biosphere Reserve in Sri Lanka, which was designated in 1977 and comprises 25,500 hectares within the tropical dry evergreen forest.
- In India, the first biosphere reserve was designated by UNESCO in 2000 within the blue mountains of the Nilgiris.
- The Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve, established in 2018, is a good model.
- It includes some of the highest ecosystems in the world, with elevations up to 8,586 meters.
- The reserve is home to orchids and rare plant species.
- The main economic activities of the 35,000 people living there are crop production, animal husbandry, fishing, dairy products and poultry farming.
- Bangladesh, India, the Maldives, and Sri Lanka all have extensive coastlines, with coral reefs and mangrove forests. These areas are exposed to extreme weather events (storms, floods, droughts), and sea level rise.
- The Maldives is recognized as the lowest lying country in the world, with a mere elevation of 1.5 meters above the high tide mark.
- Together with UNESCO, the archipelago has embarked on a plan to establish pilot sites for the conservation and restoration of coastal ecosystems, and to enhance the population’s knowledge on climate change adaptation.
- Separately, three biosphere reserves have already been created in the Maldives.
Procedure to recognize biosphere reserves:
- All biosphere reserves are internationally recognised sites on land, at the coast, or in the oceans. Governments alone decide which areas to nominate.
- Before approval by UNESCO, the sites are externally examined. If approved, they will be managed based on an agreed plan, reinforced by routine checks to ensure credibility, but all remain under the sovereignty of their national government.
- The point is that if these pockets of hope can expand, with at least one biosphere reserve per country, and with more and larger sites covering the terrestrial surface, including coastal areas with their off shore islands, it will give the realisation to millions of people that a better future is truly possible, one where we can truly live in harmony with nature.
Factors contributing Biodiversity loss
- According to the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services released in 2019 by the Intergovernmental Science Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) at the UNESCO headquarters in Paris, the main global drivers of biodiversity loss are climate change,
- invasive species,
- overexploitation of natural resources,
- pollution and
- urbanization
Way forward
- Because of our collective excesses, the ecological carrying capacity of planet earth has largely been exceeded. This trend needs to be redressed, with cleaner air, high quality drinking water, and enough food and healthy habitats to ensure that ecosystem services continue to benefit humanity without critically affecting nature’s balance
Pegasus
Context: The Supreme Court said its technical committee had so far received and tested 29 mobile devices suspected to be infected by Pegasus malware
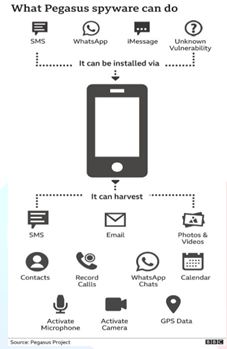
- Pegasus is a spyware developed by an Israeli firm, NSO Group, to infiltrate smartphones — Android and iOS — and turn them into surveillance devices.
- It is dangerous as it spares no aspect of a person’s identity.
- It can intercept every call and SMS, read every email and monitor each messaging app.
- Pegasus can also control the phone’s camera and microphone and has access to the device’s location data.
- In 2019, when WhatsApp sued the firm in a U.S. court, the matter came to light.
- In July 2021, Amnesty International, along with 13 media outlets across the globe released a report on how the spyware was used to snoop hundreds of individuals, including Indians.

Guidelines easing norms for GM Crops research
Context: The Department of Biotechnology (DBT) has issued guidelines easing norms for research into genetically modified (GM) crops and circumventing challenges of using foreign genes to change crops profile.
- The ‘Guidelines for Safety Assessment of Genome Edited Plants, 2022’ exempt researchers who use gene-editing technology to modify the genome of the plant from seeking approvals from the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)
- The GEAC evaluates research into GM plants and recommends, or disapproves, their release into farmer fields.
- The final call, however, is taken by the environment minister as well as States where such plants could be cultivated.
- The Environment Ministry too has sanctioned this exemption.
GM crops
- According to WHO, genetically modified organisms are the organisms in which genetic material has been altered in a way that does not occur in natural recombination.
- To produce a GM plant, new DNA is transferred into cells of a plant. These cells are then grown in tissue culture where they transform into plants. The seeds produced by these plants will have new DNA.
- All GM crops in India require approval from the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) for use in commercial production. BT cotton is the only genetically modified crop allowed in India.
Genome editing
- Genome editing involves the use of technologies that allow genetic material to be added, removed, or altered at particular locations in the genome.
- Gene editing can be used to make plants express properties not native to them.
Concerns with GM Crops
- The worry around this method is that these genes may spread to neighboring plants, where such effects are not intended and so their applications have been controversial.
- Gene editing techniques involves altering the function of genes and can cause “large and unintended consequences” that can change the “toxicity and allergenicity” of plants.
Food security in space
Context :
- Researchers at the University of Florida say they have grown plants in moon soil
About this issue:
- The researchers planted Arabidopsis (rock cress) seeds in lunar soil that was gathered about 50 years ago.
- It is the first time that scientists have shown that life can emerge from regolith, the material found on the moon’s surface.
- This soil brought by Apollo-era astronauts
How this is going to help:
Future lunar exploration:
- This research could help astronauts on lunar missions grow their own food and reduce the need for frequent supplies from Earth.
- Tourism will start develop in moon
- Settlements: In future people will settle here (it will decrease burden on Earth)
- NASA and the European Space Agency hoping to return people to the moon on the Artemis program.
Problems :
- But the scientists still don’t know how plants from Earth will interact with a real, rather than simulated, lunar environment.
- The moon is extremely dry compared with Earth, and that could change the plants’ ability to grow.
- Lets hope in the future we may the first civilisation on the moon
Indian missions in exploring the moon
Chandrayan 1 &2
Endosulfan :
Context :
- Supreme Court directed Kerala to pay 5 lakh compensation each victim of toxic Endosulfan pesticide.
Its uses
- Endosulfan is an organochlorine insecticide which was first introduced in the 1950s Sprayed on crops like cotton, cashew, fruits, tea, paddy …etc
- To control pests such as whiteflies, aphids, beetles, worms etc.
Impact :
- Bio magnification and Bio accumulation.
- Diseases ranging from physical deformities, cancer, birth disorders and damage to the brain and nervous system.
- The Supreme Court in India has banned the manufacture, sale, use, and export of Endosulfan throughout the country. (2015)
- Banned under Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants.
- The convention aims to reduce the concentration of persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
- It is also called as ‘dirty dozen’
UPSC Civil Services Daily Current Affairs 21st May 2022
Our Courses
Watch Our Videos on YouTube

